As industrialized food markets harm the environment, sustainable food systems emerge as an effective solution. It includes reducing the distance between where the food is produced and consumed, ensuring that people eat locally produced food. One promising approach is community-supported agriculture (CSA), where consumers buy a share of the expected harvest in advance, providing farmers with financial stability and a fixed consumer base while offering consumers fresh, local food.

Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
As industrialized food markets harm the environment, sustainable food systems emerge as an effective solution. It includes reducing the distance between where the food is produced and consumed, ensuring that people eat locally produced food. One promising approach is community-supported agriculture (CSA), where consumers buy a share of the expected harvest in advance, providing farmers with financial stability and a fixed consumer base while offering consumers fresh, local food.
To expand CSA, it is crucial to understand what attracts consumers to join. Previous studies have highlighted factors like access to quality food and environmental concerns. However, these studies are limited to specific contexts and regions. So, a deeper look into diverse consumers’ complex decision-making processes is needed.
Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Eco-Pork Co. Ltd., and Chulalongkorn University investigated the factors influencing consumer participation in CSA. They also examined the relationship between these factors and theorized CSA participation. Led by Mr. Sota Takagi from Tokyo Institute of Technology, the team’s paper was published in Agricultural and Food Economics on 8 July 2024.
Highlighting the motivation behind their study, Takagi says, “Socio-economical, psychological, and geographical factors influence consumers’ motivations to participate in CSA. So, a holistic understanding and systematic organization of these factors is beneficial for formulating expansion strategies, adapting the model to specific cases, and planning interventions.”
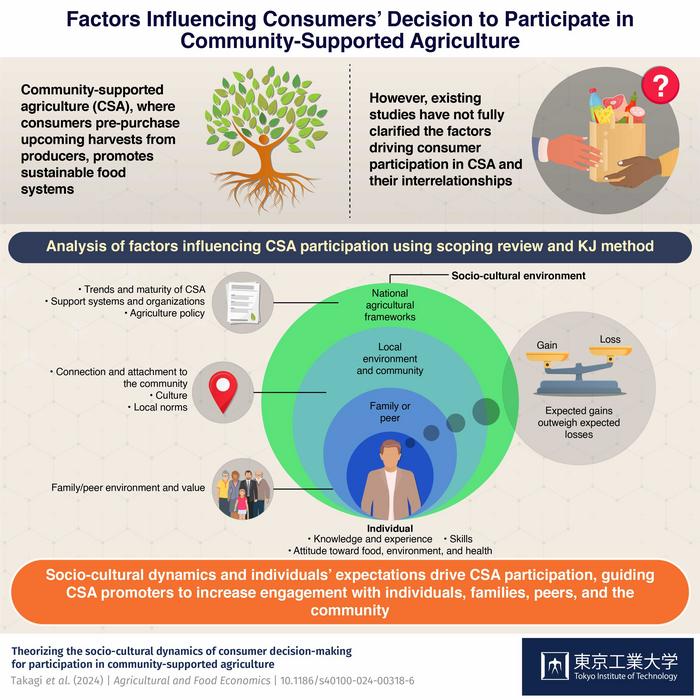
The researchers conducted a scoping review using databases like Web of Science and employed open coding to extract factors influencing consumers to participate, continue, and withdraw from CSA. They organized these factors in a diagrammatic way using the KJ method and developed a theoretical model.
According to this model, two main factors influence consumers to join CSA: the socio-cultural environment and the weighing of expected gains and losses. The socio-cultural environment, encompassing family, peers, local community, and national agricultural conditions, shapes individuals’ knowledge, experience, skills, and attitudes toward food, health, and the environment. Consumers weigh expected gains (such as access to various ingredients) against expected losses, joining CSA if the expected gains outweigh the losses. This decision is also influenced by perceptions and risk tolerance shaped by the socio-cultural environment.
Previous research suggested that among expected gains, access to various ingredients was a strong motivator for CSA participation. However, intangible gains like food education, connections with people and nature, and contributions to environmental and social issues were not found to heavily sway consumers.
