The concurrency control in deterministic databases, i.e., deterministic concurrency control, ensures that each transaction batch produces a unique result. In this way, replicas can process transactions in batches without communicating with each other to ensure consistency, which is simpler and more efficient than non-deterministic databases in achieving high availability through replication.
Early deterministic concurrency control protocols, e.g. Calvin, Bohm, PWV, rely on the prior knowledge of the read-write set, which is impractical in most scenarios. The state-of-the-art Ari breaks this limitation. However, Aria has three issues. First, it is hard for users to configure a suitable batch size when the read-write set is unknown, while the batch size has a significant impact on performance. Second, the conflicts are fixed, making Aria may suffer a large number of conflicts even in low-concurrency scenarios, e.g., a single-thread scenario. Third, the write-after-write conflicts caused by concurrently in-place-update a single version makes Aria inefficient in write-intensive workloads. The running sample of Aria is shown in Figure 1.
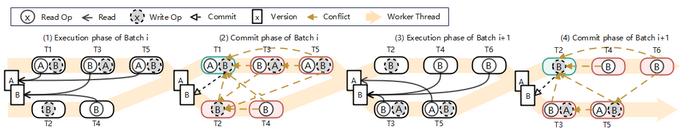
To address these issues, we propose Gria, an efficient deterministic concurrency control protocol. Gria does not rely on the prior knowledge of the read-write set and has the following properties. First, the batch size of Gria is auto-scaling. Second, Gria’s conflict probability in low-concurrency scenarios is lower than that in high-concurrency scenarios. Third, Gria has no write-after-write conflicts by adopting a multi-version structure. A running sample of Gria is shown in Figure 2. To further reduce conflicts, we propose two optimizations: a reordering mechanism as well as a rechecking strategy. The evaluation result on two popular benchmarks shows that Gria outperforms Aria by 13x.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2605-z

Credit: Xinyuan WANG, Yun PENG, Hejiao HUANG
The concurrency control in deterministic databases, i.e., deterministic concurrency control, ensures that each transaction batch produces a unique result. In this way, replicas can process transactions in batches without communicating with each other to ensure consistency, which is simpler and more efficient than non-deterministic databases in achieving high availability through replication.
Early deterministic concurrency control protocols, e.g. Calvin, Bohm, PWV, rely on the prior knowledge of the read-write set, which is impractical in most scenarios. The state-of-the-art Ari breaks this limitation. However, Aria has three issues. First, it is hard for users to configure a suitable batch size when the read-write set is unknown, while the batch size has a significant impact on performance. Second, the conflicts are fixed, making Aria may suffer a large number of conflicts even in low-concurrency scenarios, e.g., a single-thread scenario. Third, the write-after-write conflicts caused by concurrently in-place-update a single version makes Aria inefficient in write-intensive workloads. The running sample of Aria is shown in Figure 1.
To address these issues, we propose Gria, an efficient deterministic concurrency control protocol. Gria does not rely on the prior knowledge of the read-write set and has the following properties. First, the batch size of Gria is auto-scaling. Second, Gria’s conflict probability in low-concurrency scenarios is lower than that in high-concurrency scenarios. Third, Gria has no write-after-write conflicts by adopting a multi-version structure. A running sample of Gria is shown in Figure 2. To further reduce conflicts, we propose two optimizations: a reordering mechanism as well as a rechecking strategy. The evaluation result on two popular benchmarks shows that Gria outperforms Aria by 13x.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2605-z
Journal
Frontiers of Computer Science
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Gria: an efficient deterministic concurrency control protocol
Article Publication Date
15-Aug-2024