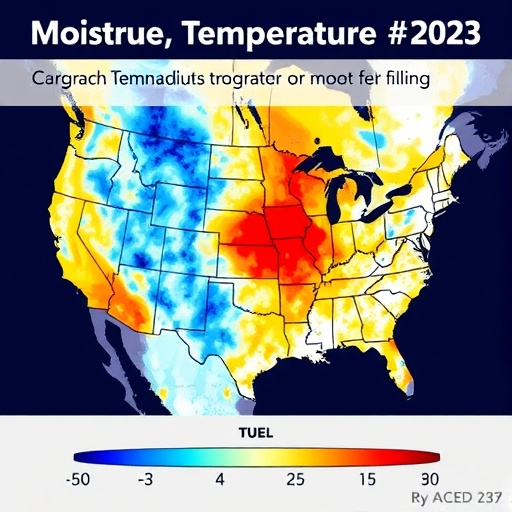
The 2023 Amazon drought has emerged as a critical environmental event, drawing attention from scientists worldwide. Recent research highlights the complex interplay of various climatic factors that led to this unprecedented dry spell. Among these, moisture and temperature sources have been identified as pivotal drivers of the anomalies witnessed during this record-breaking event. The Amazon rainforest, known as the “lungs of the Earth,” plays a vital role in regulating the global climate system, and these anomalies can have far-reaching consequences not only for the region but also for the planet.
Understanding the conditions leading to the 2023 drought requires delving into the broader meteorological context. Various climatic phenomena, such as El Niño and La Niña, significantly influence weather patterns across the globe. These oscillations impact ocean temperatures and atmospheric circulation, affecting rainfall distribution. In the case of the Amazon, the interplay of these phenomena with local weather systems created conditions conducive to severe drought. This nuanced understanding of the atmospheric dynamics is crucial for predicting future events and formulating effective interventions.
Moisture sources, specifically, have garnered attention in recent studies. The Amazon rainforest typically acts as a massive moisture pump, releasing water vapor through a process known as transpiration. This moisture contributes to local and regional precipitation patterns. However, increased temperatures, driven by climate change and land-use changes, have disrupted this delicate balance, reducing the moisture available for precipitation. The findings indicate that a combination of reduced atmospheric moisture and elevated temperatures created a perfect storm, exacerbating drought conditions in 2023.
Research conducted by Fernández-Alvarez et al. has provided significant insights into the drivers of the Amazon drought. Their analysis reveals a clear correlation between rising temperatures and declining moisture levels. During periods of prolonged drought, local vegetation struggles to sustain its health, which, in turn, amplifies the feedback loop of reduced moisture and higher temperatures. As trees become stressed, their capacity to provide moisture through transpiration diminishes, further contributing to lower precipitation levels and fostering a persistent dry environment. This dynamic emphasizes the importance of maintaining healthy ecosystems in mitigating climate impacts.
Furthermore, the research highlights the role of deforestation in exacerbating drought conditions. The Amazon rainforest has been subject to extensive deforestation for agricultural and industrial purposes. This loss of forest cover reduces the area’s overall capacity to regenerate moisture and influences local climate patterns. The consequences of such anthropogenic factors are felt not only within the immediate vicinity of deforested areas but can also have cascading effects throughout the entire Amazon basin. The interconnectivity of ecosystems demands a holistic approach to understanding environmental changes.
The socio-economic ramifications of the drought in the Amazon are also alarming. Indigenous communities and local farmers reliant on the forest’s resources face existential threats as their livelihoods become increasingly unsustainable. The decline of traditional agriculture, combined with the drying of water sources, places immense pressure on these communities. As water becomes scarce, competition for resources intensifies, leading to potential conflicts among different user groups. Addressing these socio-economic challenges will be key in ensuring the resilience of these vulnerable populations amid climate changes.
In light of these findings, proactive measures are crucial for mitigating future droughts and building resilience within the Amazon ecosystem. Conservation efforts aimed at preserving existing forest cover and restoring degraded landscapes will enhance the moisture-generating capacity of this critical region. Sustainable land management practices and policies promoting agroforestry can contribute to both environmental restoration and economic stability for local communities. Collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local stakeholders is vital in fostering a unified approach towards safeguarding the Amazon.
Global measures to combat climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, are also integral to addressing the root causes of extreme weather events. As demonstrated by the Amazon drought, climate change has direct implications for local ecosystems and, consequently, for global climate regulation. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting sustainable agriculture, and integrating climate education can collectively contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint. A concerted global effort will be essential in averting the worst scenarios predicted by scientists.
Moreover, scientific innovation plays a pivotal role in understanding and addressing drought conditions. Advances in climate modeling and remote sensing technologies can facilitate better monitoring of environmental changes and precipitation patterns. These technologies provide real-time data that can inform timely interventions and policy decisions. In an age where rapid changes occur, adaptive management strategies must be rooted in solid scientific evidence and ongoing research.
Public awareness and engagement are equally crucial in the fight against climate-induced disasters. As information about the Amazon drought circulates, it is imperative for individuals to understand their role in changing consumption patterns and promoting sustainability. Grassroots movements for environmental conservation can amplify the message for urgent action. The collective engagement of civil society brings attention to local issues while fostering a global consciousness about the interconnectedness of ecosystems.
The consequences of the 2023 Amazon drought serve as a stark reminder of the importance of protecting our natural resources. The tipping point of ecosystem degradation is becoming alarmingly apparent, and immediate action is required to avert irreversible damage. Harnessing the power of collaboration and innovation will be fundamental in addressing the challenges outlined. It is crucial to adopt a forward-thinking perspective that incorporates the complexities of climate dynamics, ecological health, and social resilience.
In conclusion, the record-breaking Amazon drought of 2023 serves as a clarion call for immediate and sustained action. The findings from recent research underscore the central role of moisture and temperature sources in shaping environmental outcomes. Understanding these intricate relationships is vital in creating effective strategies to mitigate future droughts. The urgency of this crisis propels a clear message—our actions today will determine the viability of the Amazon rainforest and its crucial role in sustaining life on Earth.
Subject of Research: Climate dynamics related to the Amazon drought.
Article Title: Moisture and temperature sources were key drivers of the anomalies for the record-breaking of 2023 Amazon drought.
Article References:
Fernández-Alvarez, J.C., Nieto, R., Vicente-Serrano, S.M. et al. Moisture and temperature sources were key drivers of the anomalies for the record-breaking of 2023 Amazon drought. Commun Earth Environ 6, 801 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-025-02771-7
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: 10.1038/s43247-025-02771-7
Keywords: Amazon drought, climate dynamics, moisture sources, temperature anomalies, deforestation, ecological impacts.