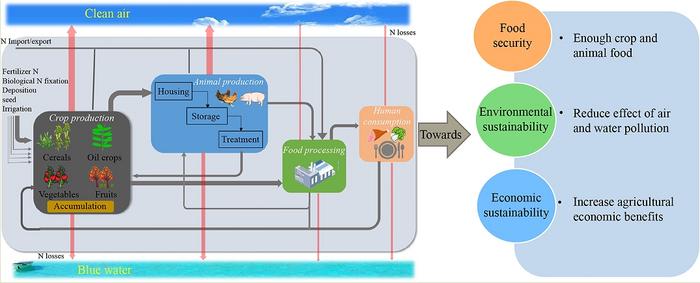
The nitrogen (N) is important nutrient for food production, which is relevant to human consumption, resource, and environment. The N accompanies fertilizers, food, feed, and other substances in the flow of food nutrients along the ‘resource–fertilizer–crop production–livestock production–household–environment’ system. The N stocks and flows are directly related to the goals of sustainable development in terms of food security, resources, environment, and economy. Particularly about the environment, only 20% of the large amount of N inputs are absorbed by plants and animals into the food system, and excessive N losses into the environment lead to problems such as air and water pollution, eutrophication, soil acidification, accumulation of nitrates in groundwater, and greenhouse gas emissions. These environmental impacts pose a serious threat to food security and environmental health, which also impede agriculture green development. Answering the question of ‘where, how much, and how to reduce’ N in food systems has been a great challenge for agricultural N management.

Credit: Fanlei MENG, Menru WANG, Yong HOU, Lin MA, Wenqi MA , Xuejun LIU , Fusuo ZHANG , Wen XU
The nitrogen (N) is important nutrient for food production, which is relevant to human consumption, resource, and environment. The N accompanies fertilizers, food, feed, and other substances in the flow of food nutrients along the ‘resource–fertilizer–crop production–livestock production–household–environment’ system. The N stocks and flows are directly related to the goals of sustainable development in terms of food security, resources, environment, and economy. Particularly about the environment, only 20% of the large amount of N inputs are absorbed by plants and animals into the food system, and excessive N losses into the environment lead to problems such as air and water pollution, eutrophication, soil acidification, accumulation of nitrates in groundwater, and greenhouse gas emissions. These environmental impacts pose a serious threat to food security and environmental health, which also impede agriculture green development. Answering the question of ‘where, how much, and how to reduce’ N in food systems has been a great challenge for agricultural N management.
Prof. Fusuo Zhang from China Agricultural University and his team are exploring an integrated assessment framework for multi-objective N management in the food system, taking Quzhou county on North China Plain as a case study. In the first step,they improved the NUFER (NUtrient flows in Food chains, Environment and Resource use) model, which combine local farmer survey data, monitoring data, and statistical data. The improved NUFER model can quantity the N flows in the food system and identify the contribution of different crops and animals. They found the N losses to environment from the food chain in Quzhou in 2020 amounted to 9400 t, with about 88% of these losses stemming from crop and animal production. The wheat, maize, vegetable, pigs, and laying hens are main responsible the N losses from crop and animal production. In the second step, the multi-objective N management target was developed, which integrated food security, and environmental and economic sustainability. In terms of food security, the primary focus is on ensuring an adequate supply of crops and animal food for the local population. For the environment sustainability, this study focused more on reducing effect of air and water pollution and improving N resource efficiency. The economic indicators are considered to promote agricultural benefits. In the third step, they used NUFER model to explore effective N management solutions to achieve multi-objectives N management through scenario analysis, which is show in a combine of summary of options for Quzhou. A combination of reduced N fertilizer, deep fertilizer placement, urease inhibitor technology, low crude protein, additives during composting and increase manure return croplands can reduce nitrate leaching by 12%, while increasing grain yield by 15% and N use efficiency of food production by 31%, achieving the emission reduction goal of multi-objective in the food system, compared the reference year-2020. To promote the implementation of N management options, it is important to foster collaboration between all stakeholders. Collaboration between government, researchers, enterprise, and local farmers to create and implement new technological approached can be effective in facilitating technology transfer and application. The Science Technology Backyard (STB) from China Agricultural University give us gives us a good example.
Agricultural sustainable N management is closely related to our food security, environmental quality, and economic development. It is an important leap in agricultural nitrogen management from farmland to food system, from single objective to multi-objective synergistic management, and from single scientific study to participation of different stakeholders. This transition is important guarantee to support agriculture green development.
This study has been published on the Journal of Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering in Volume 11, Issue 1, 2024, DOI: 10.15302/J-FASE-2024540.
Journal
Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering
Method of Research
Case study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Optimizing nitrogen management in the food system for sustainable development: a case study of Quzhou County
Article Publication Date
7-Feb-2024