New research from a Florida State University professor and colleagues explains the mathematics behind how initial predispositions and additional information affect decision making.

Credit: Courtesy of Bhargav Karamched
New research from a Florida State University professor and colleagues explains the mathematics behind how initial predispositions and additional information affect decision making.
The research team’s findings show that when decision makers quickly come to a conclusion, the decision is more influenced by their initial bias, or a tendency to err on the side of one of the choices presented. If decision makers wait to gather more information, the slower decision will be less biased. The work was published today in Physical Review E.
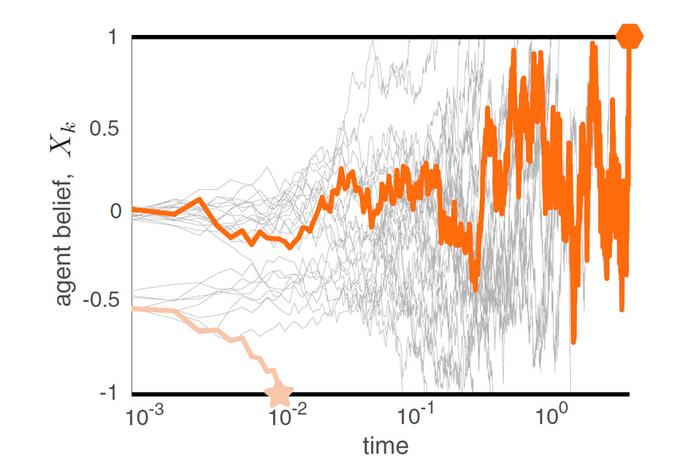
“The basic result might seem sort of intuitive, but the mathematics we had to employ to prove this was really non-trivial,” said co-author Bhargav Karamched, an assistant professor in the FSU Department of Mathematics and the Institute of Molecular Biophysics. “We saw that for the first decider in a group, the trajectory of their belief is almost a straight line. The last decider hovers around, going back and forth for a while before making a decision. Even though the underlying equation for each agent’s belief is the same except for their initial bias, the statistics and behavior of each individual is very different.”
The researchers built a mathematical model that represented a group of agents required to decide between two conclusions, one which was correct and one which was incorrect. The model assumed each actor within a group was acting rationally, that is, deciding based off their initial bias and the information they are presented, rather than being swayed by the decisions of individuals around them.
Even with evidence and assuming perfect rationality, bias toward a particular decision caused the earliest deciders in the model to make the wrong conclusion 50% of the time. The more information actors gathered, the more likely they were to behave as if they weren’t biased and to arrive at a correct conclusion.
Of course, in the real world, people are swayed by all sorts of inputs, such as their emotions, the decisions their friends made and other variables. This research offers a metric showing how individuals within a group should make decisions if they are acting rationally. Future research could compare real-world data against this metric to see where people are diverting from optimally rational choices and consider what might have caused their divergence.
The researchers’ model is known as a drift diffusion model, so called because it combines two concepts: individual actor’s tendency to “drift,” or move toward an outcome based on evidence, and the random “diffusion,” or variability of the information presented.
The work could be used, for example, to understand when people are being unduly swayed by early decisions or falling victim to groupthink. It even helps describe other complex scenarios with many individual actors, such as the immune system or the behavior of neurons.
“There is still a lot of work to do to understand decision making in more complicated situations, such as cases where more than two alternatives are presented as choices, but this is a good starting point,” Karamched said.
This research was a multi-institution collaboration involving doctoral candidate Samantha Linn and Associate Professor Sean D. Lawley of the University of Utah, Associate Professor Zachary P. Kilpatrick of the University of Colorado, and Professor Krešimir Josic of the University of Houston.
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
Journal
Physical Review E
Article Title
Fast decisions reflect biases; slow decisions do not
Article Publication Date
12-Aug-2024