“Novel senomorphic and senolytic agents can be evaluated in this model as they are identified.”

Credit: 2024 Spina et al.
“Novel senomorphic and senolytic agents can be evaluated in this model as they are identified.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 13, entitled, “Modulating in vitro lung fibroblast activation via senolysis of senescent human alveolar epithelial cells.”
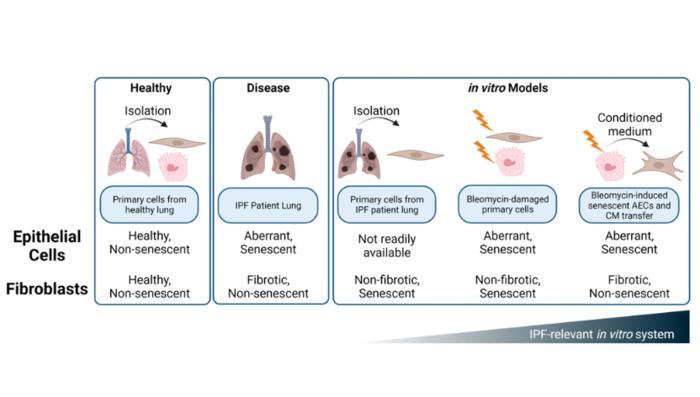
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an age-related disease with poor prognosis and limited therapeutic options. Activation of lung fibroblasts and differentiation to myofibroblasts are the principal effectors of disease pathology, but damage and senescence of alveolar epithelial cells, specifically type II (ATII) cells, has recently been identified as a potential trigger event for the progressive disease cycle. Targeting ATII senescence and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) is an attractive therapeutic strategy; however, translatable primary human cell models that enable mechanistic studies and drug development are lacking.
In this new study, researchers Joseph S. Spina, Tracy L. Carr, Lucy A. Phillips, Heather L. Knight, Nancy E. Crosbie, Sarah M. Lloyd, Manisha A. Jhala, Tony J. Lam, Jozsef Karman, Meghan E. Clements, Tovah A. Day, Justin D. Crane, and William J. Housley from AbbVie Bioresearch Center and Northeastern University describe a novel system of conditioned medium (CM) transfer from bleomycin-induced senescent primary alveolar epithelial cells (AEC) onto normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLF) that demonstrates an enhanced fibrotic transcriptional and secretory phenotype compared to non-senescent AEC CM treatment or direct bleomycin damage of the NHLFs.
“In the current study, we confirm the presence of senescent cell populations within the human IPF lung, as well as assess primary cell reagents for sensitivity to senescent cell targeting therapies.”
In this system, the bleomycin-treated AECs exhibited classical hallmarks of cellular senescence, including SASP and a gene expression profile that resembles aberrant epithelial cells of the IPF lung. Fibroblast activation by CM transfer was attenuated by pre-treatment of senescent AECs with the senolytic Navitoclax and AD80, but not with the standard of care agent Nintedanib or senomorphic JAK-targeting drugs (e.g., ABT-317, ruxolitinib). This model provided a relevant human system for profiling novel senescence-targeting therapeutics for IPF drug development.
“Taken together, the model described herein provides a physiologically relevant, primary human cell system to study the effects of alveolar epithelial cell senescence on lung fibroblasts in the context of chronic fibrotic lung disease.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205994
Corresponding Author: Tovah A. Day
Corresponding Email: t.day@northeastern.edu
Keywords: cellular senescence, fibrosis, senolytic, senomorphic, SASP, alveolar epithelial cell
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Modulating in vitro lung fibroblast activation via senolysis of senescent human alveolar epithelial cells
Article Publication Date
29-Jun-2024