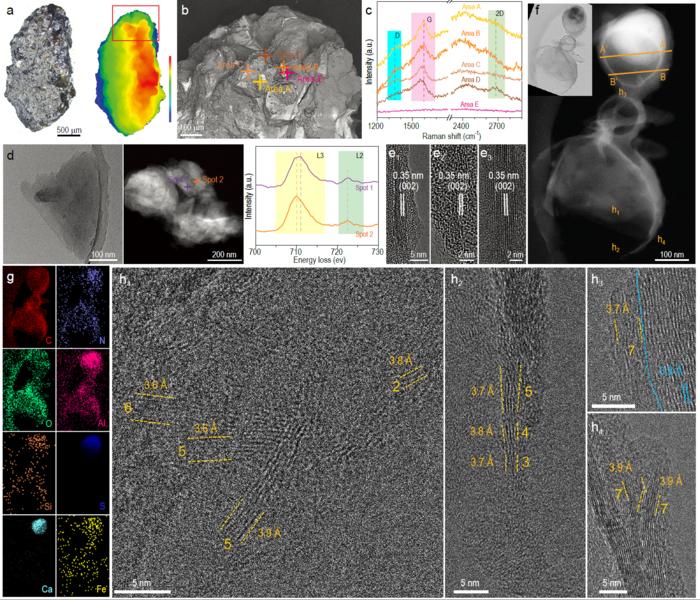
A recent study, published in National Science Review, revealed the existence of naturally formed few-layer graphene, a substance consisting of carbon atoms in a special, thin-layered structure.

Credit: ©Science China Press
A recent study, published in National Science Review, revealed the existence of naturally formed few-layer graphene, a substance consisting of carbon atoms in a special, thin-layered structure.
The team, led by professors Meng Zou, Wei Zhang and senior engineer Xiujuan Li from Jilin University and Wencai Ren from the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Metal Research, analyzed an olive-shaped sample of lunar soil, about 2.9 millimeters by 1.6 mm, retrieved from the Chang’e 5 mission in 2020.
According to the team, scientists generally believe that some 1.9 percent of interstellar carbon exists in the form of graphene, with its shape and structure determined by the process of its formation.
Using a special spectrometer, researchers found an iron compound that is closely related to the formation of graphene in a carbon-rich section of the sample. They then used advanced microscopic and mapping technologies to confirm that the carbon content in the sample comprised “flakes” that have two to seven layers of graphene.
The team proposed that the few-layer graphene may have formed in volcanic activity in the early stages of the moon’s existence, and been catalyzed by solar winds that can stir up lunar soil and iron-containing minerals that helped transform the carbon atoms’ structure. They added that impact processes from meteorites, which create high-temperature and high-pressure environments, may also have led to the formation of graphene.
On Earth, graphene is becoming a star in materials sciences due to its special features in optics, electrics and mechanics. The team believes their study could help develop ways to produce the material inexpensively and expand its use.
“The mineral-catalyzed formation of natural graphene sheds light on the development of low-cost scalable synthesis techniques of high-quality graphene,” the paper said. “Therefore, a new lunar exploration program may be promoted, and some forthcoming breakthroughs can be expected.”
###
See the article:
Discovery of natural few-layer graphene on the Moon
Journal
National Science Review