Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry (Tomo-PIV) is a 3D particle image velocimetry technology combined with computed tomography (CT), which can realize full-field quantitative measurement of spatial flow field. It has become the mainstream technical for 3D-3C flow field measurement. 3D reconstruction is one of the core steps of Tomo-PIV, which plays a crucial role in obtaining accurate three-dimensional flow field information. However, the reconstruction of 3D particle distribution from limited particle images has always been a challenging task. This is especially true for three-dimensional flow fields with high particle densities, where traditional reconstruction algorithms often struggle to achieve the desired reconstruction accuracy.

Credit: Duanyu Zhang, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology
Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry (Tomo-PIV) is a 3D particle image velocimetry technology combined with computed tomography (CT), which can realize full-field quantitative measurement of spatial flow field. It has become the mainstream technical for 3D-3C flow field measurement. 3D reconstruction is one of the core steps of Tomo-PIV, which plays a crucial role in obtaining accurate three-dimensional flow field information. However, the reconstruction of 3D particle distribution from limited particle images has always been a challenging task. This is especially true for three-dimensional flow fields with high particle densities, where traditional reconstruction algorithms often struggle to achieve the desired reconstruction accuracy.
In recent years, the development of deep learning has inspired some new methods to solve the 3D reconstruction problem for Tomo-PIV. However, the supervised learning method requires a large number of ground truth data as training information, which is very difficult to gather from experiments. Although synthetic datasets can be used as alternatives, they are still not exactly the same with the real-world experimental data .
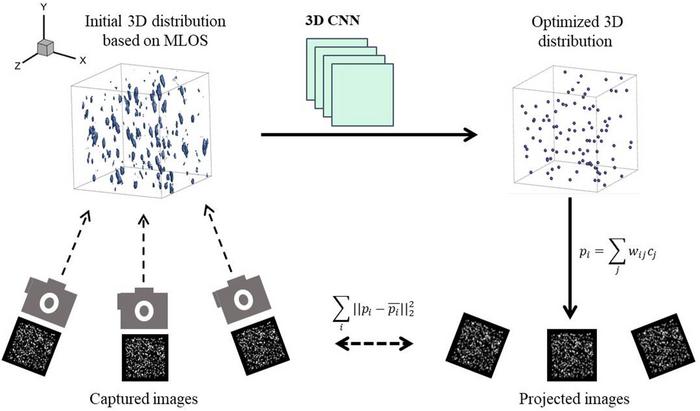
To address this problem, the research team proposed an unsupervised reconstruction technique based on the U-net named UnRTU to reconstruct the volumetric particle distribution of Tomo-PIV. Instead of using ground truth data, a projection function is used as an unsupervised loss function for network training to reconstruct particle distribution. It updates the 3D particle distribution by minimizing the difference between the original recorded images and the projected images from the reconstructed 3D particle distribution. Compared to traditional reconstruction techniques, the method demonstrates superior performance in both simulations and experiments, showing significant potential and advantages, especially for flow fields with high particle density or images with high noise level.
Because it is difficult to know the actual fluid flow field velocity information accurately, in order to quantitatively verify the measurement accuracy of the method in the actual flow, the research team developed a set of particle motion test bench using cured epoxy resin containing particles. By using different methods to reconstruct the particle distribution within the cured epoxy resin, the results demonstrated that the UnRTU achieved higher reconstruction quality compared to other methods. Furthermore, the team conducted high-speed three-dimensional flow field measurement experiments in a planar cascade, demonstrating the reconstruction performance of the technique in high-density particle fields and its feasibility in high-velocity flow fields.
“This study provides an unsupervised deep learning-based method for the 3D reconstruction of Tomographic PIV,” said Wu Zhou, a professor at the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology. Since the unsupervised reconstruction method does not require a large amount of ground truth data for network training, it has greater advantages in real experimental scenarios.
“In the next step, our research team will further evaluate and improve the performance of UnRTU. Additionally, we plan to establish a more general neural network model so that it can be generalized to other scenarios after training,” said Zhou. In this way, the researchers might expand the application scenarios of UnRTU and improve its potential for practical applications.
The research team includes Duanyu Zhang, Haoqin Huang, Wu Zhou, Mingjun Feng, Dapeng Zhang from the School of Energy and Power Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, and Limin Gao from National Key Laboratory of Aerodynamic Design and Research, Northwestern Polytechnical University.
The research is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Aerodynamic Design and Research.
Journal
Particuology
Method of Research
Imaging analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Reconstruction of particle distribution for tomographic particle image velocimetry based on unsupervised learning method
Article Publication Date
6-Aug-2024