After joining CSA, consumers’ experience, knowledge, skills, and attitudes are reshaped by the CSA community’s norms. This influences their decision to stay or withdraw. So, participating in CSA is a reflexive process where consumers keep updating their decisions based on new learnings. These decisions also depend on the difference between expected and actual gains or losses and the social capital they acquire.
Takagi emphasizes, “Individuals are heavily influenced by their socio-cultural environment, where relationships with families, peers, and the community shape their attitudes and behaviors. So, CSA promoters and farmers must consider not only the individual decision-making process but also the lifestyles and values of families and peer groups and engage with them effectively.”
Let us hope these insights help local farmers promote CSA and attract consumers, thereby fostering sustainable food systems and strengthening community resilience.
As industrialized food markets harm the environment, sustainable food systems emerge as an effective solution. It includes reducing the distance between where the food is produced and consumed, ensuring that people eat locally produced food. One promising approach is community-supported agriculture (CSA), where consumers buy a share of the expected harvest in advance, providing farmers with financial stability and a fixed consumer base while offering consumers fresh, local food.
To expand CSA, it is crucial to understand what attracts consumers to join. Previous studies have highlighted factors like access to quality food and environmental concerns. However, these studies are limited to specific contexts and regions. So, a deeper look into diverse consumers’ complex decision-making processes is needed.
Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Eco-Pork Co. Ltd., and Chulalongkorn University investigated the factors influencing consumer participation in CSA. They also examined the relationship between these factors and theorized CSA participation. Led by Mr. Sota Takagi from Tokyo Institute of Technology, the team’s paper was published in Agricultural and Food Economics on 8 July 2024.
Highlighting the motivation behind their study, Takagi says, “Socio-economical, psychological, and geographical factors influence consumers’ motivations to participate in CSA. So, a holistic understanding and systematic organization of these factors is beneficial for formulating expansion strategies, adapting the model to specific cases, and planning interventions.”
The researchers conducted a scoping review using databases like Web of Science and employed open coding to extract factors influencing consumers to participate, continue, and withdraw from CSA. They organized these factors in a diagrammatic way using the KJ method and developed a theoretical model.
According to this model, two main factors influence consumers to join CSA: the socio-cultural environment and the weighing of expected gains and losses. The socio-cultural environment, encompassing family, peers, local community, and national agricultural conditions, shapes individuals’ knowledge, experience, skills, and attitudes toward food, health, and the environment. Consumers weigh expected gains (such as access to various ingredients) against expected losses, joining CSA if the expected gains outweigh the losses. This decision is also influenced by perceptions and risk tolerance shaped by the socio-cultural environment.
Previous research suggested that among expected gains, access to various ingredients was a strong motivator for CSA participation. However, intangible gains like food education, connections with people and nature, and contributions to environmental and social issues were not found to heavily sway consumers.
After joining CSA, consumers’ experience, knowledge, skills, and attitudes are reshaped by the CSA community’s norms. This influences their decision to stay or withdraw. So, participating in CSA is a reflexive process where consumers keep updating their decisions based on new learnings. These decisions also depend on the difference between expected and actual gains or losses and the social capital they acquire.
Takagi emphasizes, “Individuals are heavily influenced by their socio-cultural environment, where relationships with families, peers, and the community shape their attitudes and behaviors. So, CSA promoters and farmers must consider not only the individual decision-making process but also the lifestyles and values of families and peer groups and engage with them effectively.”
Let us hope these insights help local farmers promote CSA and attract consumers, thereby fostering sustainable food systems and strengthening community resilience.
###
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tokyo Tech stands at the forefront of research and higher education as the leading university for science and technology in Japan. Tokyo Tech researchers excel in fields ranging from materials science to biology, computer science, and physics. Founded in 1881, Tokyo Tech hosts over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students per year, who develop into scientific leaders and some of the most sought-after engineers in industry. Embodying the Japanese philosophy of “monotsukuri,” meaning “technical ingenuity and innovation,” the Tokyo Tech community strives to contribute to society through high-impact research.
Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) will be established on October 1, 2024, following the merger between Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), with the mission of “Advancing science and human wellbeing to create value for and with society.”
Journal
Agricultural and Food Economics
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Theorizing the socio‑cultural dynamics of consumer decision‑making for participation in community‑supported agriculture
Article Publication Date
8-Jul-2024