“[…] as far as we know, we are the first to provide evidence of [stem cell depletion in aging] in a pan-tissue manner.”

Credit: 2024 Santos et al.
“[…] as far as we know, we are the first to provide evidence of [stem cell depletion in aging] in a pan-tissue manner.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 16, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 7, entitled, “Evidence of a pan-tissue decline in stemness during human aging.”
Despite their biological importance, the role of stem cells in human aging remains to be elucidated. In a new study, researchers Gabriel Arantes dos Santos, Gustavo Daniel Vega Magdaleno and João Pedro de Magalhães from the Universidade de Sao Paulo, University of Birmingham and the University of Liverpool applied a machine learning method to detect stemness signatures from transcriptome data of healthy human tissues.
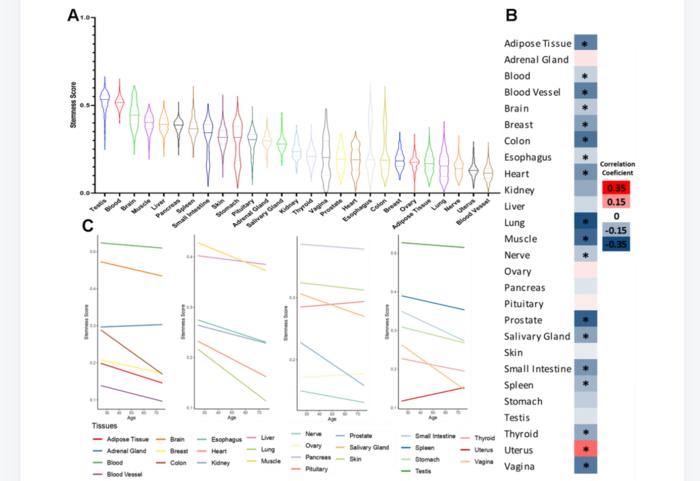
“In this work, we applied a machine learning methodology to GTEx transcriptome data and assigned stemness scores to 17,382 healthy samples from 30 human tissues aged between 20 and 79 years.”
The team found that ~60% of the studied tissues exhibit a significant negative correlation between the subject’s age and stemness score. The only significant exception was the uterus, where they observed an increased stemness with age. Moreover, the researchers observed that stemness is positively correlated with cell proliferation and negatively correlated with cellular senescence. Finally, they also observed a trend that hematopoietic stem cells derived from older individuals might have higher stemness scores.
“In conclusion, we assigned stemness scores to human samples and show evidence of a pan-tissue loss of stemness during human aging, which adds weight to the idea that stem cell deterioration may contribute to human aging.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205717
Corresponding Author: João Pedro de Magalhães – jp@senescence.info
Keywords: longevity, stem cells, transcriptomics, senescence
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Evidence of a pan-tissue decline in stemness during human aging
Article Publication Date
4-Apr-2024