Neurological disorders, such as addiction, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), affect millions of people worldwide and are often characterized by complex pathologies involving multiple brain regions and circuits. These conditions are notoriously difficult to treat due to the intricate and poorly understood nature of brain functions and the challenge of delivering therapies to deep brain structures without invasive procedures.
In the rapidly evolving field of neuroscience, non-invasive brain stimulation is a new hope for understanding and treating a myriad of neurological and psychiatric conditions without surgical intervention or implants. Researchers, led by Friedhelm Hummel, who holds the Defitchech Chair of Clinical Neuroengineering at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences, and postdoc Pierre Vassiliadis, are pioneering a new approach in the field, opening frontiers in treating conditions like addiction and depression.
Their research, leveraging transcranial Temporal Interference Electric Stimulation (tTIS), specifically targets deep brain regions that are the control centers of several important cognitive functions and involved in different neurological and psychiatric pathologies. The research, published in Nature Human Behaviour, highlights the interdisciplinary approach that integrates medicine, neuroscience, computation, and engineering to improve our understanding of the brain and develop potentially life-changing therapies.
“Invasive deep brain stimulation (DBS) has already successfully been applied to the deeply seated neural control centers in order to curb addiction and treat Parkinson, OCD or depression,” says Hummel. “The key difference with our approach is that it is non-invasive, meaning that we use low-level electrical stimulation on the scalp to target these regions.”
Vassiliadis, lead author of the paper, a medical doctor with a joint PhD, describes tTIS as using two pairs of electrodes attached to the scalp to apply weak electrical fields inside the brain. “Up until now, we couldn’t specifically target these regions with non-invasive techniques, as the low-level electrical fields would stimulate all the regions between the skull and the deeper zones—rendering any treatments ineffective. This approach allows us to selectively stimulate deep brain regions that are important in neuropsychiatric disorders,” he explains.
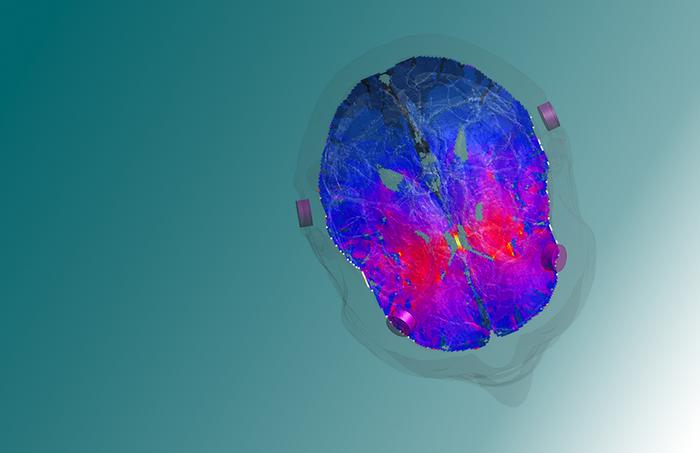
The innovative technique is based on the concept of temporal interference, initially explored in rodent models, and now successfully translated to human applications by the EPFL team. In this experiment, one pair of electrodes is set to a frequency of 2,000 Hz, while another is set to 2,080 Hz. Thanks to detailed computational models of the brain structure, the electrodes are specifically positioned on the scalp to ensure that their signals intersect in the target region.
It is at this juncture that the magic of interference occurs: the slight frequency disparity of 80 Hz between the two currents becomes the effective stimulation frequency within the target zone. The brilliance of this method lies in its selectivity; the high base frequencies (e.g., 2,000 Hz) do not stimulate neural activity directly, leaving the intervening brain tissue unaffected and focusing the effect solely on the targeted region.
The focus of this latest research is the human striatum, a key player in reward and reinforcement mechanisms. “We’re examining how reinforcement learning, essentially how we learn through rewards, can be influenced by targeting specific brain frequencies,” says Vassiliadis. By applying stimulation of the striatum at 80 Hz, the team found they could disrupt its normal functioning, directly affecting the learning process.
The therapeutic potential of their work is immense, particularly for conditions like addiction, apathy and depression, where reward mechanisms play a crucial role. “In addiction, for example, people tend to over-approach rewards. Our method could help reduce this pathological overemphasis,” Vassiliadis, who is also a researcher at UCLouvain’s Institute of Neuroscience, points out.
Furthermore, the team is exploring how different stimulation patterns can not only disrupt but also potentially enhance brain functions. “This first step was to prove the hypothesis of 80 Hz affecting the striatum, and we did it by disrupting it’s functioning. Our research also shows promise in improving motor behavior and increasing striatum activity, particularly in older adults with reduced learning abilities,” Vassiliadis adds.
