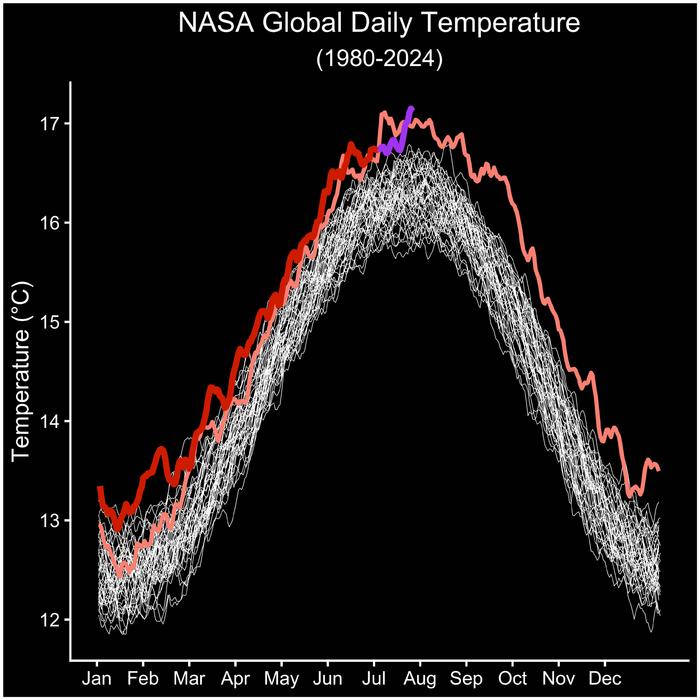
July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record, according to a NASA analysis of global daily temperature data. July 21 and 23 of this year also exceeded the previous daily record, set in July 2023. These record-breaking temperatures are part of a long-term warming trend driven by human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. As part of its mission to expand our understanding of Earth, NASA collects critical long-term observations of our changing planet.

Credit: NASA/Global Modeling and Assimilation Office/Peter Jacobs
July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record, according to a NASA analysis of global daily temperature data. July 21 and 23 of this year also exceeded the previous daily record, set in July 2023. These record-breaking temperatures are part of a long-term warming trend driven by human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. As part of its mission to expand our understanding of Earth, NASA collects critical long-term observations of our changing planet.
“In a year that has been the hottest on record to date, these past two weeks have been particularly brutal,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “Through our over two dozen Earth-observing satellites and over 60 years of data, NASA is providing critical analyses of how our planet is changing and how local communities can prepare, adapt, and stay safe. We are proud to be part of the Biden-Harris Administration efforts to protect communities from extreme heat.”
This preliminary finding comes from data analyses from Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2) and Goddard Earth Observing System Forward Processing (GEOS-FP) systems, which combine millions of global observations from instruments on land, sea, air, and satellites using atmospheric models. GEOS-FP provides rapid, near-real time weather data, while the MERRA-2 climate reanalysis takes longer but ensures the use of best quality observations. These models are run by the Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Daily global average temperature values from MERRA-2 for the years 1980-2022 are shown in white, values for the year 2023 are shown in pink, and values from 2024 through June are shown in red. Daily global temperature values from July 1 to 23, 2024, from GEOS-FP are shown in purple. The results agree with an independent analysis from the European Union’s Copernicus Earth Observation Programme. While the analyses have small differences, they show broad agreement in the change in temperature over time and hottest days.
The latest daily temperature records follow 13 months of consecutive monthly temperature records, according to scientists from NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York. Their analysis was based on the GISTEMP record, which uses surface instrumental data alone and provides a longer-term view of changes in global temperatures at monthly and annual resolutions going back to the late 19th century.