A groundbreaking study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal Genes & Diseases unveils a novel molecular mechanism pivotal to ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis (OCPM), shedding light on the complex interplay between cellular signaling pathways and cancer stemness that underlies chemoresistance. This investigation centers on the role of YWHAB, a crucial cytoplasmic retention mediator of the transcriptional coactivator YAP (Yes-associated protein), whose diminished expression in metastatic ovarian cancer cells leads to escalated YAP activity within the nucleus, thereby enhancing tumor aggressiveness and resistance to chemotherapy.
Ovarian cancer remains one of the deadliest gynecologic malignancies, primarily due to the propensity of tumor cells to metastasize throughout the peritoneal cavity and develop resistance against conventional chemotherapeutic regimens. Despite administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), a significant subset of patients experiences relapse attributed to the survival and expansion of cancer stem-like cells embedded within the peritoneal microenvironment. These cancer stem cells (CSCs) possess self-renewal capabilities and exhibit heightened resistance to cytotoxic agents, necessitating a deeper understanding of the molecular drivers that sustain their stemness.
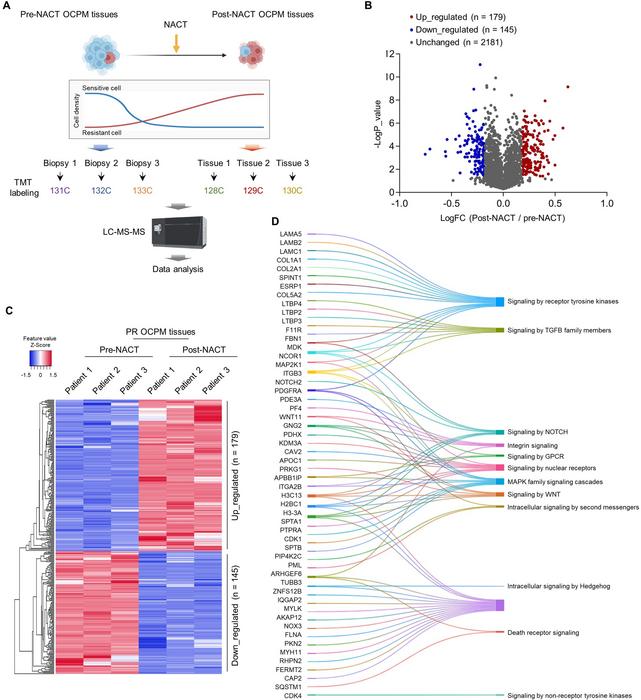
Employing sophisticated proteomic strategies including tandem mass tag (TMT) labeling combined with tissue microarray analysis, the research team meticulously characterized residual tumor tissues post-chemotherapy to identify key protein alterations associated with therapy resistance. Their findings pinpoint YWHAB as a critical regulatory factor whose down-regulation correlates with enhanced nuclear accumulation of YAP, a potent oncogenic transcriptional effector implicated in multiple tumor types. The diminished YWHAB expression disrupts its binding with YAP, fostering YAP’s translocation into the nucleus where it orchestrates the activation of downstream gene networks central to proliferation, stemness, and drug resistance.
Detailed mechanistic investigations highlight that YWHAB interacts directly with the SH3 domain of YAP, sequestering it within the cytoplasm and thereby preventing its nuclear function. The attenuation of YWHAB expression abrogates this cytoplasmic retention mechanism, resulting in increased YAP-TEAD transcriptional complex formation that triggers expression of a panel of genes facilitating tumor cell plasticity and survival in hostile conditions, such as those induced by chemotherapy. This finding underscores the importance of the YWHAB-YAP axis in maintaining cellular homeostasis and suppressing malignant progression.
Functionally, in vitro models demonstrate that silencing YWHAB significantly increases the formation and size of ovarian cancer spheroids—three-dimensional structures that serve as in vitro surrogates for tumor stemness and metastatic potential. Furthermore, YWHAB-deficient cells exhibit pronounced resistance to cisplatin, one of the frontline chemotherapeutic agents for ovarian cancer, strengthening the link between YWHAB regulation and chemoresistance. These phenotypic changes offer compelling evidence that YWHAB plays an indispensable role in modulating CSC properties in OCPM.
