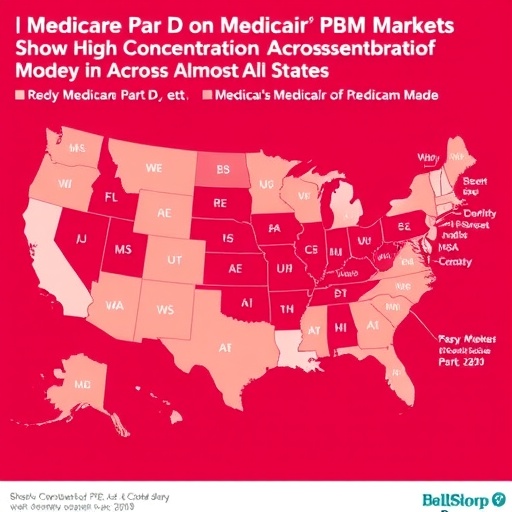
In a landscape dominated by a few powerful players, the pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) industry reveals a striking concentration across both Medicare Part D and Medicaid managed care prescription markets throughout the United States. Recent comprehensive research conducted by the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics shines a light on the extent to which this oligopolistic structure pervades retail prescription markets state by state, exposing critical challenges to competition, pricing transparency, and patient access in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Pharmacy benefit managers act as intermediaries between insurers, pharmacies, and drug manufacturers, orchestrating formulary design, negotiating rebates, and managing pharmacy networks with aims to control costs and streamline drug distribution. Yet, despite their purported role in fostering efficiency, the concentration of market power in just three dominant PBMs raises major concerns. According to this pioneering study, published February 6, 2026 in JAMA Health Forum, the retail prescription PBM market exhibits substantial consolidation, with 40 states manifesting highly concentrated PBM participation in Medicare Part D plans, and 37 states showing comparable concentration in Medicaid managed care.
Such high levels of concentration imply that a minimal number of PBMs exert disproportionate influence over pricing strategies and access to essential pharmaceutical products. Disturbingly, 31 states bear the imprint of highly concentrated markets in both Part D and Medicaid managed care sectors simultaneously, while among these, 10 states also display significant PBM concentration within commercial insurance spheres. The implications are deeply systemic: 93% of Medicaid managed care prescriptions and a striking 75% of Part D prescriptions are dispensed in states where PBM market dominance stifles meaningful competition.
The metrics underpinning the concentration diagnoses build upon a rigorous federal antitrust framework that evaluates market share distributions and competition barriers. When a handful of PBMs consolidate control, negotiating leverage shifts dramatically in their favor vis-à-vis drug manufacturers and pharmacies. This realignment threatens to elevate out-of-pocket patient expenses by constricting price competition, limiting pharmacy choice, and constraining formulary breadth. Drug adherence and therapeutic outcomes can thus be detrimentally impacted by barriers encoded within PBM-driven policies.
Detailed analysis of state-level data uncovers the contours of these concentrated markets, offering crucial insights for regulators and policy architects. This research arrives amid escalating scrutiny of PBM practices — practices which detractors argue conceal rebate pathways, obscure true net drug prices, and incentivize formulary exclusions that may not align with clinical needs. Legislative actions enacted in congressional spending packages have begun addressing these challenges through enhanced transparency mandates and restrictions targeting PBM contracting behaviors.
Dima Mazen Qato, lead investigator and senior scholar at the USC Schaeffer Center, emphasizes the ramifications of this concentrated market power: when PBMs operate with minimal competition, their ability to dictate drug coverage policies and pharmacy access grows unchecked. Such dominance also impedes efforts to drive systemic cost reductions, as market incentives skew toward maximizing PBM revenues through complex rebate schemes rather than fostering drug affordability for patients.
The study’s implications extend beyond market structure diagnostics. They provide a vital evidentiary foundation to inform federal and state interventions designed to recalibrate PBM accountability. Proposals under consideration range from imposing robust transparency standards on PBM transactions to curbing anti-competitive contracting provisions and promoting alternative reimbursement models. Moreover, ongoing enforcement initiatives are increasingly focused on scrutinizing the extent to which concentrated PBM markets may violate antitrust laws or perpetuate unfair trade practices.
From a technical perspective, this research employs advanced market concentration indices and integrates claims data across multiple payer systems, offering a granular representation of market dynamics often obscured in aggregated federal reports. By dissecting prescription fills segmented by state and program type, the study reveals nuanced regional variations in PBM dominance, facilitating targeted policy responses that acknowledge local market conditions instead of relying on broad universal mandates.
The consequences of sustained PBM market concentration ripple through the healthcare system. Pharmacies facing restrictive PBM networks experience reduced reimbursement rates, spurring closures particularly in independent and rural settings. Patients encounter hurdles accessing preferred medications or must navigate complex prior authorization requirements that introduce delays and administrative burden. Together, these trends threaten healthcare equity and undermine efforts to optimize medication adherence — a cornerstone of effective chronic disease management.
As policymakers engage with this emerging data, the urgency to balance PBM operational efficiencies against competitive fairness has never been greater. While PBMs may theoretically deliver cost savings via sophisticated rebate negotiations, these benefits are often opaque, obscured within complex financial flows that complicate payer and patient understanding. Enhancing PBM market competition and transparency is therefore pivotal to unlocking genuine efficiencies that translate to lower drug costs and better patient outcomes.
This landmark study sets a new benchmark in analyzing pharmaceutical distribution intermediaries, illustrating that the PBM industry’s structural characteristics have profound implications beyond the traditional supply chain. Insight-driven reform efforts aligned with these findings are essential to ensuring prescription drug markets function competitively and serve the public interest, making affordable, accessible medications a reality for millions of Americans dependent on Medicare and Medicaid.
Subject of Research: Pharmacy Benefit Manager market concentration within Medicare Part D and Medicaid managed care prescription markets.
Article Title: Pharmacy Benefit Manager Market Concentration for Prescriptions Filled at Retail Pharmacies by State and Payer Type
News Publication Date: 6-February-2026
Web References:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2025.6546
PBM Markets for Medicare Part D or Medicaid Are Highly Concentrated in Nearly Every State
Image Credits: USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics
Keywords: Health care policy, Drug costs, Health care costs, Pharmaceuticals, Health insurance