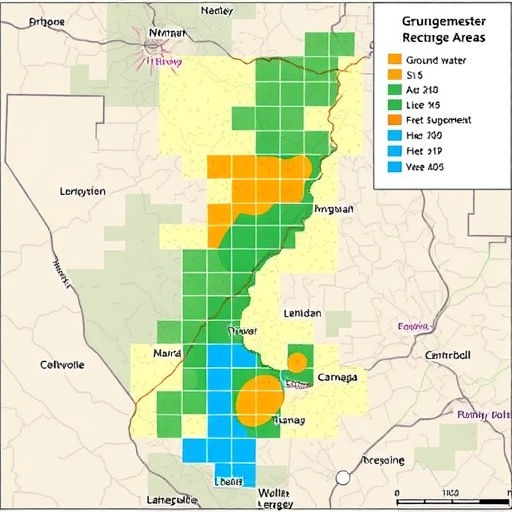
In an era where groundwater depletion poses a critical threat to sustainable development, researchers have made significant strides in understanding and mapping groundwater recharge zones. A study led by Subramani, Kamaraj, and Diriba, published in 2025, provides a novel insight into this field by applying advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technology within the Kallakurichi district of Tamil Nadu, India. The findings present an effective model that could guide future management and conservation efforts for this vital resource.
Groundwater recharge is the process through which water from rainfall, surface water bodies, and other sources percolates through the soil and replenishes aquifers. A reliable understanding of where and how this recharge occurs is critical for water resource management, especially in regions experiencing rapid population growth and associated pressure on water reserves. This research integrates state-of-the-art GIS technologies with remote sensing data to delineate recharge zones more accurately than previous methods.
The study is rooted in the recognition that traditional approaches to mapping groundwater recharge often lead to oversimplified or generalized findings. By employing advanced techniques, the researchers were able to capture a more nuanced picture of the hydrological dynamics at play in Kallakurichi. The methodologies used are significant not just for Tamil Nadu but can be adapted for similar hydraulic studies in varying geological and climatic contexts around the globe.
The research utilized satellite imagery and various GIS layers to analyze land use, soil types, and topography, essential factors that influence groundwater recharge. It went beyond simply identifying potential recharge zones; the team employed sophisticated algorithms to assess the productivity of these zones, providing an actionable framework for local policymakers and stakeholders. This systematic approach can help prioritize areas for protection and enhancement, where efforts could be directed towards increasing the replenishment of groundwater supplies.
One of the most crucial aspects of the study is its emphasis on local context. Kallakurichi, with its unique climatic and geological characteristics, presents specific challenges and opportunities regarding groundwater recharge. By tailoring their methodologies to the local environment, the researchers highlight the importance of localized data in effectively managing water resources. This localized focus serves as a model for similar studies in different regions with distinct environmental conditions.
The implications of this research extend far beyond academic interest; they touch on issues of water security, agricultural productivity, and overall community resilience. Regions like Kallakurichi, where agriculture is the heart of the economy, rely heavily on groundwater for irrigation. Understanding recharge dynamics allows farmers and local authorities to make informed decisions about water usage, ensuring that this critical resource is available for future generations.
Moreover, the study’s findings underscore the importance of integrating technology into environmental science and resource management. By harnessing GIS and remote sensing, the research not only allows for real-time monitoring of groundwater levels but also facilitates predictive modeling. Such advancements in technology empower communities to not only respond to current water challenges but also to anticipate and mitigate future scarcity.
A collaborative effort with local government bodies for implementing the research findings could lead to actionable policies that prioritize groundwater conservation. Engaging community stakeholders in this process is essential to ensure that strategies are acceptable and effective, fostering a sense of ownership over local water resources. The role of grassroots education cannot be understated; raising awareness about groundwater recharge will foster a culture of conservation among the population.
The study also opens avenues for further research, particularly in refining methodologies for assessing recharge rates in diverse ecosystems. There is much to learn about how varying climatic conditions and land use practices impact groundwater dynamics. This research therefore serves as a springboard for subsequent studies aimed at developing even more nuanced and robust models of groundwater recharge.
Despite the promising findings and methodologies, challenges remain in the path toward sustainable water resource management. Issues such as land degradation, climate change, and increased demand from urbanization continue to complicate the management of groundwater. Continuous research efforts are necessary to adapt to these challenges while educating the public and policymakers about sustainable practices.
Conclusively, the systematic GIS and remote sensing approach presented by Subramani and colleagues is a landmark contribution to groundwater studies. It illuminates a path forward for not only Kallakurichi but potentially for water-stressed regions worldwide. By focusing on innovative technologies combined with local engagement, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities surrounding groundwater recharge and ensure the long-term sustainability of this precious resource.
Ultimately, the synergy between advanced research methodologies and community action may well define the future landscape of groundwater management, potentially transforming how societies adapt to increasing water scarcity. As the world grapples with climate change and population growth, studies like this will be pivotal in safeguarding water resources for generations to come.
Subject of Research: Groundwater Recharge Mapping
Article Title: A systematic GIS and remote sensing based approach for mapping groundwater recharge zones in Kallakurichi district, Tamil Nadu, India.
Article References: Subramani, D., Kamaraj, P., Diriba, D. et al. A systematic GIS and remote sensing based approach for mapping groundwater recharge zones in Kallakurichi district, Tamil Nadu, India. Discov Sustain 6, 1424 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-025-02253-y
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-025-02253-y
Keywords: Groundwater recharge, GIS, Remote sensing, Water management, Kallakurichi, Tamil Nadu, Resource sustainability, Environmental science, Agriculture, Climate change, Community engagement, Technological innovation.