US trade tariffs have become a central focus of economic analysis, especially in the wake of escalating tensions and retaliation among major trading partners. A recent study conducted by researchers at Aston University presents an in-depth examination of the potential economic implications stemming from various US trade tariff scenarios. This comprehensive analysis underscores the precarious position of the UK and other global economies, advocating for timely and collaborative measures from UK policymakers to both mitigate risks and leverage opportunities in an ever-evolving trade environment.
As of early 2025, the imposition of tariffs by the administration of then-President Donald Trump has ignited significant global reactions. Tariffs on US imports from Mexico and Canada stand at a formidable 25%, while worldwide tariffs on imported steel and aluminum have been enacted. Notably, tariffs on China have spiked to 20%, with impending car import tariffs expected to escalate tensions further. These measures have prompted counteractions across Europe, Asia, and the Americas, highlighting a rising trend of retaliatory trade policies that reverberate through international markets.
The researchers’ report titled “Tariffs and Triumph: The UK’s Edge in a Fractured World,” authored by Professor Jun Du and Dr. Oleksandr Shepotylo, models the anticipated global economic fallout from these US tariffs and delineates a strategic framework for the UK’s response. Leveraging core economic principles alongside a structured gravity model, the report meticulously analyzes bilateral export data from 2023 in conjunction with gross domestic product (GDP) metrics for a total of 132 countries around the globe.
Among the report’s critical findings is the prediction of real GDP per capita declines in the United States alongside significant welfare declines in Canada and Mexico. Specifically, initial US tariffs are expected to prompt a 2.7% rise in prices domestically, leading to a 0.9% downturn in real GDP per capita. Canadian welfare is projected to plummet by 3.2%, while Mexico could see a stark 5% decline. If retaliation ensues from Canada, Mexico, and China, the US economic losses deepen further, with welfare declines observed in Canada reaching 5.1% and Mexico at 7.1%.
Further scenarios outlined in the report present an even bleaker picture for the US economy should tariffs be imposed on EU goods. This would likely trigger a sharp contraction in transatlantic trade, resulting in production setbacks within the European Union and a corresponding 1.5% decline in US welfare. The study predicts that, in response, the EU would retaliate with its own tariffs on US goods, leading to mutual price hikes and substantial welfare losses on both sides of the Atlantic. This tit-for-tat approach would yield complex ramifications for global trade dynamics, particularly for the UK.
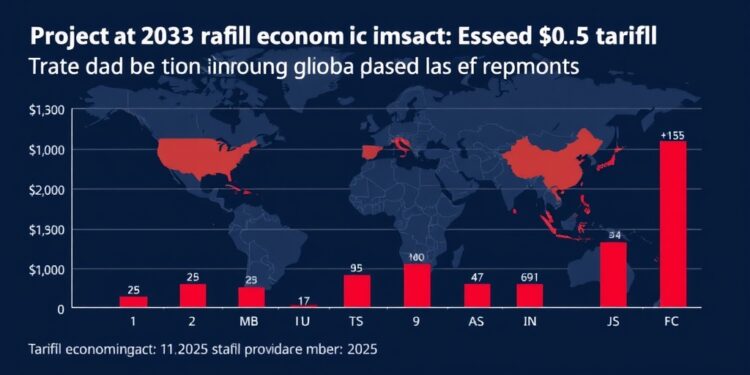
The forecast becomes dire when considering a comprehensive global tariff situation, which could induce a drastic contraction in international trade alongside significant price hikes affecting welfare across North America and trade volumes in the UK. In scenarios involving full-fledged retaliatory tariffs, the bottom line could account for a staggering $1.4 trillion loss in global welfare. Such daunting figures underscore the potential severity of escalating trade wars, necessitating proactive approaches from nations like the UK.
For the UK, reliance on imports from the US reveals critical vulnerabilities in supply chains. Under catastrophic circumstances, UK exports to the US may plummet by as much as 43.6%, which would reverberate throughout the international market and distinctly affect trade routes to Mexico and the EU. Nonetheless, a strategic response emphasizing cooperation could allow the UK to capitalize on trade diversion possibilities, potentially increasing exports to the US by up to 17.5% if the EU imposes tariffs on US goods.
Professor Jun Du stresses the urgent need for the UK to adopt a comprehensive strategy, asserting that while the landscape for tariffs is complex, opportunities also present themselves through adept navigations of trade diversions. He indicates that US tariffs, while daunting, might yield significant gains for the UK, provided there is minimal disruption to relations with the EU. The delicate balance will involve optimizing trade flows while addressing the challenges posed by political misalignment and divergence inherent in post-Brexit economic policies.
In summary, the UK’s current monetary policy framework affords it a unique degree of flexibility during this tumultuous period of global trade restructuring. While vulnerabilities persist, such as heavy dependencies on US and EU markets, avenues for progress exist. The UK might consider diversifying trade relationships, redirecting attention toward less affected regions like India and various Asian markets, thus refining supply chains and bolstering domestic production capabilities in vital sectors, such as electronics and automotive components.
The economic analysis underscores a pragmatic response, urging UK policymakers to pursue a balanced approach that harmonizes short-term gains with long-term stability. Recommendations include enhancing supply chain coordination with EU partners, embracing collaborative initiatives in global trade negotiations, and calling for reforms within the World Trade Organization (WTO). Strategic negotiations with the US could also be better positioned through parallel commitments to the EU, such as revitalizing youth mobility programs, thereby signaling a continuity of cooperation.
Ultimately, the findings of the Aston University report serve as a critical guiding framework for decision-makers as they navigate this uncertain terrain. By engaging with the complex economic scenarios laid out, UK leaders can formulate a robust strategy aimed at both safeguarding national interests and fostering resilience amid a shifting global trade landscape.
Subject of Research: Economic impact of US trade tariffs
Article Title: Tariffs and Triumph: The UK’s Edge in a Fractured World
News Publication Date: 1-Apr-2025
Web References: Aston University Research Page
References: N/A
Image Credits: N/A
Keywords: International trade, Market economics, Economics research, Gross domestic product