The development of new adenine base editors (ABE) and adenine-to-thymine/guanine base editors (AKBE) is transforming watermelon genetic engineering. These innovative tools enable precise A:T-to-G and A:T-to-T base substitutions, allowing for targeted genetic modifications. The research highlights the efficiency of these editors in generating specific mutations, such as a flowerless phenotype in ClFT (Y84H) mutant plants. This advancement not only enhances the understanding of gene function but also significantly improves molecular breeding, paving the way for more efficient watermelon crop improvement.

Credit: Horticulture Research
The development of new adenine base editors (ABE) and adenine-to-thymine/guanine base editors (AKBE) is transforming watermelon genetic engineering. These innovative tools enable precise A:T-to-G and A:T-to-T base substitutions, allowing for targeted genetic modifications. The research highlights the efficiency of these editors in generating specific mutations, such as a flowerless phenotype in ClFT (Y84H) mutant plants. This advancement not only enhances the understanding of gene function but also significantly improves molecular breeding, paving the way for more efficient watermelon crop improvement.
Traditional breeding methods for watermelon often face challenges in achieving desired genetic traits efficiently and accurately. While CRISPR/Cas9 has provided a powerful tool for genome editing, its precision and scope are sometimes limited. These limitations highlight the need for more advanced gene-editing technologies. The development of new base editors, which can introduce specific base changes, represents a significant step forward. Due to these challenges, there is a growing necessity to develop precise and efficient gene-editing techniques to enhance watermelon breeding and achieve more reliable crop improvements.
Researchers from Northwest A&F University and Northeast Agricultural University have published a study (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae123) in Horticulture Research, on April 23, 2024, detailing the development of adenine base editors (ABE) and adenine-to-thymine/guanine base editors (AKBE) base editors for watermelon. These editors allow precise genetic modifications, potentially improving crop traits and breeding efficiency.
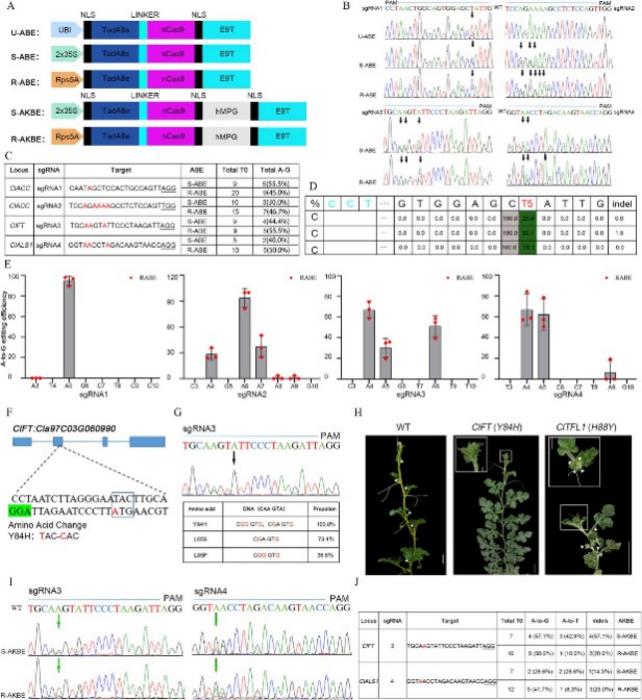
The study introduces three types of adenine base editors (U-ABE, S-ABE, and R-ABE) and evaluates their efficiency in inducing A:T-to-G substitutions in watermelon genes. Among them, R-ABE demonstrated the highest efficiency, particularly at the A5 position of the target gene. Additionally, the researchers developed S-AKBE and R-AKBE to achieve A:T-to-T mutations, with S-AKBE showing greater efficiency. The successful editing of the ClFT gene to produce the Y84H mutation resulted in a flowerless phenotype, underscoring the potential of these tools in manipulating flowering time and other traits in watermelon. The findings reveal that the Rps5A promoter used in R-ABE and R-AKBE significantly enhances editing efficiency. Overall, this study highlights the effectiveness of these base editors in achieving precise genetic modifications, paving the way for improved breeding strategies and trait enhancements in watermelon.
Dr. Xian Zhang from Northwest A&F University commented, “The development of these base editors represents a significant breakthrough in plant genetic engineering. These tools not only enhance our ability to study gene function but also pave the way for more precise and efficient crop improvement strategies.”
The implementation of ABE and AKBE base editors opens new avenues for watermelon breeding, allowing for the precise introduction of beneficial traits. Future research will focus on optimizing these tools and exploring additional target genes to further enhance the genetic improvement of watermelon and potentially other crops.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
Funding information
This work was supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U23A20208), the National Youth Talent Program (A279021801), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFE0206900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32372734), Luoyang Major Science and Technology Tackling Key Issues Project (Public Announcement and Leadership, 2301024A), Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-25), Key-Area R&D Program of Guangdong Province (2022B0202060001), Key R&D Program of Shaanxi Province (2023-YBNY-008, 2024NC-YBXM-032), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2022JM-112).
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
Journal
Horticulture Research
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Development of ABE and AKBE base editors in watermelon
Article Publication Date
23-Apr-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.