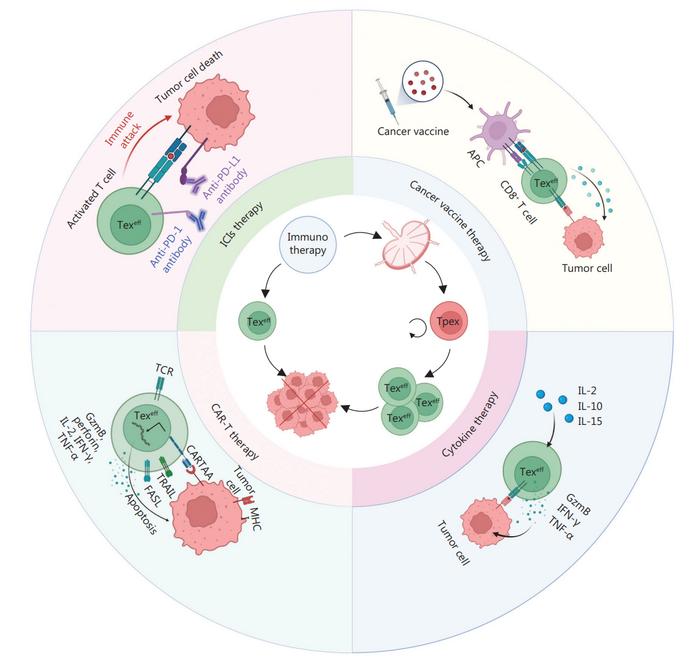
Progenitor exhausted CD8+ T (Tpex) cells have emerged as a pivotal component in tumor immunotherapy due to their unique ability to self-renew and rapidly proliferate. These cells have shown promise in expanding and differentiating into functional exhausted CD8+ T cells, significantly enhancing clinical outcomes. Understanding and leveraging Tpex cells can revolutionize immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer.
Tumor immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune system to target and eradicate cancer cells, offering a crucial treatment for patients unresponsive to surgery or conventional therapies. Despite its potential, the effectiveness of immunotherapy is often hindered by T cell exhaustion within the tumor microenvironment, leading to diminished immune response and tumor progression. Based on these challenges, exploring the role of progenitor exhausted T cells (Tpex) in overcoming immune resistance is essential for advancing immunotherapeutic strategies and improving clinical outcomes.
Researchers from the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, publishing a review (DOI:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0105) in Cancer Biology & Medicine on May 31, 2024, have delved into the characteristics and potential of progenitor exhausted CD8+ T (Tpex) cells in tumor immunotherapy. This review elucidates how Tpex cells, marked by their robust self-renewal and proliferative capacities, can transform into responsive exhausted CD8+ T cells, offering new avenues for cancer treatment.
The review reveals that Tpex cells, identified by their TCF-1 and PD-1 markers, are crucial in the tumor microenvironment. These cells exhibit stem cell-like properties, enabling them to self-renew and proliferate, thus sustaining long-term immune responses. The research highlights a strong correlation between the abundance of Tpex cells and improved clinical outcomes in cancer patients, suggesting that targeting these cells could enhance immunotherapy effectiveness. Tpex cells interact with other immune cells, such as CD4+ T cells and dendritic cells, to modulate the immune response, providing a dynamic approach to overcoming T cell exhaustion. By transforming into more functional exhausted CD8+ T cells, Tpex cells help maintain robust anti-tumor activity. This study underscores the potential of Tpex cells in developing more effective cancer immunotherapies, offering new strategies to tackle immune resistance in tumors.
Dr. Xiao Zheng from Soochow University states, “The discovery of Tpex provides a groundbreaking perspective in understanding and combating T cell exhaustion in cancer. Their unique ability to renew and proliferate opens up promising pathways for enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy, offering hope for more effective cancer treatments.”
