A groundbreaking study published in LabMed Discovery on May 16, 2025, offers compelling evidence that supplementing children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using a vitamin D3-loaded nanoemulsion considerably improves core symptoms associated with the condition. This research pioneers a novel approach in vitamin supplementation by leveraging nanotechnology to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of vitamin D3, a nutrient critically linked to neurological development and behavioral modulation. Unlike conventional supplementation, which often yields inconsistent outcomes in ASD populations, this innovative nanoemulsion formulation appears to transcend prior therapeutic limitations.
Autism spectrum disorder is characterized by multifaceted impairments in social communication, language development, adaptive behaviors, and often coexists with a variety of neurodevelopmental challenges. Emerging data has frequently identified vitamin D3 deficiency as a common biochemical deviation in children diagnosed with ASD. The vitamin’s influence spans the regulation of neuroimmune responses, neuronal differentiation, and synaptic function, aspects crucial for typical brain maturation. However, the clinical translation of vitamin D3 supplementation benefits has been historically inconclusive, largely due to issues of absorption variability and metabolic inefficiencies when using traditional oral formulations.
The researchers in this study hypothesized that nanoemulsion technology—a process of encapsulating vitamin D3 in nanoparticles—could significantly improve its gastrointestinal absorption and systemic bioavailability. Nanoemulsions are known for their enhanced surface area, enhanced solubility in aqueous environments, and improved cellular uptake. By nanoencapsulating vitamin D3, they sought to overcome the pharmacokinetic barriers that have impeded consistent clinical improvements in autism-related behavioral and cognitive parameters.
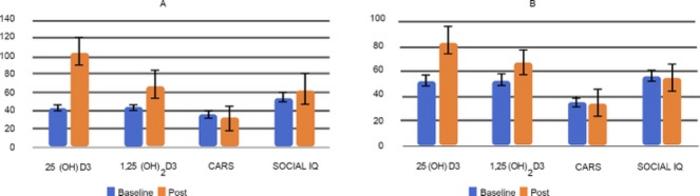
To empirically assess this hypothesis, the research team enrolled eighty children aged 3 to 6 years with clinically confirmed ASD. The participants were randomized into two groups receiving either the nanoemulsion form of vitamin D3 or a standard marketed vitamin D3 supplement. This double-arm experimental design extended over a six-month period, enabling rigorous longitudinal evaluation of the intervention’s impact on both biochemical and neurobehavioral outcomes. Baseline and post-treatment assessments employed validated scales such as the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale, and the Preschool Language Scale, ensuring comprehensive measurement of autism severity, adaptive functioning, and language proficiency.
Remarkably, results demonstrated that only the group receiving the vitamin D3 nanoemulsion exhibited statistically significant elevations in serum vitamin D3 levels, combined with clinically relevant reductions in autism severity scores. Furthermore, these children experienced marked improvements in social IQ metrics and enhancements in both receptive and expressive language skills. This contrasts starkly with outcomes from the control group, where despite an increase in blood vitamin D3 concentration, behavioral and cognitive advances were negligible.
These findings underscore the transformative potential of nanoemulsion technology in neurodevelopmental therapeutics. By improving systemic bioavailability of vitamin D3, nanoemulsion supplementation appears to not only correct a biochemical deficiency but also triggers functional neurobehavioral benefits that were previously elusive. Experimental data highlight that nanoemulsions can traverse biological membranes more effectively, protect the active ingredient from degradation in the digestive tract, and provide sustained release, attributes conducive to optimizing nutrient delivery in pediatric populations.
The molecular mechanisms underpinning the observed clinical benefits may be multifactorial. Vitamin D3 plays a critical role in modulating neurotrophic factors and inflammatory responses within the central nervous system, both implicated in ASD pathophysiology. Enhanced bioavailability could facilitate more consistent activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) pathways in neuronal and immune cells, potentially restoring altered neuroimmune homeostasis that contributes to autism symptomatology. Additionally, vitamin D3 is involved in dopamine synthesis and glutamatergic neurotransmission regulation—systems deeply intertwined with social behaviors and cognitive processing.
In the broader context of nutritional neuroscience, this study validates the importance of advancing beyond traditional supplementation paradigms. The nanoemulsion’s success serves as a prototype for employing nanotechnology to amplify the efficacy of micronutrient interventions targeting complex brain disorders. Given the global prevalence and the multifaceted nature of ASD, innovations that harness such technology could reshape preventative and therapeutic strategies that have until now been hampered by limited bioavailability of key nutrients.
Despite its promising implications, the study acknowledges certain limitations. The sample size, while robust for initial experimental validation, necessitates expansion in subsequent trials to confirm reproducibility and generalizability across diverse demographic and genetic backgrounds. Moreover, the authors call for extended follow-up periods to assess the long-term sustainability of clinical improvements and to evaluate any potential developmental safety concerns associated with chronic nanoemulsion administration. Gender-specific responses also remain an open question, prompting further research into sex-based metabolic and neurobehavioral interactions.
From a translational perspective, this research encourages clinicians and nutritional scientists to reconsider supplementation strategies in ASD and potentially other neurodevelopmental disorders marked by micronutrient deficiencies. The successful application of nanoemulsion technology in this context may inspire analogous approaches targeting vitamins and other bioactive compounds that face absorption challenges. As nanoformulated products advance toward regulatory approval and market availability, their integration into multidisciplinary ASD management protocols could become a critical component of personalized care models.
Furthermore, this study highlights the critical need for meticulously designed clinical trials encompassing biochemical assays alongside standardized behavioral assessments. Only through such integrative methodologies can the true efficacy of innovative nutraceutical interventions be accurately gauged and optimized. The positive outcomes demonstrated here reaffirm the potential for vitamin D3 to serve as a modifiable factor in autism symptom management when delivered via advanced pharmaceutical technology.
Looking forward, the intersection of nanomedicine and neuroscience holds vast potential. The capacity to deliver specific nutrients with precision and enhanced bioavailability may unlock new therapeutic frontiers beyond ASD, encompassing broader neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative conditions. The detailed mechanistic insights obtained from continuing research will be paramount in ensuring targeted, safe, and effective application of such cutting-edge technologies.
In summary, this landmark study firmly establishes that vitamin D3-loaded nanoemulsion supplementation outperforms conventional vitamin D3 preparations in raising serum levels and improving core manifestations of autism in young children. The translational impact of enhanced nutrient delivery through nanoencapsulation promises to revolutionize nutritional interventions within neurodevelopmental frameworks and invites expansive, multidisciplinary investigations into nanoparticle-based therapeutics.
Subject of Research: Effectiveness of vitamin D3-loaded nanoemulsion in improving core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in children.
Article Title: Improved core manifestations of autism following supplementation with vitamin D3-loaded nanoemulsion.
News Publication Date: 16-May-2025.
Web References: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lmd.2025.100071
Image Credits: Nagwa A. Meguid, Maha Hemimi, Gina Hussein, Ahmed Elnahry, Marwa Hasanein Asfour, Sameh Hosam Abd El-Alim, Ahmed Alaa Kassem, Abeer Salama, Amr Sobhi Gouda, Walaa Samy Nazim, Radwa Ibrahim Ali Hassan, Neveen Hassan Nashaat.
Keywords: Autism, Vitamin D, Neurodevelopmental disorders, Nanoemulsion, Nutritional intervention, Pediatric neurology, Autism severity, Social IQ, Language development, Bioavailability, Nanotechnology, Neuroimmune modulation.