Designing the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses involves numerous complex parameters and boundaries, requiring frequent reference to various cases and specifications. Traditional methods struggle to efficiently retrieve this information, leading to suboptimal designs and extended project timelines. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need for a more intelligent and efficient approach to streamline the design process, enhance accuracy, and improve project management in hydropower engineering.

Credit: He Jia, Tianjin University
Designing the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses involves numerous complex parameters and boundaries, requiring frequent reference to various cases and specifications. Traditional methods struggle to efficiently retrieve this information, leading to suboptimal designs and extended project timelines. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need for a more intelligent and efficient approach to streamline the design process, enhance accuracy, and improve project management in hydropower engineering.
Researchers from Tianjin University, in collaboration with PowerChina Kunming Engineering Corporation Limited and other institutions, have developed a novel methodology for constructing a knowledge graph for the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses. Published in the Journal of Intelligent Construction on June 18 2024, the study (DOI: 10.26599/JIC.2024.9180026) demonstrates how this knowledge graph can enhance digital intelligent design and operation of hydropower facilities.
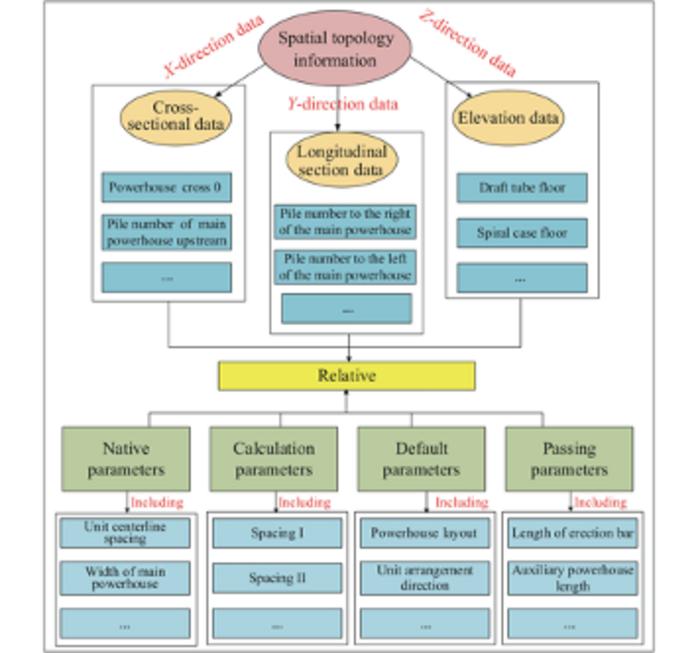
The study details a comprehensive process for constructing a knowledge graph to optimize the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses. It begins with designing an ontology skeleton to represent the knowledge organization structure. Data is collected and processed using optical character recognition (OCR) technology and the THU Lexical Analyzer for Chinese (THULAC) to handle large volumes of unstructured information. The extracted knowledge is stored in the Neo4j database, forming the basis of the knowledge graph. This graph is then used for intelligent querying and parameter recommendation, significantly enhancing design and operational efficiency. By enabling efficient retrieval and application of design knowledge, the knowledge graph addresses existing challenges in spatial arrangement, paving the way for improved accuracy and efficiency in hydropower engineering projects.
Dr. He Jia, a lead researcher from Tianjin University, stated, “The implementation of a knowledge graph in the design of underground powerhouses marks a significant step forward in the field of hydropower engineering. This approach not only improves the efficiency of design processes but also provides a robust foundation for future advancements in intelligent construction and operation.”
The application of this knowledge graph methodology extends beyond underground powerhouses, offering potential benefits for various fields of engineering that require complex spatial arrangements. By enabling more efficient retrieval and application of design knowledge, this approach can lead to significant cost savings, improved safety, and enhanced project management in large-scale construction projects. The continuous update capability of the knowledge graph ensures its long-term relevance and adaptability to evolving industry needs.
This work is supported by Innovation Fund Projects from Tianjin University (No. 2023XJD-0065).
About Journal of Intelligent Construction
Journal of Intelligent Construction (JIC), sponsored by Tsinghua University and the China National Committee on Large Dams, published by Tsinghua University Press (TUP) and exclusively available via SciOpen, is a peer-reviewed journal for publishing original research papers, case studies, reviews and comments regarding the use of novel technologies in all domains of civil engineering, e.g., hydraulic engineering, structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, transportation, and construction management. The journal focuses on the application of advanced theories, methodologies, and tools, such as machine learning, sensors, robotics, 5G, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, building information modelling, and computational methods, etc., in all stages of the construction life cycle, which makes the process more intelligent and efficient. The journal also covers other essential areas of civil engineering, e.g., planning and design, operation and maintenance, and disaster mitigation.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
Journal
Journal of Intelligent Construction
Article Title
Construction and application of a knowledge graph for the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses
Article Publication Date
18-Jun-2024