Credit: Cyborg and Bionic Systems
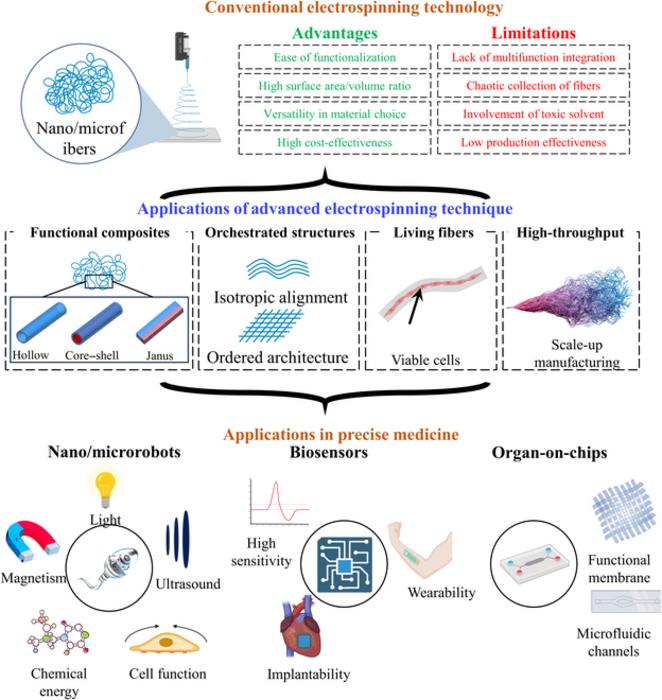
Precise medicine, aimed at tailoring healthcare to individual patients by considering their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle differences, has long sought more effective ways to integrate advanced technology in medical applications. The research led by Dr. Jinhua Li and Dr. Ge Gao focuses on overcoming the limitations of traditional electrospinning methods, which include issues like limited material compatibility, uncontrollable fiber orientation, and low production scalability.
The team’s work introduces modified electrospinning processes that allow for the manufacturing of highly specialized and functional composites, living constructs, and orchestrated structures, thereby expanding the potential applications in medicine significantly. These advanced techniques facilitate the integration of delicate biological components such as cells and enzymes, improving the structural and functional diversity of the produced materials.
One of the significant breakthroughs reported involves the development of core-sheath fibers, which enable the encapsulation of sensitive molecules and living cells within biocompatible materials, protecting them from mechanical stress and increasing their functional viability when implanted or applied externally on patients. This technique is especially promising for developing next-generation biosensors that can monitor physiological signals with unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity.
Furthermore, the research highlights the utilization of electrospinning in creating microfabricated environments that mimic human tissues, offering a more sophisticated approach to organ-on-chip applications. These devices can replicate human organ functions and interactions more accurately, which is crucial for drug testing and disease modeling.
Dr. Li emphasized the potential impact of their findings, stating, “Our work not only pushes the boundaries of nanotechnology in medicine but also paves the way for creating more personalized and precise treatments. The ability to craft custom-tailored biomedical products that can integrate seamlessly with the patient’s body will significantly enhance the efficacy of medical treatments and interventions.”
As the demand for more effective and less invasive medical technologies grows, the innovations presented by Dr. Li, Dr. Gao, and their team could represent a major step forward in the field of precise medicine. By advancing the capabilities of electrospinning techniques, this research supports the ongoing shift towards more individualized treatment options, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of healthcare technology.
The paper, “Recent Advances in Electrospinning Techniques for Precise Medicine,” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on May 22, 2024, at DOI: