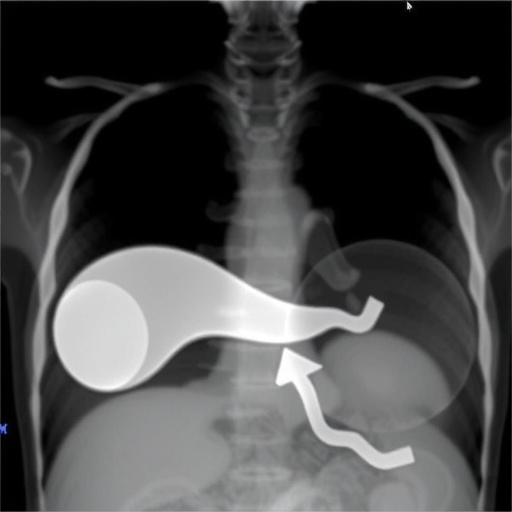
In the intricate realm of human anatomy, the spleen occupies a space that often garners little attention compared to its more famous counterparts, such as the heart or lungs. However, recent studies have illuminated a perplexing condition known as wandering spleen syndrome, prompting a deeper exploration into its complexities and clinical implications. This condition, characterized by an anomalous positioning of the spleen within the abdominal cavity, has long posed challenges to medical practitioners, particularly in pediatric settings. The recent report by Al Blooshi et al. delves into three distinct cases managed at a tertiary care institution, offering a treasure trove of insights into this rare phenomenon.
Wandering spleen syndrome occurs when the spleen, rather than remaining anchored in its typical location in the upper left abdomen, becomes mobile due to a laxity or absence of the ligaments that ordinarily stabilize it. This pathological condition not only increases the risk of abdominal pain and splenic torsion but can also complicate surgical interventions. The significance of understanding and managing wandering spleen syndrome lies in recognizing its potential to escalate from a benign condition to one that poses life-threatening complications, particularly in pediatric patients.
In the reported cases, the subjects presented with a variety of symptoms ranging from abdominal discomfort to acute complications such as splenic torsion. The troublesome nature of wandering spleen syndrome is its oftentimes asymptomatic presentation, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Notably, the cases elucidate the importance of clinical awareness among healthcare providers, as timely intervention can be critical in preventing severe outcomes. The presentation in pediatric cases is particularly noteworthy because children may exhibit non-specific symptoms that do not immediately indicate an underlying splenic irregularity.
The diagnostic pathway for wandering spleen syndrome typically involves imaging studies. Ultrasound (US) often serves as the first-line investigation, allowing for the visualization of splenic position and any related abnormalities. In instances where US results are inconclusive, advanced imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can offer detailed anatomical insights. The role of imaging cannot be understated, as it not only aids in diagnosis but also assists in surgical planning, should intervention be required.
Once diagnosed, the management of wandering spleen syndrome requires a tailored approach based on the presence of symptoms and the overall health of the patient. In asymptomatic cases, careful monitoring may be appropriate, while symptomatic presentations often necessitate surgical intervention. The recently documented cases illustrate the spectrum of management options, from conservative approaches to laparoscopic splenectomy, depending on the acuity of the presentation and the clinician’s assessment of risk versus benefit.
One of the key highlights of Al Blooshi et al.’s report is the emphasis on the multidisciplinary management of wandering spleen syndrome. The involvement of pediatric surgeons, radiologists, and pediatricians ensures that each case is handled with a comprehensive understanding of the complexities involved. Involving multiple specialists not only enhances the decision-making process but also facilitates more holistic patient care, ensuring that all aspects of a child’s health are considered during diagnosis and treatment.
Within the context of the three managed cases, issues surrounding post-operative care and follow-up are crucial. After surgical intervention, monitoring for any complications, whether immediate or long-term, remains a priority. The authors note that patients must be informed about potential risks, including the likelihood of infections due to asplenia if a splenectomy is performed, and the need for vaccinations against encapsulated organisms. The role of education in post-operative management serves as a key component in enhancing patient outcomes.
Furthermore, this study serves as a reminder of the adaptability required within the pediatric field. Each patient’s unique presentation demands an individualized approach, which can often be challenging in the context of a rare condition like wandering spleen syndrome. The documentation of these cases not only adds to the existing literature but potentially empowers practitioners to recognize similar presentations and act swiftly, ultimately improving patient care in similar situations.
A curious aspect of wandering spleen syndrome is its etiology. While the precise cause remains unclear, hormonal influences during adolescence, congenital factors, and trauma have all been proposed as potential contributors. Exploring these avenues can foster a better understanding of the condition, facilitating future research aimed at identifying those at risk and improving prevention strategies.
The pediatric population deserves particular attention regarding wandering spleen syndrome because their anatomical and physiological characteristics differ markedly from adults. As children grow, their bodies undergo numerous changes; thus, understanding how these changes affect the spleen’s mobility and anatomy is paramount. Research efforts in pediatrics must continue to evolve, addressing the unique challenges posed by this rare condition.
Moreover, the growing awareness and documentation of wandering spleen syndrome may pave the way for enhanced educational efforts within medical training programs. Inculcating knowledge about rare disorders will better prepare future healthcare professionals to recognize, diagnose, and manage such cases proficiently. Initiatives to promote recognition can be critical in enacting change and improving outcomes for affected patients.
Looking ahead, the implications of this report extend beyond individual cases to the broader landscape of pediatric care and medical research. By elucidating the complexities of wandering spleen syndrome, more targeted studies can emerge, focusing on preventive care, early diagnosis, and innovative treatment methodologies. Collaboration across specialties will be vital in driving forward our understanding and management of this enigmatic condition.
In summary, the exploration of wandering spleen syndrome sheds light on a fascinating aspect of human anatomy that has broader implications for pediatric care. The recent cases reported by Al Blooshi et al. serve as a critical reminder of the need for continued vigilance, multidisciplinary collaboration, and knowledge-sharing within the medical community. This enigmatic condition is not just a simple anatomical curiosity; it represents a challenge that demands thorough examination, preparation, and innovation in the quest for improved pediatric health outcomes.
Subject of Research: Wandering spleen syndrome in pediatric patients
Article Title: The enigmatic wandering spleen: managing three cases in a tertiary setting
Article References:
Al Blooshi, M., Aboelkheir, A., Hiremath, A. et al. The enigmatic wandering spleen: managing three cases in a tertiary setting.
BMC Pediatr 25, 631 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-06005-9
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: 10.1186/s12887-025-06005-9
Keywords: wandering spleen, pediatric care, abdominal pain, splenic torsion, case report, splenectomy, imaging studies, multidisciplinary approach, post-operative care, medical education.