Hummel, a trained neurologist, sees this technology as the beginning of a new chapter in brain stimulation, offering personalized treatment with less invasive methods. “We’re looking at a non-invasive approach that allows us to experiment and personalize treatment for deep brain stimulation in the early stages,” he says. Another key advantage of tTIS is its minimal side effects. Most participants in their studies reported only mild sensations on the skin, making it a highly tolerable and patient-friendly approach.
Hummel and Vassiliadis are optimistic about the impact of their research. They envision a future where non-invasive neuromodulation therapies could be readily available in hospitals, offering a cost-effective and expansive treatment scope.

Credit: EPFL
Neurological disorders, such as addiction, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), affect millions of people worldwide and are often characterized by complex pathologies involving multiple brain regions and circuits. These conditions are notoriously difficult to treat due to the intricate and poorly understood nature of brain functions and the challenge of delivering therapies to deep brain structures without invasive procedures.
In the rapidly evolving field of neuroscience, non-invasive brain stimulation is a new hope for understanding and treating a myriad of neurological and psychiatric conditions without surgical intervention or implants. Researchers, led by Friedhelm Hummel, who holds the Defitchech Chair of Clinical Neuroengineering at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences, and postdoc Pierre Vassiliadis, are pioneering a new approach in the field, opening frontiers in treating conditions like addiction and depression.
Their research, leveraging transcranial Temporal Interference Electric Stimulation (tTIS), specifically targets deep brain regions that are the control centers of several important cognitive functions and involved in different neurological and psychiatric pathologies. The research, published in Nature Human Behaviour, highlights the interdisciplinary approach that integrates medicine, neuroscience, computation, and engineering to improve our understanding of the brain and develop potentially life-changing therapies.
“Invasive deep brain stimulation (DBS) has already successfully been applied to the deeply seated neural control centers in order to curb addiction and treat Parkinson, OCD or depression,” says Hummel. “The key difference with our approach is that it is non-invasive, meaning that we use low-level electrical stimulation on the scalp to target these regions.”
Vassiliadis, lead author of the paper, a medical doctor with a joint PhD, describes tTIS as using two pairs of electrodes attached to the scalp to apply weak electrical fields inside the brain. “Up until now, we couldn’t specifically target these regions with non-invasive techniques, as the low-level electrical fields would stimulate all the regions between the skull and the deeper zones—rendering any treatments ineffective. This approach allows us to selectively stimulate deep brain regions that are important in neuropsychiatric disorders,” he explains.
The innovative technique is based on the concept of temporal interference, initially explored in rodent models, and now successfully translated to human applications by the EPFL team. In this experiment, one pair of electrodes is set to a frequency of 2,000 Hz, while another is set to 2,080 Hz. Thanks to detailed computational models of the brain structure, the electrodes are specifically positioned on the scalp to ensure that their signals intersect in the target region.
It is at this juncture that the magic of interference occurs: the slight frequency disparity of 80 Hz between the two currents becomes the effective stimulation frequency within the target zone. The brilliance of this method lies in its selectivity; the high base frequencies (e.g., 2,000 Hz) do not stimulate neural activity directly, leaving the intervening brain tissue unaffected and focusing the effect solely on the targeted region.
The focus of this latest research is the human striatum, a key player in reward and reinforcement mechanisms. “We’re examining how reinforcement learning, essentially how we learn through rewards, can be influenced by targeting specific brain frequencies,” says Vassiliadis. By applying stimulation of the striatum at 80 Hz, the team found they could disrupt its normal functioning, directly affecting the learning process.
The therapeutic potential of their work is immense, particularly for conditions like addiction, apathy and depression, where reward mechanisms play a crucial role. “In addiction, for example, people tend to over-approach rewards. Our method could help reduce this pathological overemphasis,” Vassiliadis, who is also a researcher at UCLouvain’s Institute of Neuroscience, points out.
Furthermore, the team is exploring how different stimulation patterns can not only disrupt but also potentially enhance brain functions. “This first step was to prove the hypothesis of 80 Hz affecting the striatum, and we did it by disrupting it’s functioning. Our research also shows promise in improving motor behavior and increasing striatum activity, particularly in older adults with reduced learning abilities,” Vassiliadis adds.
Hummel, a trained neurologist, sees this technology as the beginning of a new chapter in brain stimulation, offering personalized treatment with less invasive methods. “We’re looking at a non-invasive approach that allows us to experiment and personalize treatment for deep brain stimulation in the early stages,” he says. Another key advantage of tTIS is its minimal side effects. Most participants in their studies reported only mild sensations on the skin, making it a highly tolerable and patient-friendly approach.
Hummel and Vassiliadis are optimistic about the impact of their research. They envision a future where non-invasive neuromodulation therapies could be readily available in hospitals, offering a cost-effective and expansive treatment scope.
Journal
Nature Human Behaviour
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Non-invasive stimulation of the human striatum disrupts reinforcement learning of motor skills.
Article Publication Date
29-May-2024