Extending their analyses to in vivo systems, the researchers employed murine xenograft models to validate the tumorigenic impact of YWHAB deficiency. Mice implanted with YWHAB knockdown ovarian cancer cells developed larger tumors with increased metastatic dissemination compared to controls, confirming the pro-oncogenic consequences of disrupting YWHAB-mediated YAP retention. This in vivo validation substantiates the clinical relevance of targeting the YWHAB-YAP molecular interaction as a promising strategy to stifle ovarian cancer progression and metastasis.
Concurrently, epigenetic profiling revealed alterations in the promoter region of the YWHAB gene in chemoresistant tumor cells, suggesting that epigenetic repression contributes to its diminished expression. These epigenetic modifications potentially serve as upstream regulators diminishing YWHAB availability, which in turn unleashes unchecked YAP activity. Such insights into the regulatory landscape provide novel angles for therapeutic intervention, including epigenetic reprogramming to reinstate YWHAB expression.
The study’s revelations about the YWHAB-YAP signaling nexus not only deepen the molecular understanding of ovarian cancer stemness and chemoresistance but also open new avenues for targeted therapy development. By disrupting YAP’s nuclear activity or reinforcing YWHAB function, it may be possible to curb tumor relapse and improve patient survival. Notably, the identified necessity of the SH3 domain within YAP for YWHAB binding points to potential sites for small molecule or peptide inhibitor design.
Given the high mortality rate associated with ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis and limited efficacy of current therapeutic options, these findings offer a beacon of hope in the ongoing quest to personalize and enhance treatment paradigms. Clinical translations aimed at modulating the YWHAB-YAP axis require further investigation, yet the present study lays a foundation for such endeavors by furnishing robust experimental and translational evidence.
In conclusion, this landmark research underscores the criticality of YWHAB in maintaining cellular equilibrium by tethering YAP in the cytoplasm, thereby curbing the malignant phenotypes driven by YAP nuclear transcriptional activity. The disruption of this balance propels stemness and chemoresistance, which are formidable barriers in treating ovarian cancer metastasis. Targeting this pathway could revolutionize therapeutic strategies and yield substantial improvements in patient outcomes.
As elucidated in these comprehensive proteomic and functional assays, future research focused on developing pharmacological agents to reinforce YWHAB-mediated YAP retention or directly inhibit YAP nuclear functions holds promise. Such targeted interventions, combined with existing chemotherapy, may overcome the challenge of resistant ovarian cancer stem cells, ultimately reducing relapse rates and extending survival.
This study epitomizes the importance of dissecting cancer’s molecular underpinnings to reveal vulnerabilities that can be exploited for clinical benefit. The elucidation of YWHAB’s restraining role on YAP adds a crucial piece to the ovarian cancer puzzle and paves the way for innovative anti-cancer therapies tackling metastasis and drug resistance at their core.
Subject of Research: Ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis, cancer stemness, chemoresistance
Article Title: Restriction of YWHAB-mediated YAP cytoplasmic retention is a novel mechanism underlying stemness maintenance and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis
Web References: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101519
References: Chang Liu, Lei Shi, Zijun Meng, Manlin Zhang, Zhiqi Zhang, Yunzhe Li, Kaiwen Du, Muyao Yang, Lin Qiu, Jing Feng, Yuchen He, Jiayun Liu, Hua Zhang, Hongbin Zhang, Tingyuan Lang, Zhuo Yang, Genes & Diseases, 2025, 101519
Image Credits: Genes & Diseases
Keywords: Ovarian cancer, peritoneal metastasis, chemoresistance, cancer stem cells, YWHAB, YAP, proteomics, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, tumor stemness, epigenetics, SH3 domain, transcriptional regulation