“Our research findings suggest that miR-377 could potentially serve as a valuable therapeutic strategy for the treatment of prostate cancer (PCa).”

Credit: 2024 Azimi et al.
“Our research findings suggest that miR-377 could potentially serve as a valuable therapeutic strategy for the treatment of prostate cancer (PCa).”
BUFFALO, NY- May 21, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on May 16, 2024, entitled, “Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on the proliferative and invasive behaviors of prostate cancer cells through the modulation of MYC mRNA via its interaction with BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4.”
The MYC gene is a regulatory and proto-oncogenic gene that is overexpressed in the majority of prostate cancers (PCa). Numerous studies have indicated that aberrant expression of microRNAs is involved in the initiation and progression of prostate cancer. In this new study, researchers Yasamin Azimi, Sara Hajibabaei, Ghazal Azimi, Fatemeh Rahimi-Jamnani, and Masoumeh Azizi from the Pasteur Institute of Iran and Islamic Azad University assessed the impact of miR-377 on MYC through luciferase assay.
“[…] it is of utmost importance to conduct research on the molecular pathways underlying the progression of PCa, as this may potentially lead to the development of a novel approach for targeted treatment of the disease [3].”
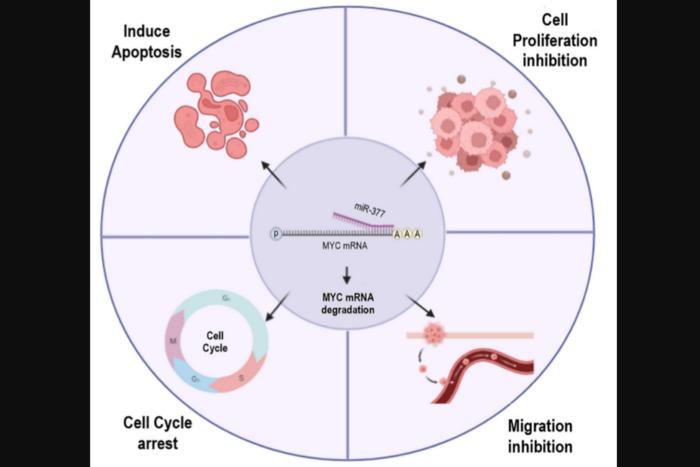
Real-time PCR was employed to determine whether miR-377 could reduce the levels of MYC mRNA in transfected PCa cell lines (PC-3 and DU145) and change in the mRNA levels of BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4 as a consequence of MYC downregulation. Moreover, the researchers analyzed the effects of miR-377 on apoptosis, proliferation, cell cycle, and wound healing.
Their findings demonstrate that miR-377 effectively targets MYC mRNA, as confirmed by luciferase assay and Real-time PCR. They observed a significant reduction in BCL-2 and CDK4 expression, along with an increase in Bax and PTEN, in prostate cancer cell lines upon MYC suppression. Additionally, elevated levels of miR-377 in PCa cell lines induced apoptosis, inhibited proliferation and migration, and arrested the cell cycle.
“Taken together, these results unveil the inhibitory role of miR-377 in MYC function within PCa, thereby suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target for the treatment of this malignancy.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.236
Correspondence: Masoumeh Azizi – Email: mazizi528@gmail.com
Keywords: miR-377, prostate cancer, MYC; PTEN, CDK4
About Genes & Cancer: Genes & Cancer covers all aspects of the structure and function of oncogenes, growth suppressor and apoptotic genes, their role in signal transduction and the mechanisms by which their expression and function are altered during tumor development. In addition to publishing manuscripts that directly relate to these areas of research, Genes & Cancer also aims to attract papers in the areas of genomics, drug development and systems biology.
To learn more about Genes & Cancer, visit www.genesandcancer.com and connect with us on social media:
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Genes & Cancer Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1C
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-212-659-5400
###
Journal
Genes & Cancer
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on the proliferative and invasive behaviors of prostate cancer cells through the modulation of MYC mRNA via its interaction with BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4
Article Publication Date
16-May-2024