With the advent of smart technology and the Internet of Things (IoT), wearable devices have surged in popularity, enhancing the way we monitor our health and lifestyle. Among these innovations are wireless body area networks (WBANs), which utilize wireless sensors to provide real-time physiological monitoring. This technology not only contributes significantly to health management, but also presents unique opportunities for disease prevention and rehabilitation. The emergence of WBANs signifies a step forward in personal health technology, promising a future where individuals can track their health metrics with unprecedented ease and accuracy.
Despite the potential benefits of wearable technologies, many devices currently on the market utilize conventional silicon-based processors and electronics. These traditional components, while effective, introduce several limitations. The rigidity of silicon-based processors often makes them challenging to integrate seamlessly with soft textiles, which is particularly important in wearable applications. Additionally, the reliance on external power sources complicates the user experience, as frequent battery recharges are necessary, raising costs and limiting usability over extended periods. Such challenges highlight the need for more adaptable, integrated solutions within the realm of wearable technology.
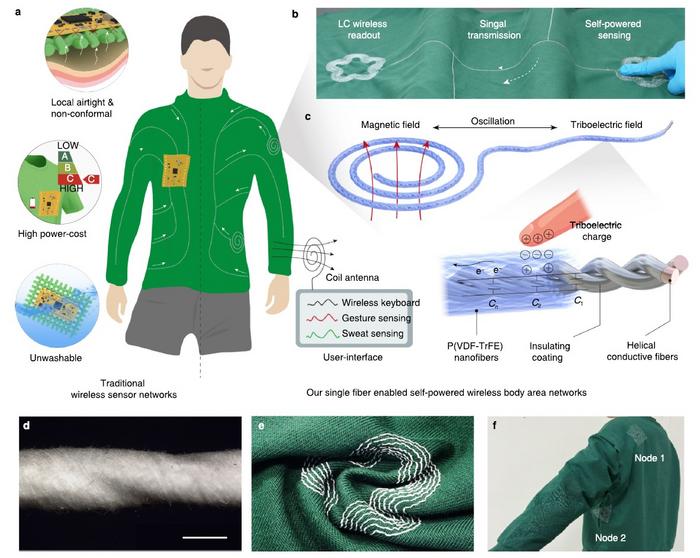
To address these issues, an innovative research team from Donghua University in Shanghai, in collaboration with ETH Zurich, has developed a new type of wireless sensing network employing a single, fabric-based fiber. This groundbreaking approach focuses on a multifunctional fiber that can generate energy, sense signals, and transmit data wirelessly, contributing to the design of self-powered, chipless smart clothing systems. The significance of their research lies in a unique combination of functionality and comfort, challenging the status quo of how wearable technologies are typically conceived and realized.
The practical applications of this newly developed fiber extend beyond conventional health tracking. One of the remarkable advancements includes the ability of the fiber-WBAN to serve as an extension to existing smartwatches. By operating as a wireless fabric keyboard, users can control applications seamlessly, demonstrating the potential for interactive clothing that enhances everyday activities, such as playing games or navigating digital content. This dimension not only enhances user engagement but also exemplifies how clothing can evolve into smart technology platforms that interact with our daily lives.
Furthermore, the fiber-WBAN is designed to be embroidered directly onto garments, allowing it to naturally conform to human movement. Such integration not only facilitates comfort and wearability but also paves the way for gesture recognition applications. Users can leverage the fiber’s potential to engage with their environment through movements, effectively building a network of human interaction that is responsive and intuitive. This transformative feature represents a leap forward in the way we conceive the intersection of digital experiences and physical clothing.
In addition to facilitating interaction, the fiber-WBAN also boasts capabilities in quantitative signal sensing. One particular application includes sweat monitoring, where the fiber reacts to different concentrations of sodium and chloride ions found in human sweat. Such monitoring could be invaluable for fitness enthusiasts and healthcare professionals, as it allows for precise tracking of hydration levels and electrolyte balance. The implications of such capabilities extend to a broader audience, reflecting a significant advancement in personal health monitoring, particularly for athletic individuals or those with specific health concerns.
Research leader Hongzhi Wang emphasizes the innovative nature of their work, stating that their findings illustrate the potential for textiles to bridge the gap between technology and everyday wearables. This research opens new avenues for harnessing electromagnetic properties and designing systems that can operate seamlessly alongside the human body. By merging the concepts of wearable electronics with textile engineering, this research allows for advancements in both user experience and technological integration that were previously unattainable.
As the drive for more efficient, user-friendly wearable devices continues, this research represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of smart textiles. The combination of energy generation, signal processing, and wireless communication within a single fiber not only showcases the promise of modern textile technology but also illustrates the vast potential to reshape how we approach personal health monitoring. This innovation signifies a move away from bulky, power-dependent devices toward sleek, integrated solutions that prioritize comfort and usability.
The study presented by the researchers from Donghua University and ETH Zurich is a testament to the ongoing advancements in the field of wearable technology. Their pioneering work represents not only a technological breakthrough but also a commitment to enhancing user experience. As this field continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly inspire further innovation and research that prioritizes seamless integration, comfort, and functionality in wearable technology.
In conclusion, the development of the single-fiber-enabled, self-powered wireless body area network embodies a significant leap forward in the world of wearable technology. As researchers and innovators build upon this foundation, we can expect to see emerging trends that dramatically alter how we interact with clothing and technology. The implications extend beyond individual health monitoring, offering a glimpse into a future where smart textiles redefine our interaction with the digital world, enhancing both our lifestyles and our understanding of health.
As we stand at the precipice of this technological revolution, it is essential that we embrace the possibilities that these innovations present. The integration of technology into our clothing not only has the potential to revolutionize health management but also holds the promise of transforming our day-to-day experiences. Ultimately, this research will inspire future advancements that challenge the boundaries of wearable technology and redefine the way we perceive our interactions with the world around us.
Subject of Research:
Article Title:
News Publication Date:
Web References:
References:
Image Credits: