One of the most beautiful aspects of Nature is the endless variety of shapes, colours and behaviours exhibited by organisms. These traits help organisms survive and find mates, like how a male peacock’s colourful tail attracts females or his wings allow him to fly away from danger. Understanding traits is crucial for biologists, who study them to learn how organisms evolve and adapt to different environments.

Credit: Montanaro et al.
One of the most beautiful aspects of Nature is the endless variety of shapes, colours and behaviours exhibited by organisms. These traits help organisms survive and find mates, like how a male peacock’s colourful tail attracts females or his wings allow him to fly away from danger. Understanding traits is crucial for biologists, who study them to learn how organisms evolve and adapt to different environments.
To do this, scientists first need to describe these traits in words, like saying a peacock’s tail is “vibrant, iridescent, and ornate”. This approach works for small studies, but when looking at hundreds or even millions of different animals or plants, it’s impossible for the human brain to keep track of everything.
Computers could help, but not even the latest AI technology is able to grasp human language to the extent needed by biologists. This hampers research significantly because, although scientists can handle large volumes of DNA data, linking this information to physical traits is still very difficult.
To solve this problem, researchers from the Finnish Museum of Natural History, Giulio Montanaro and Sergei Tarasov, along with collaborators, have created a special language called Phenoscript. This language is designed to describe traits in a way that both humans and computers can understand. Describing traits with Phenoscript is like programming a computer code for how an organism looks.
Phenoscript uses something called semantic technology, which helps computers understand the meaning behind words, much like how modern search engines know the difference between the fruit “apple” and the tech company “Apple” based on the context of your search.
“This language is still being tested, but it shows a lot of promise. As more scientists start using Phenoscript, it will revolutionise biology by making vast amounts of trait data available for large-scale studies, boosting the emerging field of phenomics,” explains Montanaro.
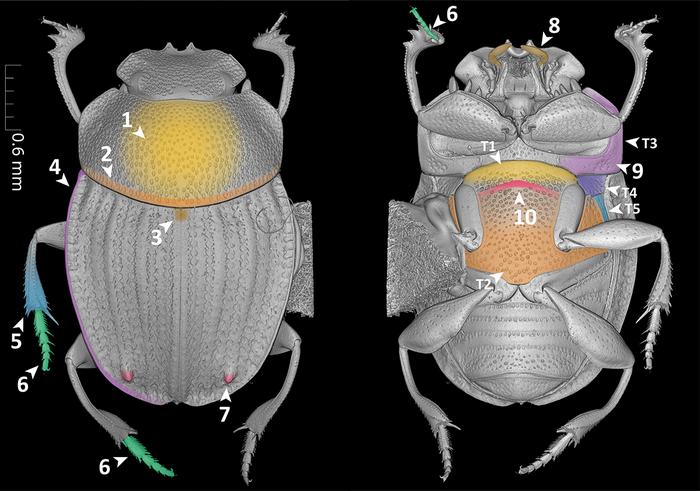
In their research article, newly published in the open-access, peer-reviewed Biodiversity Data Journal, the researchers make use of the new language for the first time, as they create semantic phenotypes for four species of dung beetles from the genus Grebennikovius. Then, to demonstrate the power of the semantic approach, they apply simple semantic queries to the generated phenotypic descriptions.
Finally, the team takes a look yet further ahead into modernising the way scientists work with species information. Their next aim is to integrate semantic species descriptions with the concept of nanopublications, “which encapsulates discrete pieces of information into a comprehensive knowledge graph”. As a result, data that has become part of this graph can be queried directly, thereby ensuring that it remains Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable (FAIR) through a variety of semantic resources.
***
Research paper:
Montanaro G, Balhoff JP, Girón JC, Söderholm M, Tarasov S (2024) Computable species descriptions and nanopublications: applying ontology-based technologies to dung beetles (Coleoptera, Scarabaeinae). Biodiversity Data Journal 12: e121562.
***
The hereby study is the latest addition to the special topical collection: “Linking FAIR biodiversity data through publications: The BiCIKL approach”, launched and supported by the recently concluded Horizon 2020 project: Biodiversity Community Integrated Knowledge Library (BiCIKL). The collection aims to bring together scientific publications that demonstrate the advantages and novel approaches in accessing and (re-)using linked biodiversity data.