“The present studies demonstrated that GZ17-6.02 interacted with irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor and HER2 to kill uveal melanoma cells.”

Credit: 2024 Booth et al.
“The present studies demonstrated that GZ17-6.02 interacted with irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor and HER2 to kill uveal melanoma cells.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 22, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on May 17, 2024, entitled, “GZ17-6.02 kills PDX isolates of uveal melanoma.”
In this new study, researchers Laurence Booth, Jane L. Roberts, Ivan Spasojevic, Kaitlyn C. Baker, Andrew Poklepovic, Cameron West, John M. Kirkwood, and Paul Dent from Virginia Commonwealth University, Duke University School of Medicine, Genzada Pharmaceuticals, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, and University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute defined the biology of GZ17-6.02 in UM cells and in parallel determined its interaction with irreversible ERBB inhibitors (afatinib, neratinib) and with the cytotoxic agent doxorubicin.
“GZ17-6.02 is a novel compound, containing the synthetically manufactured components: curcumin, harmine and isovanillin and has undergone phase I safety evaluation in cancer patients (NCT03775525).”
GZ17-6.02 has undergone phase I evaluation in patients with solid tumors (NCT03775525). The RP2D is 375 mg PO BID, with an uveal melanoma patient exhibiting a 15% reduction in tumor mass for 5 months at this dose. Studies in this manuscript have defined the biology of GZ17-6.02 in PDX isolates of uveal melanoma cells.
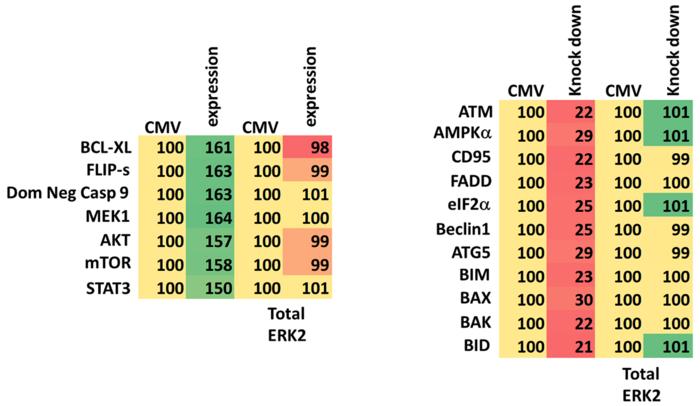
GZ17-6.02 killed uveal melanoma cells through multiple convergent signals including enhanced ATM-AMPK-mTORC1 activity, inactivation of YAP/TAZ and inactivation of eIF2α. GZ17-6.02 significantly enhanced the expression of BAP1, predictive to reduce metastasis, and reduced the levels of ERBB family RTKs, predicted to reduce growth. GZ17-6.02 interacted with doxorubicin or ERBB family inhibitors to significantly enhance tumor cell killing which was associated with greater levels of autophagosome formation and autophagic flux.
Knock down of Beclin1, ATG5 or eIF2α were more protective than knock down of ATM, AMPKα, CD95 or FADD, however, over-expression of FLIP-s provided greater protection compared to knock down of CD95 or FADD. Expression of activated forms of mTOR and STAT3 significantly reduced tumor cell killing. GZ17-6.02 reduced the expression of PD-L1 in uveal melanoma cells to a similar extent as observed in cutaneous melanoma cells whereas it was less effective at enhancing the levels of MHCA. The components of GZ17-6.02 were detected in tumors using a syngeneic tumor model.
“Our data support future testing GZ17-6.02 in uveal melanoma as a single agent, in combination with ERBB family inhibitors, in combination with cytotoxic drugs, or with an anti-PD1 immunotherapy.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28586
Correspondence to: Paul Dent
Email: paul.dent@vcuhealth.org
Keywords: autophagy, ER stress, GZ17-6.02, doxorubicin, afatinib, neratinib
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
Journal
Oncotarget
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
GZ17-6.02 kills PDX isolates of uveal melanoma
Article Publication Date
17-May-2024