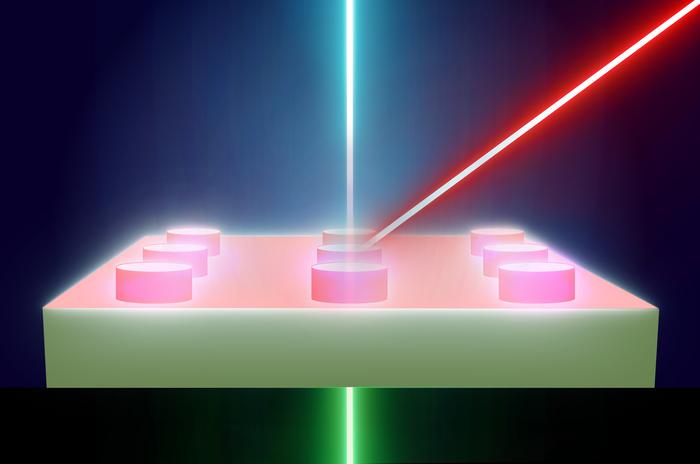
Metamaterials, engineered at the nanoscale, exhibit unique properties not found in naturally occurring materials. These properties arise from their nanoscale building blocks, which, until now, have been challenging to observe directly due to their size being smaller than the wavelength of light. The team’s research overcomes this limitation by employing a new microscopy technique that can simultaneously reveal both the nano and macro structures of these materials.

Credit: © FHI
Tailoring light with Nanomaterials
Metamaterials, engineered at the nanoscale, exhibit unique properties not found in naturally occurring materials. These properties arise from their nanoscale building blocks, which, until now, have been challenging to observe directly due to their size being smaller than the wavelength of light. The team’s research overcomes this limitation by employing a new microscopy technique that can simultaneously reveal both the nano and macro structures of these materials.
A New Window into the Nano World
The key finding of this research is a methodological breakthrough that enables the visualization of structures previously too small to be seen with traditional microscopy. By using light in innovative ways, the scientists have discovered how to “trap” one color of light within the structure, and use a mixing with a second color that can leave the structure to visualize this trapped light. This trick reveals the hidden world of nanoscale optical metamaterials.
Over Five Years of Development
This achievement is the result of more than five years of dedicated research and development, utilizing the unique features of the Free Electron Laser (FEL) at the Fritz Haber Institute. This type of microscopy is particularly special because it allows for a deeper understanding of metasurfaces, paving the way for advancements in technologies such as lens design, with the ultimate goal of creating flatter, more efficient optical devices.
The Future of Flat Optics
By enhancing our understanding of metasurfaces, this research opens the door to the development of novel light sources and the design of coherent thermal light sources. „We are just at the beginning,” states the research team, „but the implications of our work for the field of flat optics and beyond are immense. Our technique not only allows us to see the complete performance of these nanostructures but also to improve upon them, shrinking 3D optics down to 2D, and making everything smaller and flatter.”
Metamaterials, engineered at the nanoscale, exhibit unique properties not found in naturally occurring materials. These properties arise from their nanoscale building blocks, which, until now, have been challenging to observe directly due to their size being smaller than the wavelength of light. The team’s research overcomes this limitation by employing a new microscopy technique that can simultaneously reveal both the nano and macro structures of these materials.
A New Window into the Nano World
The key finding of this research is a methodological breakthrough that enables the visualization of structures previously too small to be seen with traditional microscopy. By using light in innovative ways, the scientists have discovered how to “trap” one color of light within the structure, and use a mixing with a second color that can leave the structure to visualize this trapped light. This trick reveals the hidden world of nanoscale optical metamaterials.
Over Five Years of Development
This achievement is the result of more than five years of dedicated research and development, utilizing the unique features of the Free Electron Laser (FEL) at the Fritz Haber Institute. This type of microscopy is particularly special because it allows for a deeper understanding of metasurfaces, paving the way for advancements in technologies such as lens design, with the ultimate goal of creating flatter, more efficient optical devices.
The Future of Flat Optics
By enhancing our understanding of metasurfaces, this research opens the door to the development of novel light sources and the design of coherent thermal light sources. „We are just at the beginning,” states the research team, „but the implications of our work for the field of flat optics and beyond are immense. Our technique not only allows us to see the complete performance of these nanostructures but also to improve upon them, shrinking 3D optics down to 2D, and making everything smaller and flatter.”
Metamaterials, engineered at the nanoscale, exhibit unique properties not found in naturally occurring materials. These properties arise from their nanoscale building blocks, which, until now, have been challenging to observe directly due to their size being smaller than the wavelength of light. The team’s research overcomes this limitation by employing a new microscopy technique that can simultaneously reveal both the nano and macro structures of these materials.
A New Window into the Nano World
The key finding of this research is a methodological breakthrough that enables the visualization of structures previously too small to be seen with traditional microscopy. By using light in innovative ways, the scientists have discovered how to “trap” one color of light within the structure, and use a mixing with a second color that can leave the structure to visualize this trapped light. This trick reveals the hidden world of nanoscale optical metamaterials.
Over Five Years of Development
This achievement is the result of more than five years of dedicated research and development, utilizing the unique features of the Free Electron Laser (FEL) at the Fritz Haber Institute. This type of microscopy is particularly special because it allows for a deeper understanding of metasurfaces, paving the way for advancements in technologies such as lens design, with the ultimate goal of creating flatter, more efficient optical devices.
The Future of Flat Optics
By enhancing our understanding of metasurfaces, this research opens the door to the development of novel light sources and the design of coherent thermal light sources. „We are just at the beginning,” states the research team, „but the implications of our work for the field of flat optics and beyond are immense. Our technique not only allows us to see the complete performance of these nanostructures but also to improve upon them, shrinking 3D optics down to 2D, and making everything smaller and flatter.”
Journal
Advanced Materials
Article Title
Spectroscopic and Interferometric Sum-Frequency Imaging of Strongly Coupled Phonon Polaritons in SiC Metasurfaces
Article Publication Date
19-Jun-2024