The eventual prevalence of a piece of misinformation may depend on its topic and the country in which it spreads, with notable differences between the UK, Germany, France and Italy, according to a study published May 8, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fabiana Zollo from the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy, and colleagues. This finding suggests that policies to combat misinformation and polarization may need to be context-specific in order to be effective, the authors say.

Credit: Baqir et al., 2024, PLOS ONE, CC-BY 4.0 (
The eventual prevalence of a piece of misinformation may depend on its topic and the country in which it spreads, with notable differences between the UK, Germany, France and Italy, according to a study published May 8, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fabiana Zollo from the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy, and colleagues. This finding suggests that policies to combat misinformation and polarization may need to be context-specific in order to be effective, the authors say.
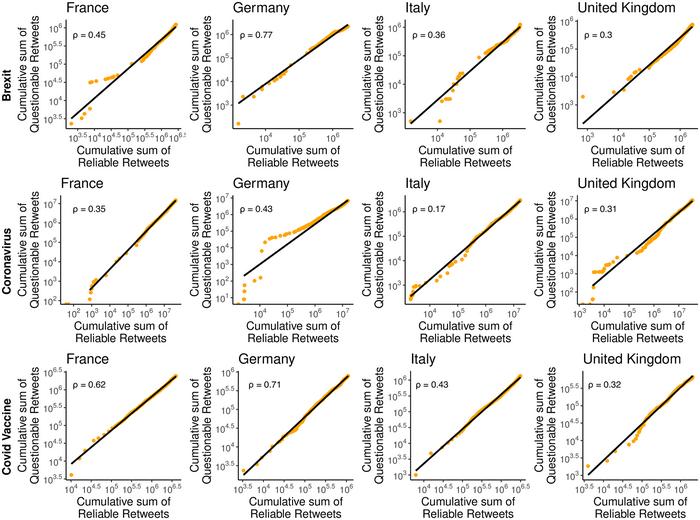
Researchers analyzed news activity on Twitter (now X) in France, Germany, Italy and the UK from 2019 to 2021, including a focus on news about Brexit, the coronavirus, and the Covid vaccines. Each news source they analyzed was rated as either “Reliable” or “Questionable” based upon their NewsGuard (a tool that evaluates the reliability of news outlets based on nine journalistic criteria) score.
Across all four countries, the vast majority of users only ever consumed reliable news sources on each of the three topics. But in every country and in each topic, there were always a small percentage of users who only ever consumed questionable news sources — with very few people consuming a mix of both reliable and questionable sources.
The ratio of questionable news vs reliable news consumption and spread varied between countries. Overall, Germany had the highest ratio of questionable news retweets to reliable news retweets on all three topics, with France in second, followed by Italy, and the UK had the lowest proportion of questionable news retweets overall. However, measures of misinformation varied by topic. Italy, for example, had the lowest proportion of questionable news retweets for the topic of the coronavirus – but had the highest percentage of people consuming only questionable news sources on Brexit. These kinds of differences could emphasize that “cultural nuances” will be important when it comes to fighting misinformation, the authors write.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE:
Citation: Baqir A, Galeazzi A, Zollo F (2024) News and misinformation consumption: A temporal comparison across European countries. PLoS ONE 19(5): e0302473.
Author Countries: Italy
Funding: F.Z. acknowledges financial support from the European Union’s Rights, Equality and Citizenship project EUMEPLAT grant no. 101004488. A.G. and F.Z. acknowledge partial support from the IRIS Academic Research Coalition (UK government, grant no. SCH-00001-3391). F.Z. acknowledges the partial support received from SERICS (PE00000014), which is funded under the MUR National Recovery and Resilience Plan by the European Union’s NextGenerationEU initiative. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. There was no additional external funding received for this study.
Journal
PLoS ONE
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
News and misinformation consumption: A temporal comparison across European countries
Article Publication Date
8-May-2024
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.