Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/11/24) – Emissions of nitrous oxide – a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane – continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.

Credit: Global Carbon Project
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/11/24) – Emissions of nitrous oxide – a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane – continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.
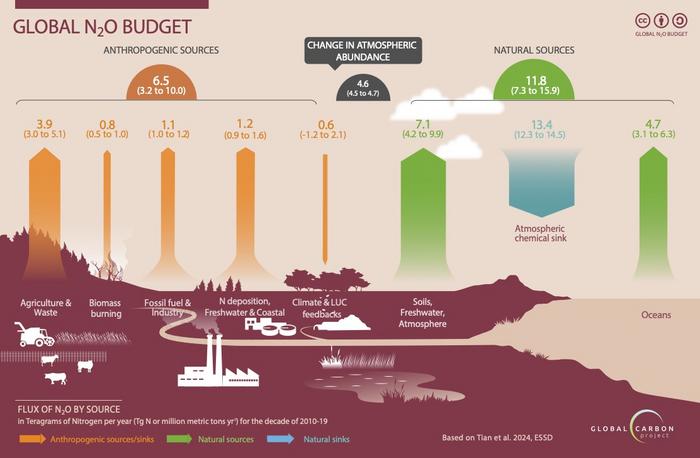
Agricultural production accounted for 74 percent of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s – attributed primarily to the use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands – according to the report “Global Nitrous Oxide Budget 2024”, led by researchers from Boston College and published today in the journal Earth System Science Data.
In an era when greenhouse gas emissions must decline to reduce global warming, in 2020 and 2021 nitrous oxide flowed into the atmosphere at a faster rate than at any other time in history, the international team of researchers reported. On Earth, excess nitrogen contributes to soil, water, and air pollution. In the atmosphere, it depletes the ozone layer, and exacerbates climate change.
Agricultural emissions reached 8 million metric tons in 2020, a 67 percent increase from the 4.8 million metric tons released in 1980, according to the study, the most comprehensive study of global nitrous oxide emissions and sinks produced by a team of 58 researchers from 55 organizations in 15 countries.
“Nitrous oxide emissions from human activities must decline in order to limit global temperature rise to 2°C as established by the Paris Agreement,” said the report’s lead author, Hanqin Tian, the Schiller Institute Professor of Global Sustainability at Boston College. “Reducing nitrous oxide emissions is the only solution since at this point no technologies exist that can remove nitrous oxide from the atmosphere.”
The concentration of atmospheric nitrous oxide reached 336 parts per billion in 2022, a 25 percent increase over pre-industrial levels that far outpaces predictions previously developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, said Tian, director of the Center for Earth System Science and Global Sustainability at BC’s Schiller Institute for Integrated Science and Society.
“This emission increase is taking place when the global greenhouse gasses should be rapidly declining towards net zero emissions if we have any chances to avoid the worst effects of climate change,” said Tian, who coordinated the research on behalf of the Global Carbon Project.
The world’s farmers used 60 million metric tons of commercial nitrogen fertilizers in 1980. By 2020, the sector used 107 million metric tons. That same year, animal manure contributed 101 million metric tons for a combined 2020 usage of 208 million metric tons.
The unfettered increase in a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential approximately 300 times larger than carbon dioxide, presents dire consequences for the planet.
Drawing on millions of nitrous oxide measurements taken during the past four decades on land and in the atmosphere, freshwater systems, and the ocean, Tian said the researchers have generated the most comprehensive assessment of global nitrous oxide to date.
The researchers examined data collected around the world for all major economic activities that lead to nitrous oxide emissions and reported on 18 anthropogenic and natural sources and three absorbent “sinks” of global nitrous oxide.
The top 10 nitrous oxide emission-producing countries are: China, India, the United States, Brazil, Russia, Pakistan, Australia, Indonesia, Turkey, and Canada, the researchers found.
Some countries have seen success implementing policies and practices to reduce nitrous oxide emissions, according to the report. Emissions in China have slowed since the mid 2010s; as have emissions in Europe during the past few decades.
In the U.S., agricultural emissions continue to creep up while industrial emissions have declined slightly, leaving overall emissions rather flat. Natural sources of nitrous oxide emissions from soil, fresh- and saltwater have remained stable
Established in 2001, The Global Carbon Project analyzes the impact of human activity on greenhouse gas emissions and Earth systems, producing global budgets for the three dominant greenhouse gasses – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide – that assess emissions and sinks to inform further research, policy, and international action.
Improved agricultural practices that limit the use of nitrogen fertilizers and animal waste can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. Tian said there is a need for more frequent assessments so mitigation efforts can target high-emission regions and activities. An improved inventory of sources and sinks will be required if progress is going to be made toward the objectives of the Paris Agreement.
“While there have been some successful nitrogen reduction initiatives in different regions, we found an acceleration in the rate of nitrous oxide accumulation in the atmosphere in this decade”, said Global Carbon Project Executive Director Josep Canadell, a research scientist at CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency. “The growth rates of atmospheric nitrous oxide in 2020 and 2021 were higher than any previous observed year and more than 30 percent higher than the average rate of increase in the previous decade.”
Journal
Earth System Science Data
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Global Nitrous Oxide Budget (1980-2020)
Article Publication Date
11-Jun-2024
COI Statement
None