Salvia miltiorrhiza, known as Danshen, is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. The medicinal properties of Danshen are primarily attributed to its two major bioactive compounds: tanshinones and phenolic acids. Despite their importance, the genetic and regulatory mechanisms underlying their biosynthesis remain poorly understood. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need for in-depth research to uncover the molecular pathways involved in the production of these compounds.
Researchers from the Institute of Medicinal Plant Development and Chengdu Medical College have made a significant stride in this field. Their study (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae047), published in the prestigious journal Horticulture Research on February 23, 2024, explores the role of the Smi-miR858a-SmMYB module in regulating the biosynthesis of tanshinones and phenolic acids.
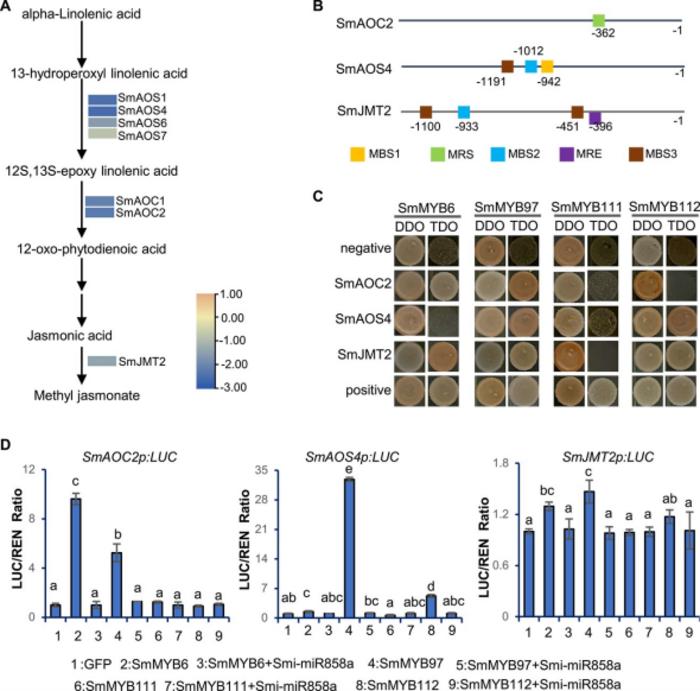
The researchers discovered that overexpression of Smi-miR858a in Salvia miltiorrhiza leads to significant reductions in tanshinone and phenolic acid levels. This miRNA targets and cleaves the transcripts of multiple MYB transcription factors, including SmMYB6, SmMYB97, SmMYB111, and SmMYB112. These MYBs are known to activate genes involved in the biosynthesis pathways of these bioactive compounds. Additionally, Smi-miR858a affects the biosynthesis of methyl jasmonate, an important elicitor of secondary metabolism in plants. The study used computational predictions, degradome analysis, RNA-seq, yeast one-hybrid assays, and transient transcriptional activity assays to validate these findings. The dual regulatory pathways revealed by this research offer promising strategies for enhancing the production of medicinal compounds in Danshen through genetic manipulation.
Dr. Shanfa Lu, the corresponding author of the study, commented, “Our findings elucidate a novel function of miR858 in regulating the biosynthesis of crucial bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Understanding these regulatory mechanisms opens up new possibilities for improving the quality of Danshen through targeted genetic interventions, which could significantly benefit traditional medicine and modern pharmaceuticals.”
The study’s findings could transform medicinal plant breeding, enabling targeted enhancement of bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza. This advancement may not only augment the plant’s therapeutic potency but also inform strategies for improving other medicinal crops. The potential for optimizing plant-based treatments is a significant step forward in the quest for more effective and sustainable pharmaceuticals.

Credit: Binding of SmMYBs to MeJA biosynthesis-related genes.
Salvia miltiorrhiza, known as Danshen, is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. The medicinal properties of Danshen are primarily attributed to its two major bioactive compounds: tanshinones and phenolic acids. Despite their importance, the genetic and regulatory mechanisms underlying their biosynthesis remain poorly understood. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need for in-depth research to uncover the molecular pathways involved in the production of these compounds.
Researchers from the Institute of Medicinal Plant Development and Chengdu Medical College have made a significant stride in this field. Their study (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae047), published in the prestigious journal Horticulture Research on February 23, 2024, explores the role of the Smi-miR858a-SmMYB module in regulating the biosynthesis of tanshinones and phenolic acids.
The researchers discovered that overexpression of Smi-miR858a in Salvia miltiorrhiza leads to significant reductions in tanshinone and phenolic acid levels. This miRNA targets and cleaves the transcripts of multiple MYB transcription factors, including SmMYB6, SmMYB97, SmMYB111, and SmMYB112. These MYBs are known to activate genes involved in the biosynthesis pathways of these bioactive compounds. Additionally, Smi-miR858a affects the biosynthesis of methyl jasmonate, an important elicitor of secondary metabolism in plants. The study used computational predictions, degradome analysis, RNA-seq, yeast one-hybrid assays, and transient transcriptional activity assays to validate these findings. The dual regulatory pathways revealed by this research offer promising strategies for enhancing the production of medicinal compounds in Danshen through genetic manipulation.
Dr. Shanfa Lu, the corresponding author of the study, commented, “Our findings elucidate a novel function of miR858 in regulating the biosynthesis of crucial bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Understanding these regulatory mechanisms opens up new possibilities for improving the quality of Danshen through targeted genetic interventions, which could significantly benefit traditional medicine and modern pharmaceuticals.”
The study’s findings could transform medicinal plant breeding, enabling targeted enhancement of bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza. This advancement may not only augment the plant’s therapeutic potency but also inform strategies for improving other medicinal crops. The potential for optimizing plant-based treatments is a significant step forward in the quest for more effective and sustainable pharmaceuticals.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
Funding information
This work was supported by the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2022-I2M-2-001) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (31370327).
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
Journal
Horticulture Research
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
The Smi-miR858a-SmMYB module regulates tanshinone and phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza
Article Publication Date
23-Feb-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.