The world of robotics is witnessing a transformative shift with the rise of soft robotics, which offers unparalleled flexibility and adaptability in various applications, from medical interventions to intricate rescue operations. A groundbreaking review article by Zhou et al. published in Cyborg Bionic Systems in 2024, sheds light on this evolution, highlighting the crucial integration of actuation and sensing technologies that pave the way for truly intelligent soft robots.

Credit: Shuai Zhou, Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Design and Manufacture of Micro-Nano Biomedical Instruments.
The world of robotics is witnessing a transformative shift with the rise of soft robotics, which offers unparalleled flexibility and adaptability in various applications, from medical interventions to intricate rescue operations. A groundbreaking review article by Zhou et al. published in Cyborg Bionic Systems in 2024, sheds light on this evolution, highlighting the crucial integration of actuation and sensing technologies that pave the way for truly intelligent soft robots.
Soft robots, unlike their rigid counterparts, are made from materials that mimic the mechanical properties of living tissues, allowing them to move and adapt with a life-like grace. This capability makes them ideal for operating in unstructured and unpredictable environments where traditional robots might falter. The innovative research spearheaded by the team from Southeast University in Nanjing, China, focuses on merging actuation—the ability to move and interact with surroundings—with sensing, which involves collecting data about the environment. This integration is essential for developing soft robots that can react and adapt to their surroundings autonomously.
Actuation technologies enable soft robots to perform diverse tasks, such as navigating rough terrain or delicately handling objects. Sensing technologies, on the other hand, allow these robots to perceive their environment, from detecting obstacles to assessing the properties of the objects they interact with. By integrating these two capabilities, soft robots can perform complex tasks more effectively and with greater autonomy.
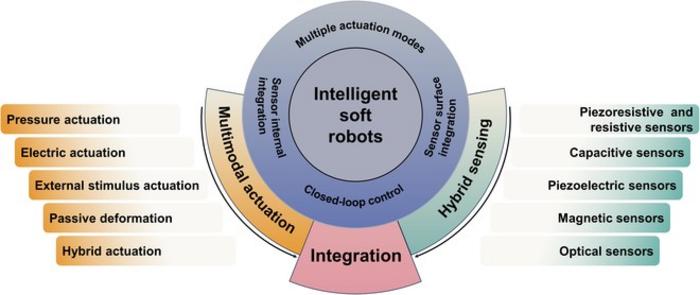
Zhou and colleagues discuss various actuation methods, including pressure-driven, electrically driven, and those utilizing shape memory materials. These methods have allowed soft robots to achieve complex movements such as rotation, crawling, and bending. On the sensing side, the researchers explore advancements in proprioceptive (self-perception) and haptic (touch-based) sensing, which enable robots to understand their body position and react to physical contact.
One of the review’s highlights is the detailed examination of three integration methodologies for actuation and sensing:
Sensor Surface Integration: Embedding sensors on the surface of the robot to provide real-time feedback on external interactions.
Sensor Internal Integration: Incorporating sensors within the robot’s body to monitor internal states, enhancing the robot’s ability to adapt its movements based on dynamic internal and external conditions.
Closed-loop System Integration: Utilizing sensor feedback to create systems where actuation and sensing are continuously informing and optimizing each other’s functions.
Despite the promising advancements, the review identifies several challenges facing the field. These include the need for more durable and reliable integration techniques, the development of materials that can withstand diverse operational environments, and the creation of more sophisticated models for predicting and controlling robot behavior.
The future directions suggested by the research team include enhancing the load capacity of these robots, improving their energy efficiency, and refining the technologies that allow them to operate in extreme conditions. These improvements could revolutionize the way robots are used in fields such as deep-sea exploration, disaster recovery, and health-care.
Zhou,Li et al.’s review not only summarizes the current state of soft robotics but also serves as a call to action for researchers. It encourages further exploration into the integration of actuation and sensing to realize the full potential of soft robots. As this field evolves, it promises to bring forth robots that are not only more adaptable and safe for human interaction but also capable of performing tasks that are currently unimaginable.
The paper, “Integrated Actuation and Sensing: Toward Intelligent Soft Robots,” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Apr 18, 2024, at DOI:
Journal
Cyborg and Bionic Systems
Article Title
Integrated Actuation and Sensing: Toward Intelligent Soft Robots
Article Publication Date
18-Apr-2024