Since its launch, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has embarked on an extraordinary journey, covering over 15 billion miles into the vast expanse of deep space. This astounding distance, however, represents less than one percent of the journey to Alpha Centauri, the closest star system to our sun. As humanity aspires to explore beyond our solar system, the challenge of achieving faster-than-ever space travel becomes increasingly urgent. Innovative propulsion methods are being sought to reduce travel times to nearby stars from thousands of years to just decades. Recently, a groundbreaking study from researchers in the United States and the Netherlands might hold the key to making interstellar travel feasible.
This cutting-edge research focuses on the concept of a “lightsail,” a lightweight, reflective membrane designed to be propelled by light, much like the sails of a boat are driven by wind. Lightsails offer a tantalizing potential to harness the immense energy of laser light, significantly increasing the speed of spacecraft on their journeys. With the appropriate engineering, this technology could potentially shorten the travel time to celestial neighbors, transforming the pace and possibilities of deep space exploration.
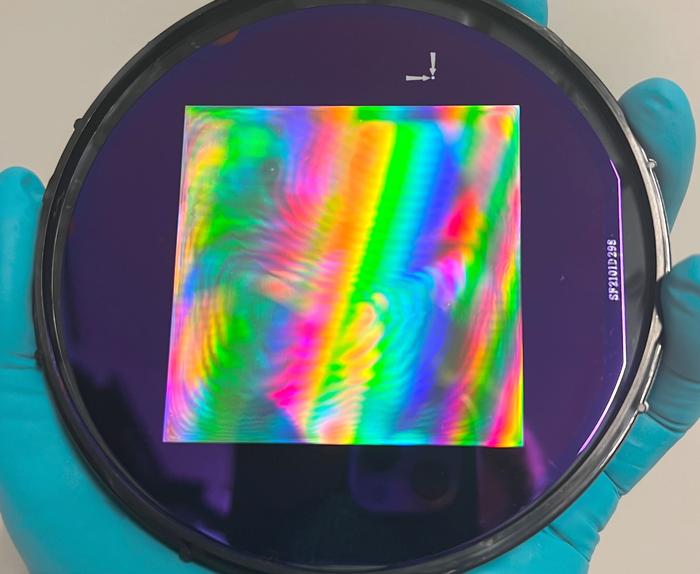
The collaborative effort between researchers from Brown University and Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) has resulted in the development of an ultra-thin, ultra-reflective lightsail membrane. The study, published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, introduces a brilliantly engineered lightsail measuring 60 millimeters square, yet only 200 nanometers thick. To put that in perspective, this thickness is a mere fraction of the width of a human hair. This innovative design incorporates an intricate pattern of billions of nanoscale holes, optimizing both weight and reflectivity, essential attributes for effective acceleration in the vacuum of space.
Recent advances in engineering and materials science have made the manufacturing of such a lightsail viable. Researchers Miguel Bessa and Richard Norte, who co-led the study, emphasize the significance of this work, noting that it combines theoretical design with practical fabrication. Their approach enables the creation of a highly reflective lightsail featuring the largest aspect ratio documented to date. The scalability and economic feasibility of their production techniques open new avenues for interstellar missions, a remarkable potential considering previous methods would take up to 15 years and require exorbitant budgets.
Central to the lightsail’s design is the choice of materials. The researchers opted for a single-layer of silicon nitride, a material known for its lightweight and high-strength characteristics. This material is not only suitable but also essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the lightsail at such reduced thickness. By maximizing reflectivity while minimizing weight, the researchers created a membrane that promises to utilize light pressure effectively, translating into faster acceleration and propulsion.
To achieve this remarkable design, Bessa’s team utilized advanced artificial intelligence methods for optimization. They meticulously crafted the nanoscale hole patterns whose diameters are smaller than the wavelength of light. The placement and shape of these holes are critical, as they directly influence the reflectivity and overall performance of the lightsail. Integration of machine learning into the design process has introduced a novel dimension to engineering challenges previously deemed insurmountable, thereby enhancing the functionality of these lightweight materials.
Once the theoretical design was complete, the fabrication phase began, spearheaded by Norte’s team at TU Delft. A new gas-based etching technique developed by the team allows for precision material removal, resulting in a suspended lightsail that boasts remarkable robustness. This method signifies a critical advance in manufacturing capabilities, reducing both time and cost compared to traditional techniques. The swift production cycle is pivotal, providing a means to rapidly iterate on designs and potentially field-test various configurations in the near future.
The implications of this research extend beyond the immediate goal of interstellar travel. The researchers indicate that this new lightsail design could lend itself to other applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The optimization strategies derived from the machine learning algorithms may eventually impact a broader range of engineering challenges, suggesting benefits that could be wildly transformative for various sectors. As the boundaries of materials science are pushed further, the potential for innovation expands exponentially.
This research aligns closely with ambitious initiatives aimed at revolutionizing human space exploration. The Starshot Breakthrough Initiative, championed by prominent figures such as Yuri Milner and the late Stephen Hawking, seeks to utilize powerful ground-based lasers to propel meter-scale lightsails carrying miniature spacecraft. The innovative designs coming from Bessa and Norte’s teams could soon play a crucial role in realizing these visionary goals, paving the way for humanity’s first forays into interstellar distances.
In conclusion, the development of lightweight, high-performance lightsails heralds a significant turning point in the journey towards exploring other star systems. The combined expertise of theoretical research and hands-on engineering has culminated in a design that promises to propel humanity closer to the dream of interstellar travel. As researchers continue to refine and test these new technologies, the prospect of reaching distant stars transforms from mere science fiction into a tangible future.
The potential applications of this technology are far-reaching, and the ability to develop scalable solutions that rely on cutting-edge optimization techniques reflects a promising outlook for materials research. As this area of study progresses, the next generation of explorers may inherit tools that allow them to journey to the stars, chasing the ambitious dream of venturing beyond our solar system.
Subject of Research: Advanced Lightsail Membrane Design for Interstellar Travel
Article Title: Pentagonal Photonic Crystal Mirrors: Scalable Lightsails with Enhanced Acceleration via Neural Topology Optimization
News Publication Date: March 25, 2025
Web References: Nature Communications Article
References: N/A
Image Credits: Norte lab, TU Delft/Bessa lab, Brown University
Keywords
Applied sciences and engineering, Space sciences, Space exploration, Space flight