The insights from this study pave the way for developing targeted therapies that leverage Tpex cells to improve immunotherapy outcomes. By enhancing the understanding of Tpex cell functions and interactions within the tumor microenvironment, future research can focus on devising strategies to maintain their effector stage, thus potentially transforming cancer treatment protocols and significantly improving patient survival rates.

Credit: Cancer Biology & Medicine
Progenitor exhausted CD8+ T (Tpex) cells have emerged as a pivotal component in tumor immunotherapy due to their unique ability to self-renew and rapidly proliferate. These cells have shown promise in expanding and differentiating into functional exhausted CD8+ T cells, significantly enhancing clinical outcomes. Understanding and leveraging Tpex cells can revolutionize immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer.
Tumor immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune system to target and eradicate cancer cells, offering a crucial treatment for patients unresponsive to surgery or conventional therapies. Despite its potential, the effectiveness of immunotherapy is often hindered by T cell exhaustion within the tumor microenvironment, leading to diminished immune response and tumor progression. Based on these challenges, exploring the role of progenitor exhausted T cells (Tpex) in overcoming immune resistance is essential for advancing immunotherapeutic strategies and improving clinical outcomes.
Researchers from the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, publishing a review (DOI:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0105) in Cancer Biology & Medicine on May 31, 2024, have delved into the characteristics and potential of progenitor exhausted CD8+ T (Tpex) cells in tumor immunotherapy. This review elucidates how Tpex cells, marked by their robust self-renewal and proliferative capacities, can transform into responsive exhausted CD8+ T cells, offering new avenues for cancer treatment.
The review reveals that Tpex cells, identified by their TCF-1 and PD-1 markers, are crucial in the tumor microenvironment. These cells exhibit stem cell-like properties, enabling them to self-renew and proliferate, thus sustaining long-term immune responses. The research highlights a strong correlation between the abundance of Tpex cells and improved clinical outcomes in cancer patients, suggesting that targeting these cells could enhance immunotherapy effectiveness. Tpex cells interact with other immune cells, such as CD4+ T cells and dendritic cells, to modulate the immune response, providing a dynamic approach to overcoming T cell exhaustion. By transforming into more functional exhausted CD8+ T cells, Tpex cells help maintain robust anti-tumor activity. This study underscores the potential of Tpex cells in developing more effective cancer immunotherapies, offering new strategies to tackle immune resistance in tumors.
Dr. Xiao Zheng from Soochow University states, “The discovery of Tpex provides a groundbreaking perspective in understanding and combating T cell exhaustion in cancer. Their unique ability to renew and proliferate opens up promising pathways for enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy, offering hope for more effective cancer treatments.”
The insights from this study pave the way for developing targeted therapies that leverage Tpex cells to improve immunotherapy outcomes. By enhancing the understanding of Tpex cell functions and interactions within the tumor microenvironment, future research can focus on devising strategies to maintain their effector stage, thus potentially transforming cancer treatment protocols and significantly improving patient survival rates.
###
References
DOI
10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0105
Original Source URL
Funding information
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32270955), the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline (Grant No. YXZDXK202236), the Key Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (Grant No. K2023069), and the Science and Technology Support Plan (Social Development) Project of Changzhou (Grant No. CE20235058).
About Cancer Biology & Medicine
Cancer Biology & Medicine (CBM) is a peer-reviewed open-access journal sponsored by China Anti-cancer Association (CACA) and Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital. The journal monthly provides innovative and significant information on biological basis of cancer, cancer microenvironment, translational cancer research, and all aspects of clinical cancer research. The journal also publishes significant perspectives on indigenous cancer types in China. The journal is indexed in SCOPUS, MEDLINE and SCI (IF 5.6, 5 year IF 5.9), with all full texts freely visible to clinicians and researchers all over the world (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/journals/2000/).
Journal
Cancer Biology & Medicine
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Revolutionizing tumor immunotherapy: unleashing the power of progenitor exhausted T cells
Article Publication Date
31-May-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.