In recent advancements within the medical imaging field, a notable study has emerged focusing on enhancing low-dose Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images through the innovative application of a Diffused Multi-scale Generative Adversarial Network (DMGAN). The study, set to be published in 2025 in the journal “BioMedical Engineering OnLine,” addresses a crucial aspect of medical imaging—the delicate balance between minimizing radiation exposure to patients and maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
With the increasing prevalence of cancer and other diseases requiring PET imaging, there is a pressing demand for techniques that can reduce the dosage of radiation administered to patients. Traditional methods often compromise image quality in order to achieve lower radiation doses, presenting a dilemma for healthcare professionals. The DMGAN introduced in this study aims to tackle this issue by converting low-dose PET (L-PET) images into high-quality full-dose PET (F-PET) images, thereby maximizing diagnostic efficacy while keeping patient safety at the forefront.
The study outlines a two-module structure: the diffusion generator and the u-net discriminator. These components work synergistically to transform L-PET images into F-PET images while enhancing the visual quality and retaining critical diagnostic details. The diffusion generator collects different information levels from the input images, which boosts its capacity to generalize across varying conditions, ultimately improving training stability. This innovative approach marks a significant leap forward in the application of generative adversarial networks in the medical imaging arena.
Furthermore, the generated images are fed into the u-net discriminator, designed to extract intricate details through both holistic and focused perspectives. This dual-processing strategy ensures that the resultant F-PET images capture the essential characteristics required for medical evaluation. The comprehensive nature of this approach is indicative of a shift in medical imaging paradigm, where artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in enhancing image fidelity.
To benchmark the performance of DMGAN against traditional reconstruction methods, the researchers deployed a combination of qualitative assessments and quantitative metrics. In terms of quantitative analysis, two specific measures were utilized: the Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) and the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR). These metrics provide a robust framework for evaluating image quality, enabling a clear comparison of the efficacy between various imaging reconstruction techniques.
The results demonstrated that the DMGAN method achieved superior PSNR and SSIM scores compared to other methods under evaluation. Impressively, the PSNR improved by a notable 6.2% over the next best alternatives. This enhancement reflects the algorithm’s capability to synthesize images that not only optimize quality but also preserve the critical metabolic information contained within the PET scans.
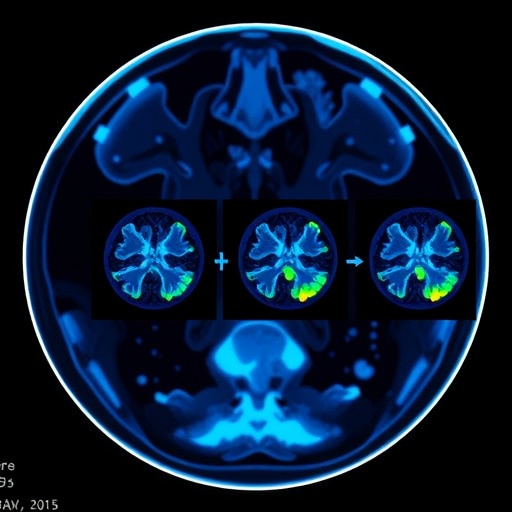
One of the most striking outcomes of this study lies in the demonstration of the synthesized F-PET image’s ability to represent a more accurate voxel-wise metabolic intensity distribution. This is particularly valuable in the detection and characterization of medical conditions such as epilepsy, where precise imaging of brain activity can influence treatment decisions and outcomes. The detailed depiction of the epilepsy focus stands to benefit both clinicians and patients by enabling more informed diagnostic processes.
As the healthcare sector continues to explore ways to harness technology for better patient outcomes, the findings of this study underscore the significance of integrating deep learning techniques within medical imaging workflows. The balance between reducing radiation exposure and maintaining diagnostic performance is not only a technical challenge but a moral imperative that this research effectively addresses.
The conclusion drawn from this pioneering investigation is that the DMGAN approach provides a formidable solution for the reconstruction of low-dose PET images. By restoring original details more effectively than existing models trained on similar datasets, this method stands poised to reshape the landscape of PET imaging. The implications of such advancements extend far beyond technical efficiency; they illustrate a commitment to patient safety and the ongoing evolution of medical diagnostics.
In summary, the introduction of the DMGAN in transforming low-dose PET images heralds a new era in medical imaging, characterized by enhanced image quality and decreased radiation exposure. The research paves the way for future studies to explore and refine these techniques further, with the potential to significantly impact clinical practice and patient care standards. As the results garner attention, they contribute to the evolving narrative of how artificial intelligence and advanced imaging technologies can collaboratively enhance healthcare delivery.
This research symbolizes a significant milestone in leveraging artificial intelligence to confront pressing challenges in medical diagnostics, and as such, offers a glimpse into a future where patients can enjoy both safety and high-quality imaging.
Subject of Research: Low-Dose PET Image Reconstruction Using GANs
Article Title: Diffused Multi-scale Generative Adversarial Network for low-dose PET images reconstruction
Article References: Yu, X., Hu, D., Yao, Q. et al. Diffused Multi-scale Generative Adversarial Network for low-dose PET images reconstruction.
BioMed Eng OnLine 24, 16 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-025-01348-x
Image Credits: Scienmag.com
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-025-01348-x
Keywords: Low-dose PET imaging, Generative Adversarial Networks, Medical Imaging, Radiation Exposure, Diagnostic Performance.