In a groundbreaking new study published in Frontiers in Medicine, researchers have unveiled compelling evidence that practicing Transcendental Meditation® (TM) can significantly reduce the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in Black men and women who are at elevated risk for heart disease. This randomized controlled trial marks a pivotal advancement in the search for accessible, non-pharmacological interventions to address the persistent racial disparities that plague cardiovascular health outcomes in the United States.
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of mortality among Black Americans, a disparity exacerbated by socio-economic stressors, healthcare inequities, and psychosocial pressures. This recent trial specifically targeted this vulnerable population by enrolling 200 Black adults diagnosed with cardiovascular disease or identified as having a heightened risk due to traditional factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol. The participants were followed for an extended period of up to 14 years, providing a robust data set to evaluate long-term outcomes.
Participants were randomly assigned to either a Transcendental Meditation program or a comprehensive health education intervention modeled on the American Heart Association’s guidelines, which prioritized diet and exercise. While both groups showed promising results in halting the progression of carotid artery atherosclerosis, as assessed by carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT), only those practicing TM exhibited a statistically significant and sustained decline in the actual occurrence of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events after 5 and 10 years.
The clinical implications of these findings are profound. TM, a simple, stress-reducing meditation practice, appears to confer substantial cardiovascular protection beyond the conventional benefits of lifestyle education alone. This suggests a physiological mechanism through which TM may mediate favorable changes in autonomic nervous system balance, reducing sympathetic overdrive and lowering systemic inflammation—key pathological drivers in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia.
The trial’s lead author, Dr. Keith Norris from UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine, emphasized the importance of addressing psychosocial stress as a modifiable risk factor. “Our study highlights the potential of Transcendental Meditation to transform cardiovascular outcomes particularly within marginalized communities facing systemic challenges,” Dr. Norris stated. The randomized nature and extended follow-up period lend strong credence to the reliability of these results, distinguishing this investigation as one of the largest and longest longitudinal trials assessing meditation’s impact on cardiovascular risk.
The senior investigator, Dr. Robert Schneider, Director of Maharishi International University’s Center for Natural Medicine and Prevention, underscored the significance of sustained practice and institutional support. “Participants in the TM group had ongoing access to meditation support beyond the initial year, which may contribute to the durability of cardiovascular benefits.” This ongoing engagement contrasts with the health education group, whose intervention ceased after the initial study period, possibly explaining differences in long-term event reduction.
Mechanistically, TM’s cardiovascular benefits may be linked to its influence on blood pressure regulation, endothelial function, and metabolic parameters. Previous NIH-funded studies have documented TM’s efficacy in reducing hypertension, improving insulin sensitivity, and mitigating inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and interleukin-6. This new trial corroborates and extends these findings within a high-risk, real-world cohort.
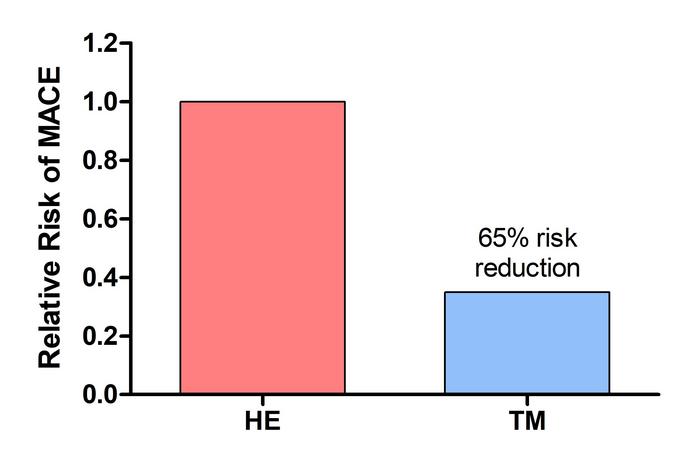
Furthermore, the observed 65% relative risk reduction in MACE after 5 years in the TM group is clinically significant, rivaling or exceeding many contemporary pharmacological therapies for heart disease prevention. This positions TM as a potentially scalable, low-cost adjunct therapy capable of bridging health disparities through community-based implementation.
Importantly, the carotid intima-media thickness measurements conducted in this study serve as a validated surrogate endpoint, reflecting early atherosclerotic changes that precede clinical events. The similarity in cIMT progression suppression between groups suggests that TM’s superior effect on actual cardiovascular outcomes may involve additional pathways, possibly neuroendocrine or psychosocial, warranting further mechanistic exploration.
The study was conducted at King-Drew Medical Center in Los Angeles, a facility serving many underserved minority populations, enhancing the generalizability of the results. The randomized controlled trial design, coupled with rigorous follow-up and blinded outcome adjudication, fortify the scientific robustness of the conclusions drawn.
In light of these findings, integrating TM into public health strategies aimed at reducing cardiovascular disease burden among high-risk populations emerges as a promising avenue. This holistic, stress-modulating approach could complement existing clinical interventions, empowering patients through self-care practices that are both scientifically validated and culturally adaptable.
Looking ahead, future research should explore the molecular underpinnings of meditation-induced cardiovascular protection, evaluate cost-effectiveness in broader populations, and assess implementation frameworks within various healthcare settings. Given the persistent inequities in cardiovascular mortality among Black Americans, innovative interventions such as TM-based programs hold transformative potential.
In summary, this landmark study furnishes compelling evidence that Transcendental Meditation, by mitigating stress and physiological dysregulation, can dramatically reduce the risk of severe cardiovascular complications in Black adults at high risk. TM’s incorporation into multimodal cardiac care paradigms could reshape prevention strategies and alleviate the burden of heart disease in disproportionately affected communities worldwide.
Subject of Research: People
Article Title: A randomized controlled trial of meditation and health education on carotid intima-media thickness and major adverse cardiovascular events in Black men and women.
News Publication Date: 18-Mar-2025
Web References:
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1513699
References:
Norris K, Salerno J, Bairey Merz CN, Kaushik V, Gelleta S, Castillo A, Nidich S, Gaylord-King C, Schneider RH (2025). A randomized controlled trial of meditation and health education on carotid intima-media thickness and major adverse cardiovascular events in Black men and women. Frontiers in Medicine. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1513699
Image Credits: Maharishi International University
Keywords: Transcendental Meditation, cardiovascular disease, Black Americans, major adverse cardiovascular events, randomized controlled trial, psychosocial stress, carotid intima-media thickness, atherosclerosis prevention, heart disease disparities, meditation, stress reduction, integrative medicine