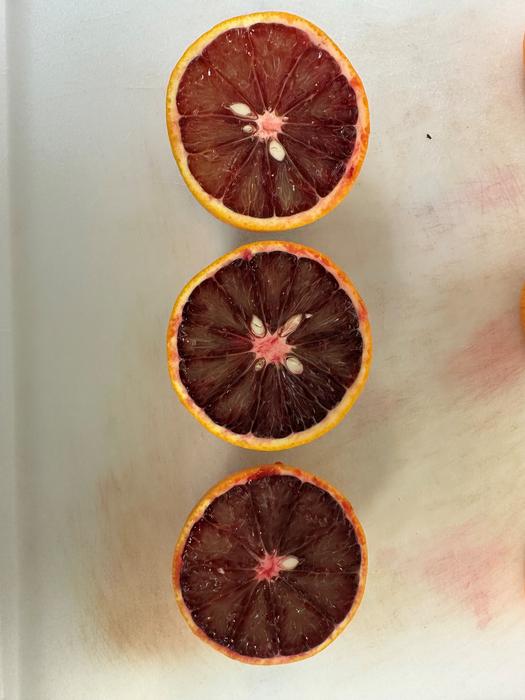
An orange teeming with antioxidants and other health benefits may be a shot in the arm for consumers and citrus growers, if the fruit is stored at cool temperatures, a new University of Florida study shows.

Credit: Ali Sarkhosh, UF/IFAS
An orange teeming with antioxidants and other health benefits may be a shot in the arm for consumers and citrus growers, if the fruit is stored at cool temperatures, a new University of Florida study shows.
But it’s too soon to know if the so-called “blood oranges” are a viable crop for the Florida citrus industry, says Ali Sarkhosh, a UF/IFAS associate professor of horticultural sciences. Sarkhosh’s post-doctoral associate Fariborz Habibi explains further.
“Although blood oranges typically command higher prices than other common varieties, such as navel or Valencia oranges, it is unclear if farmers could substantially increase their per-acre income by adding them to their crop selection and then storing them for internal color development,” said Habibi, lead author of the study. “Improved fruit quality from the storage method presents a promising opportunity for the Florida citrus industry. However, further study is needed before recommending anything to growers.”
The fruit is rich in anthocyanins, which have been linked to various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. They also contain other beneficial phytochemicals such as vitamin C, flavonoids and dietary fiber.
“Fruit can also develop internal color under similar conditions at home. However, the fruit in the supermarket should have a good internal color and be ready for consumption,” Sarkhosh said.
For this research, scientists harvested fruit from a research plot at the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center in Quincy.
Scientists found that storing the blood oranges at 40 to 53 degrees enhances anthocyanin, phenolic content, and antioxidants. When they lowered the temperatures 43 to 46 degrees, they also preserved fruit firmness, weight loss and sugar content.
“Attributes such as firmness are crucial for maintaining the overall quality, texture and taste of the blood oranges during storage,” said Habibi.
Blood oranges get their name from their deep red flesh. Their skin contains a type of antioxidant pigment. The fruit is commonly grown in countries like Italy and Spain, which have the Mediterranean climate – cold, but above 32 degrees — that helps them grow. In the United States, blood oranges grow primarily in California, but are not grown commercially yet in Florida.
Anthocyanin develops when the fruit is exposed to cold temperatures between 46 and 59 degrees for at least 20 days. Such conditions are rare in Florida’s subtropical climate.
Journal
Food Chemistry Advances
Article Title
Postharvest storage temperature strategies affect anthocyanin levels, total phenolic content, antioxidant activity, chemical attributes of juice, and physical qualities of blood orange fruit
Article Publication Date
20-Jun-2024