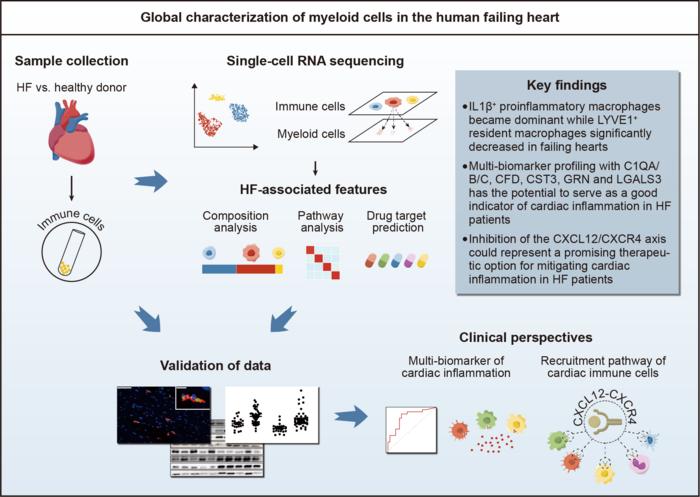
This study was led by Prof. Xiang Cheng (Department of Cardiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology). In this study, researchers employed single-cell RNA sequencing on cardiac immune cells from heart failure patients (ischemic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy) undergoing heart transplantation and from healthy donors. Transcriptomic characteristics associated with heart failure were identified. In addition to the bioinformatics analysis, experimental validations were conducted to further substantiate the reliability of the findings.

Credit: ©Science China Press
This study was led by Prof. Xiang Cheng (Department of Cardiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology). In this study, researchers employed single-cell RNA sequencing on cardiac immune cells from heart failure patients (ischemic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy) undergoing heart transplantation and from healthy donors. Transcriptomic characteristics associated with heart failure were identified. In addition to the bioinformatics analysis, experimental validations were conducted to further substantiate the reliability of the findings.
Macrophages emerged as the most abundant immune cells in normal and failing hearts, with differential expression of genes related to tissue residency, inflammation and fibrosis. In normal human hearts, Mac-LYVE1 expressing resident macrophage-associated genes dominated the macrophage population, but their proportion decreased in failing hearts. In contrast, Mac-IL1β, which surged significantly in failing hearts, exhibited high expression of genes linked to proinflammatory and antigen-presenting function.
Heart samples from patients with heart failure are typically unavailable for clinical assessment, posing a challenge to directly evaluating cardiac inflammation. Inflammatory biomarkers signaling cardiac inflammation have emerged as a viable alternative approach. In this study, a multi-biomarker profiling utilizing complement C1q, complement factor D, cystatin C, progranulin, and galectin-3 demonstrated promising potential as reliable indicators of cardiac inflammation in heart failure.
Chemokine receptor analysis plays a crucial role in unraveling the mechanisms of immune cell migration, which is of great significance for immunotherapies. A key finding of this research is the upregulation of CXCR4 in myeloid cell clusters within failing hearts compared to those in normal hearts. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis potentially orchestrates the recruitment of myeloid cells to failing hearts, highlighting it as a promising therapeutic target for addressing heart failure.
Additionally, drug prediction analysis revealed drugs that potentially target myeloid cell subpopulations associated with heart failure, some of which have demonstrated potential efficacy in impeding the progression of heart failure.
###
See the article:
Global characterization of myeloid cells in the human failing heart
Journal
Science Bulletin