Shenqi Fuzheng (SQ) extract, a revered formulation in traditional Chinese medicine, has long been associated with immunomodulatory effects and the enhancement of Qi. However, the intricate landscape of its bioactive components and their pharmacokinetic profiles has remained an enigma, critically hindering a thorough understanding of its medicinal potential. Recent investigations have emerged in the field, aiming to map out the chemical components of SQ and delineate their absorption patterns when subjected to oral administration. The latest study leveraging ultra-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS) marks a significant stride in bridging these knowledge gaps.
In this innovative study, researchers undertook a comprehensive analysis employing the UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS technology to dissect SQ extract comprehensively. This advanced analytical methodology facilitates not only the identification of a multitude of chemical constituents but also provides invaluable quantitative insights regarding their presence in the bloodstream following oral ingestion. The deployment of this cutting-edge technique has allowed for a nuanced understanding of the pharmacokinetics associated with SQ, ultimately contributing to the broader discourse on herbal formulations in modern pharmacology.
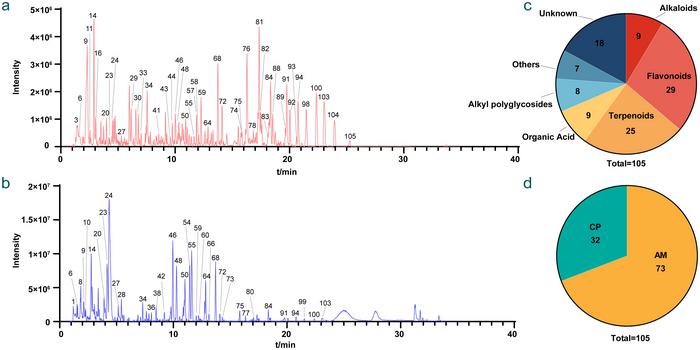
The analysis yielded an astounding repertoire of over 100 identified compounds from the SQ extract, showcasing the richness of its chemical diversity. Among the 105 distinct compounds cataloged, roughly 40 were documented to manifest in the rat plasma post-administration. This finding underscores the effectiveness of SQ’s absorption despite the inherent complexity of herbal matrices. Notably, this detailed cataloging of SQ’s biochemical landscape lays a foundation for future explorations into its therapeutic mechanisms and efficacy.
The dynamic interplay between the various bioactive compounds excavated from SQ demonstrates intriguing absorption kinetics. For instance, organic acids and amino acids emerged as prominent constituents in the plasma, suggesting their crucial roles in the extract’s overall functional profile. Within a mere five minutes after administration, compounds identified as Astragalosides were detected in the bloodstream, hinting at their rapid bioavailability and potential enthusiastic impact on physiological functions. The temporal absorption correlations derived from this study could potentially influence how traditional formulas are optimized for clinical use.
As the research further elucidated, flavonoids presented a more gradual absorption profile, with their concentrations peaking approximately 15 to 30 minutes following administration. This could suggest that different classes of compounds within SQ may serve varying, albeit complementary, roles in achieving the extract’s holistic therapeutic effects. Such insights afford researchers an opportunity to tailor SQ formulations by emphasizing specific compounds that align with desired therapeutic outcomes.
Understanding the peak absorption times of distinct compound classes within SQ is pivotal; the peak concentrations of alkaloids, for example, appeared roughly one hour post-administration. This knowledge provides fertile ground for future pharmacokinetic studies that could encompass clinical trials or further explorations on dosage optimization. The study intricately demonstrates that temporal pharmacokinetic data amassed through advanced chromatographic techniques can enhance the understanding of complex herbal formulations and their multifaceted effects.
Importantly, beyond the identification of constituents and their pharmacokinetic profiles, this study has also initiated discourse on the potential synergistic effects of the identified compounds within SQ. Ancillary studies could pave the way for understanding how these compounds interact not only biochemically but also at the level of physiological responses. The concept of synergy is foundational in traditional Chinese medicine, where the combined effects of various herbs are believed to yield superior efficacy compared to isolated compounds.
The findings presented in this research enrich the existing knowledge surrounding SQ, growing body of literature that champions the advancement of scientific methods in evaluating traditional medicines. Such investigations inherently help dispel myths surrounding traditional remedies by providing empirical evidence that supports their use and enhances research rigor. Increasing the visibility and credibility of such studies could invigorate interest and investment in further investigation into traditional herbal formulations, contributing to global health paradigms.
Moving forward, scholarly inquiries should not only investigate the pharmacological activities of the constituents identified in this study but also delve deeper into their potential interactions and mechanisms. The implications of this research stretch far beyond just clarification of SQ’s components; they set a precedent for the rigorous scientific exploration of herbal compounds that have historically remained under-studied. The scientific community’s embrace of such methodologies signals a promising direction for comprehensive assessments of traditional medicines.
In summary, this groundbreaking study on SQ extract contributes to a deeper recognition of the importance of understanding the chemistry behind herbal formulations. The use of UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS technology in elucidating the complexities of SQ’s chemical constituents and their pharmacokinetics marks a substantial advancement in the Pharmacology of Chinese medicine, paving the way for future research endeavours. As traditional medicine increasingly intersects with modern scientific inquiry, a richer understanding can emerge, leading to enhanced therapeutic strategies and improved public health outcomes.
Such cross-pollination of traditional knowledge with contemporary scientific methodology can redefine the landscape of alternative medicine. It brings to light the significant contributions of long-utilized herbal formulations in health maintenance and disease prevention, proving crucial as the world seeks integrative solutions for increasingly complex health challenges. Ultimately, as research progresses, we may witness a renaissance of interest in traditional practices enhanced through the lens of modern science.
In conclusion, this exploration illustrates that understanding Shenqi Fuzheng extract may just be the tip of the iceberg in uncovering the vast potential hidden within traditional Chinese medicine. Further empirical studies holding fidelity to meticulous scientific standards are essential for revealing the plurality of benefits inherent in these time-honored practices.
Subject of Research: Chemical Constituents and Blood-absorbed Components of Shenqi Fuzheng Extract
Article Title: Identification of Chemical Constituents and Blood-absorbed Components of Shenqi Fuzheng Extract Based on UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS Technology
News Publication Date: 4-Dec-2024
Web References: Future Integrative Medicine
References: DOI link
Image Credits: Xiaohui Fan, Menglei Wang, Bingjie Zhu
Keywords
Traditional Chinese medicine, Pharmacokinetics, Drug studies, Scientific publishing, Blood chemical analysis, Clinical research, Liquid chromatography, Mass spectrometry, Drug research.