A research team has developed an improved DeepLabv3+ algorithm for accurately detecting and localizing safflower filament picking points. By utilizing the lightweight ShuffleNetV2 network and incorporating convolutional block attention, the method achieved high accuracy with a mean pixel accuracy of 95.84% and mean intersection over union of 96.87%. This advancement reduces background interference and enhances filament visibility. The method shows potential for improved harvesting robot performance, offering promising applications for precise filament harvesting and agricultural automation.

Credit: The authors
A research team has developed an improved DeepLabv3+ algorithm for accurately detecting and localizing safflower filament picking points. By utilizing the lightweight ShuffleNetV2 network and incorporating convolutional block attention, the method achieved high accuracy with a mean pixel accuracy of 95.84% and mean intersection over union of 96.87%. This advancement reduces background interference and enhances filament visibility. The method shows potential for improved harvesting robot performance, offering promising applications for precise filament harvesting and agricultural automation.
Safflower is a crucial crop for various uses, but current labor-intensive harvesting methods are inefficient. Existing research on flower segmentation using deep learning shows promise but struggles with near-color backgrounds and blurred contours.
A study (DOI: 10.34133/plantphenomics.0194) published in Plant Phenomics on 7 May 2024. This study addresses these challenges by proposing a filament localization method based on an improved DeepLabv3+ algorithm, incorporating a lightweight network and attention modules.
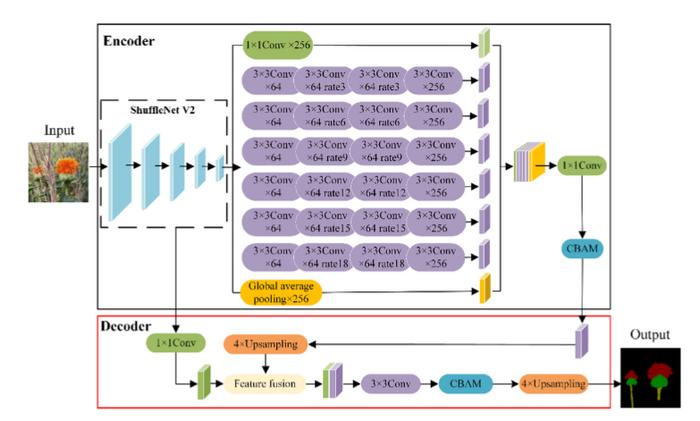
To improve the algorithm’s performance and decrease overfitting, the SDC-DeepLabv3+ algorithm was trained with an initial learning rate of 0.01, a batch size of eight, and 1,000 iterations. Using the SGD optimizer, the learning rate was adjusted if accuracy did not increase within 15 rounds. The training process showed a rapid decrease in loss value in the first 163 rounds, stabilizing after 902 rounds. The mean pixel accuracy (mPA) reached 92.61%, indicating successful convergence. Ablation tests revealed that integrating ShuffletNetV2 and DDSC-ASPP improved the mean intersection over union (mIoU) to 95.84% and mPA to 96.87%. Compared to traditional DeepLabv3+, the enhanced algorithm reduced parameters and increased FPS, highlighting its efficiency. Further comparisons showed that SDC-DeepLabv3+ outperformed other segmentation algorithms, achieving higher accuracy and faster prediction speeds. Tests under various weather conditions confirmed the algorithm’s robustness, with the highest success rates for filament localization and picking observed on sunny days. Depth-measurement tests identified an optimal range of 450-510 mm, minimizing visual-localization errors. The improved algorithm demonstrated significant potential for precise and efficient safflower harvesting in complex environments.
According to the study’s lead researcher, Zhenguo Zhang, “The results show that the proposed localization method offers a viable approach for accurate harvesting localization.”
In summary, this study developed a method to accurately detect and localize safflower filament picking points using an improved DeepLabv3+ algorithm. Future research will focus on extending the algorithm to different safflower varieties and similar crops, and optimizing the attention mechanisms to further improve segmentation performance.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.34133/plantphenomics.0194
Authors
Zhenyu Xing1, 3, Zhenguo Zhang1, 2, *, Yunze Wang1, Peng Xu1, Quanfeng Guo1, ChaoZeng1, Ruimeng Shi1
Affications
1 College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Xinjiang Agricultural University,Urumqi 830052, China
2 Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Intelligent Agricultural Equipment, Urumqi 830052, China
3 Key Laboratory of Intelligent Equipment and Robotics for Agriculture of ZhejiangProvince, Hangzhou 310058, China
*Address correspondence to: zhangzhenguo@xjau.edu.cn
Funding information
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52265041 and 31901417]; the Open Subjects of Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Agricultural Intelligent Equipment and Robotics, China [grant number2022ZJZD2202], and the Graduate School-level Research and Innovation Program of Xinjiang Agricultural University, China [grant number XJAUGRI2023021].
About Plant Phenomics
Plant Phenomics is an Open Access journal published in affiliation with the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics & Germplasm Enhancement, Nanjing Agricultural University (NAU) and published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Like all partners participating in the Science Partner Journal program, Plant Phenomics is editorially independent from the Science family of journals. Editorial decisions and scientific activities pursued by the journal’s Editorial Board are made independently, based on scientific merit and adhering to the highest standards for accurate and ethical promotion of science. These decisions and activities are in no way influenced by the financial support of NAU, NAU administration, or any other institutions and sponsors. The Editorial Board is solely responsible for all content published in the journal. To learn more about the Science Partner Journal program, visit the SPJ program homepage.
Journal
Plant Phenomics
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
SDC-DeepLabv3+: Lightweight and precise localization algorithm for safflower-harvesting robots
Article Publication Date
7-May-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.