In the evolving landscape of hemophilia treatment, a recent study sheds light on the comparative effectiveness of prophylactic therapies for patients suffering from Hemophilia B. The focus of this research is on extended half-life factor IX therapies, specifically the innovations represented by rIX-FP as compared to rFIXFc and N9-GP. These treatments have been designed to enhance patient outcomes, streamline treatment regimens, and improve overall quality of life. With Hemophilia B being a rare but serious bleeding disorder, controlling bleeding episodes and maintaining a stable factor IX level is critical for patient health and wellbeing.
Hemophilia B, caused by a deficiency of clotting factor IX, presents unique challenges for patients and their healthcare providers. Traditional treatments often required frequent infusions, resulting in a significant burden for both patients and caregivers. The development of extended half-life factors represents a significant advancement in therapy, potentially reducing the frequency of infusions and enhancing the overall management of the disease. This latest research by Olivieri et al. emphasizes the clinical implications of such therapies, offering valuable insights into their real-world effectiveness.
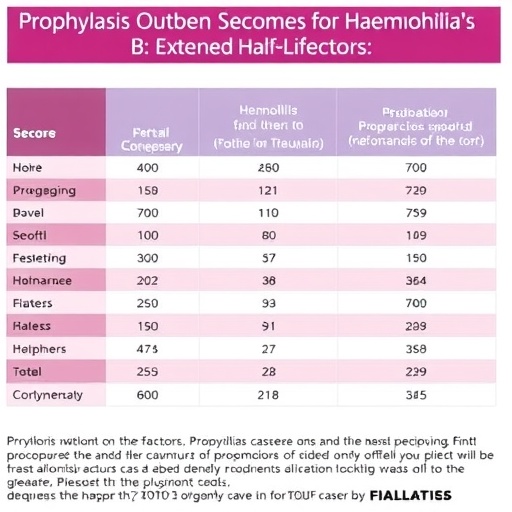
The study utilizes a comprehensive analysis of medical chart data from Germany, capturing the experiences of patients undergoing treatment with different extended half-life factor IX therapies. By leveraging real-world evidence, the researchers aim to bridge the gap between clinical trial findings and everyday patient outcomes. This approach acknowledges the complexity of individual patient experiences and treatment responses, making the findings particularly relevant for clinicians and patients alike.
In comparing rIX-FP to rFIXFc and N9-GP, the study seeks to delineate the practical advantages of each therapy. Initial findings suggest that rIX-FP may offer superior bleeding control, which is a pivotal factor in enhancing the quality of life for individuals living with this disorder. Effective prophylaxis can mean the difference between a life constrained by the fear of bleeding episodes and one where patients can confidently engage in daily activities. Highlighting these differences can assist healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions tailored to individual patient needs.
One compelling aspect of the study is its design, which draws on a robust sample size from various medical centers across Germany, ensuring a diverse representation of the patient population. The use of real-world data significantly enhances the validity and applicability of the findings. By analyzing outcomes in a clinical setting, the study addresses ecological validity, providing a clearer picture of how these therapies function outside the controlled environment of clinical trials.
Moreover, the implications of this research extend beyond immediate patient care. By demonstrating the effectiveness of rIX-FP in managing Hemophilia B, the study reinforces the value of investing in innovative therapies. It serves as a clarion call to stakeholders in healthcare—pharmaceutical companies, policymakers, and clinicians—regarding the importance of supporting the continued development of advanced treatment options that can fundamentally improve patient outcomes.
Side effects and treatment adherence are critical components of any therapeutic regimen, particularly for chronic conditions like Hemophilia B. The research addresses these facets by analyzing patient adherence rates and the incidence of adverse events associated with each therapy. Preliminary data suggests that extended half-life therapies may lead to improved adherence, owing to the reduced frequency of infusions required. Patients who face lesser treatment burdens are often more likely to adhere to their prescribed regimens.
The benefits of prolonged factor half-life are further accentuated by considerations of cost-effectiveness, a pressing concern in current healthcare discussions. As therapies become more innovative, their costs can escalate, raising questions about accessibility for patients. This study also hints at the economic implications of using extended therapy, suggesting that improved outcomes and reduced bleeding events may potentially offset the higher upfront costs associated with newer treatments.
The patients participating in this study represent a range of ages and demographic backgrounds, which enriches the data collected. By analyzing outcomes across different populations, the research aims to identify any disparities or variations in treatment effectiveness. This focus adds depth to the understanding of how these therapies perform across diverse patient bases, ultimately informing tailored treatment approaches that consider unique patient profiles.
As the findings from this study are disseminated within the medical community, there is a significant opportunity for ongoing education regarding the management of Hemophilia B. Medical practitioners must stay abreast of new evidence in treatment options, as the field is rapidly evolving. The research provides a platform for discussing treatment refinements and the necessity of continuous assessment of practices based on emerging data.
In conclusion, the comparative analysis of extended half-life factor IX therapies provides invaluable insights into the management of Hemophilia B. With potential benefits such as improved adherence, decreased bleeding episodes, and overall enhancements in quality of life, the implications for patients are profound. Ongoing research and real-world evidence are essential components in the journey towards better patient-centered care in the field of hematology.
This pivotal study not only contributes significantly to the existing body of knowledge on Hemophilia B treatments but also opens avenues for future research. As the scientific community continues to explore the nuances of hemophilia management, patients stand to benefit greatly from advancements that arise from rigorous studies and real-world observations.
Given that the landscape of hemophilia treatment is always changing, continuous dialogue between researchers, clinicians, and patients is critical. It is important for all stakeholders to engage in conversations about the findings from such research studies, ensuring that insights translate effectively into practice. Only then can the full potential of emerging treatments be realized for the benefit of patients living with Hemophilia B.
Subject of Research: Real-World Outcomes of Prophylaxis with Extended Half-life Factor IX in Hemophilia B.
Article Title: Comparing Real-World Outcomes of Prophylaxis with Extended Half-life Factor IX (rIX-FP vs. rFIXFc and N9-GP) for Haemophilia B: An Analysis of Medical Chart Data from Germany.
Article References:
Olivieri, M., Yan, S., Yang, Y. et al. Comparing Real-World Outcomes of Prophylaxis with Extended Half-life Factor IX (rIX-FP vs. rFIXFc and N9-GP) for Haemophilia B: An Analysis of Medical Chart Data from Germany.
Adv Ther (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-025-03336-y
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: Hemophilia B, Factor IX, rIX-FP, rFIXFc, N9-GP, Prophylactic therapies, Treatment adherence, Real-world evidence, Bleeding control, Quality of life, Economic implications.