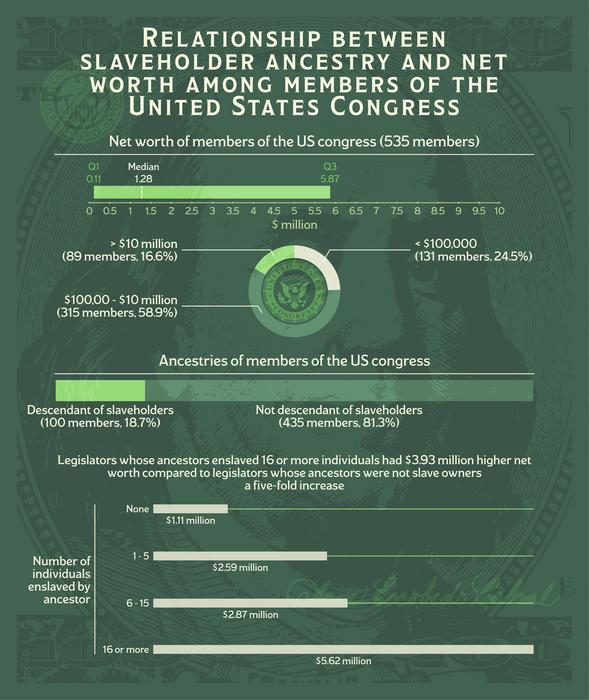
Per a new study, as of April 2021, US Congress members whose ancestors enslaved 16 or more people had a net worth that was five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves. Neil Sehgal of the University of Pennsylvania, US, and Ashwini Sehgal of Case Western Reserve University, US present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 21, 2024.

Credit: Anne-Lise Paris, (www.in-graphidi.com), PLOS, CC-BY 4.0
Per a new study, as of April 2021, US Congress members whose ancestors enslaved 16 or more people had a net worth that was five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves. Neil Sehgal of the University of Pennsylvania, US, and Ashwini Sehgal of Case Western Reserve University, US present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 21, 2024.
Prior research has linked slavery’s intergenerational effects to contemporary inequality, poverty, education, voting behavior, and life expectancy in the US However, the extent to which past slavery in the US contributes to today’s social and economic conditions remains unclear.
In 2023, Reuters released an investigative series that captured information on slaveholder ancestry for all 535 individuals who were US Congress members as of April 15, 2021. To boost understanding of US slavery’s potential contemporary effects, Sehgal and Sehgal cross-referenced information from that report with legislators’ self-disclosed finances.
Statistical analysis of the data revealed that the net worth of US Congress members whose ancestors had 16 or more slaves was about five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves—even after accounting for demographic factors that could also be linked to net worth, including age, sex, race, ethnicity, and education.
The researchers note that legislators are not personally responsible for their ancestors’ actions. Nonetheless, the findings provide new evidence suggesting the possibility that past slaveholding practices in the US may continue to affect people today.
The authors outline a number of limitations of their study. For instance, the findings do not point to any specific mechanism by which slave ownership by ancestors might affect contemporary legislators’ wealth. In addition, the dataset is small, does not account for ancestors’ history of slavery prior to the founding of the U.S. in 1776, and may lack certain financial assets and information that legislators are not required to disclose. And because US Congress members tend to be wealthier, the findings cannot be extrapolated to other US politicians or the general public.
Additional research in these areas could help clarify links between slaveholder ancestry and current wealth, which may aid efforts to address contemporary social and economic disparities.
The authors add: “Members of Congress hold significant power to shape policies and set national agendas. Understanding the wealth disparities within this influential group can drive conversations about economic equity and motivate legislators to support policies addressing historical injustices.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0308351
Citation: Sehgal NKR, Sehgal AR (2024) Slaveholder ancestry and current net worth of members of the United States Congress. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0308351. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0308351
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Journal
PLoS ONE
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Publication Date
21-Aug-2024
COI Statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.