Recent advancements in imaging technology are profoundly transforming the landscape of medical diagnostics, particularly in neurology. The innovative research conducted by Miura et al. offers groundbreaking insights into the evaluation of neuromelanin through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Their study, titled “Visual Assessment of Neuromelanin MR Imaging: A Comparison of PROPELLER and FSE Sequences with and Without Deep Learning Reconstruction,” represents a significant leap forward in how neuromelanin is assessed, explores the application of advanced imaging sequences, and incorporates cutting-edge deep learning techniques.
Neuromelanin, a dark pigment found in various areas of the brain, has become a focal point in the study of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. As researchers delve into the structural and functional implications of neuromelanin, its relevance in clinical settings cannot be overstated. This pigment’s presence and changes in concentration can reflect alterations in dopaminergic neurons, making it an essential variable in understanding various neurological conditions.
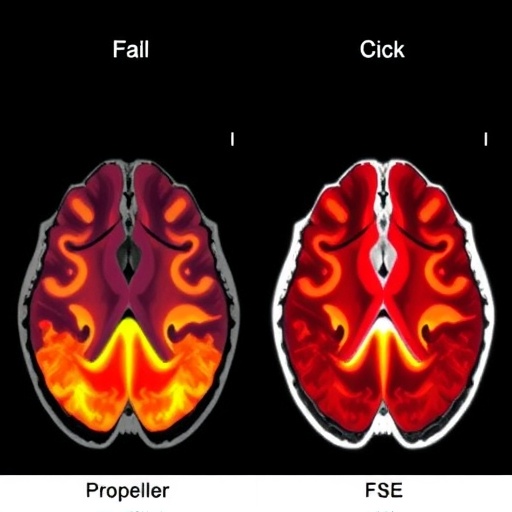
In this study, the authors meticulously compared two advanced imaging sequences: PROPELLER (Periodically Rotated Overlapping ParalleL Lines with Enhanced Reconstruction) and Fast Spin Echo (FSE). Each imaging modality presents unique benefits and challenges, creating a layered understanding of the diagnostic potential for neuromelanin visualization. PROPELLER, with its ability to obtain high-quality images even in the presence of motion artifacts, contrasts sharply with FSE, which is often favored for its rapid acquisition times.
The integration of deep learning reconstruction techniques further enhances the imaging capabilities of both methodologies. Deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, leverages neural networks to analyze complex data patterns and improve image clarity. The study showcases how deep learning can refine the quality of MRI images, thereby facilitating a more accurate visual assessment of neuromelanin. By employing this innovative technology, there is a significant improvement in diagnostic efficacy, substantially impacting patient outcomes.
The design of the comparative study involved a rigorous methodology, including a thorough selection of participants diagnosed with varying degrees of neurodegenerative conditions. The MRI images were evaluated by trained radiologists who employed systematic visual assessment techniques to identify and analyze neuromelanin levels, drawing attention to the subtle nuances of each imaging sequence. This meticulous approach ensures that the conclusions drawn from the study are robust and reliable.
As both PROPELLER and FSE sequences were evaluated with and without deep learning reconstruction, the research team aimed to ascertain how these enhancements change the landscape of neuromelanin imaging. Early findings indicate that deep learning not only amplifies the visibility of neuromelanin but also aids in the differentiation of pathological from healthy brain regions, a critical factor in early diagnosis and intervention.
Moreover, the research underscores the importance of developing a standard for visual assessment to facilitate easier integration of these imaging techniques into clinical practice. The need for clear protocols can maximize the potential of these technologies, enabling widespread usage in both research and clinical environments. As techniques evolve, establishing a consistent framework for interpretation will be vital for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of neuromelanin assessments across various institutions.
The implications of this study extend beyond mere imaging advancements; they carry profound consequences for predicting disease trajectories and tailoring patient management strategies. With accurate neuromelanin quantification, clinicians will be better equipped to design personalized treatment plans based on each patient’s unique neurochemical profile. This tailored approach holds promise not only for enhancing care coordination but also for improving overall patient satisfaction and outcomes.
Moreover, the attention to detail in the research has also highlighted potential areas for further exploration. Areas such as the longitudinal tracking of neuromelanin changes in relation to therapeutic interventions, or the comparative effectiveness of these imaging techniques across different demographic populations, could provide fertile ground for future studies. This could ultimately lead to broader insights into the mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration and its progression.
In addition to shaping clinical practices, the findings may also have significant ramifications for research funding and emphasis. As the medical community recognizes the essential role of neuromelanin in neurological assessments, increased resources may be allocated towards training, technology development, and further investigations into its implications. This could accelerate the pace of innovation in the field, fostering a collaborative approach that includes radiologists, neurologists, and data scientists.
The importance of interdisciplinary collaboration cannot be understated. The interplay between medical imaging specialists, neurologists, and engineers in deep learning demonstrates that tackling complex medical challenges necessitates an inclusive and multifaceted approach. As seen in this study, the synergistic effects of diverse expertise can yield remarkable innovations that enhance diagnostic capabilities and patient care.
The ongoing dialogue regarding the utility of advanced imaging techniques in clinical practice promises to be exciting. As technologies continue to evolve at a breakneck pace, the combination of traditional methodologies with novel approaches like deep learning presents opportunities to redefine medical diagnostics. This research exemplifies how critical these advancements are in enabling medical professionals to navigate the complexities of neurological diseases.
In conclusion, the work significantly contributes to our understanding of neuromelanin and its implications in neuropathology. As demonstrated by Miura et al., the combination of PROPELLER and FSE imaging sequences with deep learning techniques illuminates new pathways for both diagnosis and treatment in neurodegenerative diseases. The implications of this research are broad and vital, as they signal a transformative shift in how we visualize and understand the complexities of the human brain.
In summary, the future of neuromelanin imaging holds great promise, with innovative imaging and analytical techniques pushing the boundaries of medical exploration. As these advancements continue to unfold, the potential to improve outcomes for patients with neurodegenerative conditions becomes ever more tangible.
Subject of Research:
Neuromelanin MR Imaging Techniques in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Article Title:
Visual Assessment of Neuromelanin MR Imaging: A Comparison of PROPELLER and FSE Sequences with and Without Deep Learning Reconstruction
Article References:
Miura, A., Takahashi, H., Nakagawa, T. et al. Visual Assessment of Neuromelanin MR Imaging: A Comparison of PROPELLER and FSE Sequences with and Without Deep Learning Reconstruction. J. Med. Biol. Eng. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-025-01001-x
Image Credits:
AI Generated
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-025-01001-x
Keywords:
Neuromelanin, MR Imaging, PROPELLER, FSE, Deep Learning, Neurodegeneration