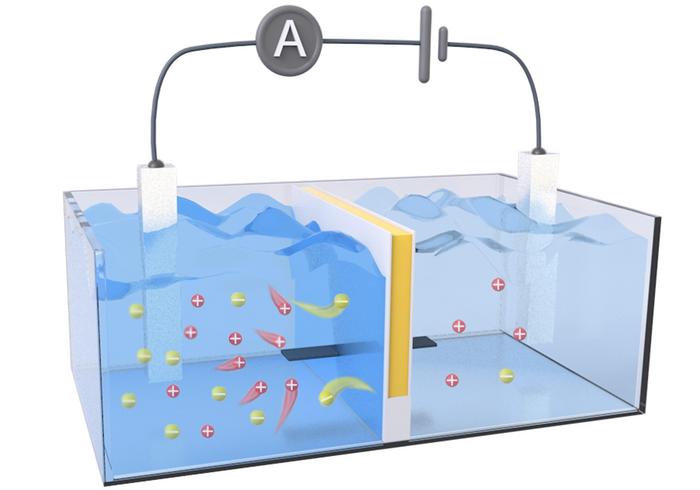
Estuaries — where freshwater rivers meet the salty sea — are great locations for birdwatching and kayaking. In these areas, waters containing different salt concentrations mix and may be sources of sustainable, “blue” osmotic energy. Researchers in ACS Energy Letters report creating a semipermeable membrane that harvests osmotic energy from salt gradients and converts it to electricity. The new design had an output power density more than two times higher than commercial membranes in lab demonstrations.

Credit: Adapted from ACS Energy Letters 2024, DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00320
Estuaries — where freshwater rivers meet the salty sea — are great locations for birdwatching and kayaking. In these areas, waters containing different salt concentrations mix and may be sources of sustainable, “blue” osmotic energy. Researchers in ACS Energy Letters report creating a semipermeable membrane that harvests osmotic energy from salt gradients and converts it to electricity. The new design had an output power density more than two times higher than commercial membranes in lab demonstrations.
Osmotic energy can be generated anywhere salt gradients are found, but the available technologies to capture this renewable energy have room for improvement. One method uses an array of reverse electrodialysis (RED) membranes that act as a sort of “salt battery,” generating electricity from pressure differences caused by the salt gradient. To even out that gradient, positively charged ions from seawater, such as sodium, flow through the system to the freshwater, increasing the pressure on the membrane. To further increase its harvesting power, the membrane also needs to keep a low internal electrical resistance by allowing electrons to easily flow in the opposite direction of the ions. Previous research suggests that improving both the flow of ions across the RED membrane and the efficiency of electron transport would likely increase the amount of electricity captured from osmotic energy. So, Dongdong Ye, Xingzhen Qin and colleagues designed a semipermeable membrane from environmentally friendly materials that would theoretically minimize internal resistance and maximize output power.
The researchers’ RED membrane prototype contained separate (i.e., decoupled) channels for ion transport and electron transport. They created this by sandwiching a negatively charged cellulose hydrogel (for ion transport) between layers of an organic, electrically conductive polymer called polyaniline (for electron transport). Initial tests confirmed their theory that decoupled transport channels resulted in higher ion conductivity and lower resistivity compared to homogenous membranes made from the same materials. In a water tank that simulated an estuary environment, their prototype achieved an output power density 2.34 times higher than a commercial RED membrane and maintained performance during 16 days of non-stop operation, demonstrating its long-term, stable performance underwater. In a final test, the team created a salt battery array from 20 of their RED membranes and generated enough electricity to individually power a calculator, LED light and stopwatch.
Ye, Qin and their team members say their findings expand the range of ecological materials that could be used to make RED membranes and improve osmotic energy-harvesting performance, making these systems more feasible for real-world use.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The paper’s abstract will be available on April 24 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here:
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Journal
ACS Energy Letters
Article Title
Decoupled Ionic and Electronic Pathways for Enhanced Osmotic Energy Harvesting
Article Publication Date
24-Apr-2024