A groundbreaking development in water treatment technology is making waves in the scientific community, as researchers at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) unveil a novel approach to address the pressing issue of water purification and nutrient recovery. This innovative solution comes in the form of a "sea urchin-shaped" nanostructured material that not only excels in removing harmful phosphorus from wastewater but also effectively disinfects harmful microorganisms. Such advancements are crucial in an era where water scarcity and pollution pose significant challenges to both environmental sustainability and public health.
The purifying process undertaken in wastewater treatment plants is vital in safeguarding our waterways, as treated water is often discharged back into rivers. Unfortunately, this water can still contain residual harmful substances, including phosphorus, which is a key contributor to algae blooms in aquatic environments. Algae blooms not only deplete oxygen levels in water bodies, but they also disrupt aquatic ecosystems, rendering water unsafe for consumption and recreational activities. Thus, the KIST research team’s mission to improve phosphorus recovery and disinfection in wastewater is incredibly timely.
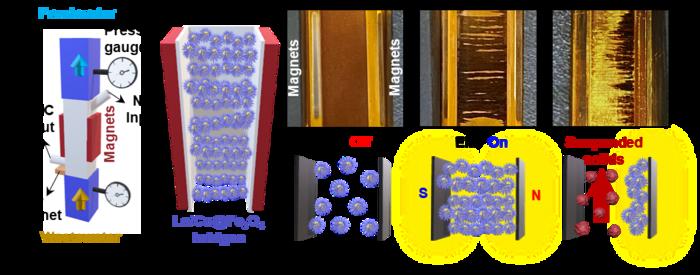
Led by Dr. Jae-Woo Choi and Dr. Kyungjin Cho, the research team has developed a dual-function water treatment material that dramatically enhances phosphorus recovery while simultaneously disinfecting water. The unique material is capable of recovering an impressive 1.1 kilograms of phosphate per kilogram in just five minutes—a feat that sets this technique apart from existing wastewater treatment technologies. This rapid recovery system represents a significant leap forward in the quest for efficient water purification processes.
The sea urchin-shaped nanostructure utilized in their research not only enhances purification performance but also simplifies the recovery of phosphorus—a nutrient critical for various agricultural and industrial applications. In the past, conventional systems faced challenges in efficiently removing phosphorus, often leading to the nutrient’s harmful re-entry into aquatic ecosystems. KIST’s innovative material holds the potential to transform traditional wastewater treatment practices into more efficient and environmentally friendly systems.
Moreover, this cutting-edge technology operates without the need for electricity, making it not only more sustainable but also economically advantageous. By harnessing the power of magnetic fields, the position and motion of the treatment material can be carefully controlled. This precise control results in an energy consumption reduction of over 99% when compared to conventional technologies. Such reduced energy requirements translate to diminished carbon emissions and operating costs—a compelling proposition for resource-constrained wastewater treatment facilities.
The KIST team’s research also addresses the growing concern about energy efficiency in water treatment processes. By eliminating the reliance on electricity, the innovative system significantly lowers the ecological footprint of water purification. In a world striving for sustainable development, this breakthrough offers a pathway to address climate change challenges while simultaneously improving water quality.
The versatility of the KIST-developed materials extends beyond wastewater treatment facilities. This technology has applicability in multiple environments, including livestock and industry wastewater treatment sites, where nutrient concentrations are often alarmingly high. Notably, the simultaneous removal of algae-inducing substances while recovering valuable resources enhances the value proposition of the KIST technology, supporting the transition towards a circular economy.
In discussing the broader impacts of their work, Dr. Jae-Woo Choi emphasized the importance of integrating phosphorus recovery and microbial inactivation into a single processing system. He remarked on the potential for developing a low-energy disinfection strategy that relies on non-chlorine methods, which compromises neither safety nor effectiveness. This innovation is a significant complement to traditional water treatment options that often involve harsh chemicals.
The potential applications for KIST’s novel technology are extensive, with prospects for portable water treatment devices, emergency purification systems during natural disasters, and mobile facilities tailored for underserved regions. This focus aligns closely with global initiatives aimed at improving water access and quality in developing countries, where inadequacies in water infrastructure can have dire public health consequences.
Dr. Youngkyun Jung, the first author of the study, highlighted the dual capabilities of the research team’s material, emphasizing its strength in phosphorus retrieval and the precision control afforded by magnetic fields. This dual functionality positions the technology for further innovation and expansion into multi-purpose water treatment platforms, thereby enhancing its real-world utility.
Through the publication of their findings in the journal "Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials," the KIST research team is paving the way for new paradigms in wastewater management. Their research not only underscores the significance of interdisciplinary approaches in advancing environmental technologies but also showcases the potential for transformative shifts in how we recover resources from wastewater.
As scientists and policymakers alike attempt to forge paths towards sustainability, the implications of this groundbreaking research extend beyond simple purification. It exemplifies the marriage of science and practical application, as researchers take significant steps toward harnessing wastewater as a resource rather than viewing it solely as a waste product.
With increasing attention on the importance of resource recovery and water reuse, advancements like those from KIST will undoubtedly garner global interest. The innovative approach to water purification offers hope for mitigating some of the most pressing environmental challenges, with phosphorus recovery at its core.
The integration of such advanced technologies in our water treatment processes is not merely an improvement in existing methods; it is a crucial step toward achieving a sustainable balance between human needs and environmental health. As researchers and institutions continue to innovate, the transition to cleaner and more efficient water treatment systems is not only an aspiration but an achievable reality.
Subject of Research: Advanced water treatment technologies for phosphorus recovery and disinfection
Article Title: Electromagnetic-field-sensitive bridges based on urchin-like La/Cu-Fe3O4 nanocapsules for ultra-efficient phosphate recovery and water disinfection
News Publication Date: 10-Apr-2025
Web References: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s42114-025-01303-3
References: [To be added if available]
Image Credits: Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Keywords
Water treatment, phosphorus recovery, wastewater purification, nanotechnology, magnetic guidance, eco-friendly systems, environmental sustainability, circular economy, clean water technology, microbial disinfection.