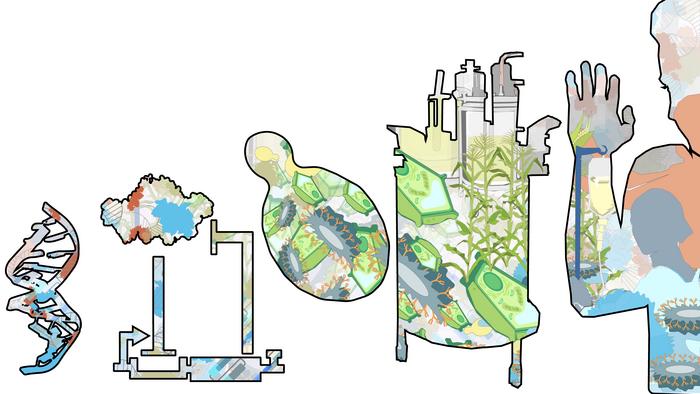
The field of synthetic biology, the science of manipulating biology, has a lot of “cooks in the kitchen,” which has both helped it flourish and made it unusually difficult to create a cohesive, consistent curriculum for students at every level of study. Each discipline involved — from chemical engineering to ethics — has a unique approach to teaching and literature, which creates inconsistencies between what scientists learn.

Credit: Lucks lab
The field of synthetic biology, the science of manipulating biology, has a lot of “cooks in the kitchen,” which has both helped it flourish and made it unusually difficult to create a cohesive, consistent curriculum for students at every level of study. Each discipline involved — from chemical engineering to ethics — has a unique approach to teaching and literature, which creates inconsistencies between what scientists learn.
Now, Northwestern University researchers propose a new way to teach synthetic biology that uses different levels of organization — starting at the molecular scale and growing to the societal scale — to teach core principles and a holistic view of developing sustainable synthetic biology technologies. The approach incorporates components from many disciplines, allowing people from many different backgrounds to access synthetic biology education.
A paper detailing the framework was published yesterday (June 26) in the journal Nature Communications.
“Early versions of synthetic biology courses lacked a conceptual foundation,” said Julius Lucks, a synthetic biology expert and lead author. “From an educational perspective, you saw a kind of hodgepodge depending on which department you were in. We set ourselves the challenge of trying to figure out, how can you merge all those disciplines, somehow develop a common framework and create a common language?”
Lucks is a professor of chemical and biological engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering and co-director of the Center for Synthetic Biology (CSB).
When genetic engineering emerged in the 1970s, the idea to reuse, repurpose and reconfigure biological systems to address challenges in society — the core of synthetic biology — became possible. With CRISPR’s advent around 1990, synthetic biology was popularized and, without any curriculum to turn to, faced an identity problem.
“One of the biggest problems we saw in our students and labs are that they tend to be focused on a very specific problem,” said Ashty Karim, a Northwestern research assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering and the paper’s first author.
“For example, if you’re looking at how CRISPR works, you might be studying the localized protein machinery that makes edits to the DNA. But if you’re going to create a technology based on CRISPR, there are many other important facets than the molecular scale workings. How does it work in the context of a cell or a population of cells within someone’s body across different tissues? How does that interact with current healthcare systems? These are discussions that we need to be having and might influence the science that we do.”
Karim is the director of research at CSB and a core member of its faculty.
From this came the idea of breaking down biology into scales, developed originally from a conversation about how most introductory biology courses present a continuum that moves from DNA to tissue to organism. There are emerging behaviors that appear at different levels of organization; society behaves differently from an organism, and so on. Synthetic biology, according to the paper, can be broken down into five components: molecular, circuit/network, cellular, biological communities and societal.
Key to the proposed framework is the presence of robust ethics at each scale.
By piloting the curriculum with undergraduate and graduate students at Northwestern, the authors said they found that different core principles, like thermodynamics and kinetics, mapped onto different scales naturally. For instance, do you need to understand a principle all the time? Or can you “ignore” it up to a certain scale?
Curriculum should also be underpinned by case studies that help learners analyze how engineering choices made at one scale affect biological function at another, assemble potential solutions to global challenges across scales and identify the impact of synthetic biology on societal goals and ethical issues. Case studies can also be tailored to the institution or instructor implementing the curriculum.
Presenting the approach to classes has been greatly successful, according to Lucks and Karim, who both said the concept “clicked” for students even the first time they taught the course. The scales concept has been so successful that in fact, the Northwestern Center for Synthetic Biology uses it to organize its cutting-edge collaborative research.
The researchers also hope the curriculum can be implemented much more broadly and have provided resources and ideas that others may use to adapt the approach to their needs and interests.
The development of the deconstruction approach was supported by the National Science Foundation through the SynBAS NRT program (grant number 2021900) and by the Bachrach Family Foundation.
Journal
Nature Communications
Article Title
Deconstructing synthetic biology across scales: a conceptual approach for training synthetic biologists
Article Publication Date
26-Jun-2024