In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has witnessed unprecedented growth, largely driven by groundbreaking advancements in foundation models (FMs) like the GPT-n series developed by OpenAI, and large language models (LLMs) such as the Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer, or ChatGPT. These sophisticated platforms have made significant inroads into multiple industries, particularly healthcare, where they are reshaping the landscape of medical science and practice. The impressive capabilities of these technologies are not only enhancing diagnostic accuracy but are also fostering an environment rife with opportunities for innovative medical applications.
A recent review published in the Chinese Medical Journal delves into the evolving role of FMs and LLMs in medical artificial intelligence. With the advent of models like MedPaLM from Google, which has shown an ability to achieve expert-level results on the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination, the potential of AI in medicine has become glaringly apparent. These technologies are not just tools for clinicians; rather, they represent a paradigm shift in how healthcare is delivered, showcasing their vast application in medical diagnostics, education, and beyond.
Moreover, the integration of AI in healthcare is being supported by notable initiatives promoting global medical imaging data sharing and regulatory frameworks from health authorities like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Such advancements are indicative of a burgeoning era where AI can play an instrumental role in enhancing diagnostic capabilities and ultimately improving patient care. These innovations demonstrate that the healthcare sector is entering a new phase, where efficiency and precision are paramount.
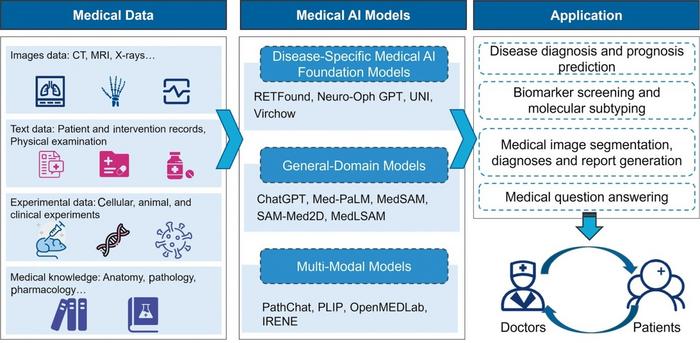
However, the deployment of medical AI is not without its hurdles. The review led by a distinguished team from Macau University of Science and Technology highlights several challenges associated with the use of FMs and LLMs in clinical settings. As this technology becomes more prevalent, it is critical to address various limitations surrounding data processing and analysis. The complex nature of medical data—which spans imaging data like CT, MRI, and X-rays, as well as textual information derived from patient records—creates a challenging landscape for AI models to navigate.
In terms of classification, the researchers propose a framework that categorizes medical AI models into disease-specific, general-domain, and multi-modal models. Disease-specific models target particular conditions and offer notable examples such as RetFound for eye diseases, Neuro-Oph GPT in neuro-ophthalmology, and Virchow, which aids in cancer detection. In contrast, general-domain models like ChatGPT and MedPaLM connote broader functionalities, thus overcoming the restrictive scope presented by their disease-specific counterparts. These distinctions serve to highlight the versatility of AI tools, as they adapt to varying medical contexts and requirements.
The emergence of multi-modal models, which incorporate data from various sources, is another exciting development in the realm of medical AI. Platforms such as PathChat and OpenMEDLab enhance the fusion of textual and image-based data, bridging crucial gaps and paving the way for comprehensive data analysis. Such innovations hold promise for areas like medical image segmentation, biomarker screening, and medical question answering, all of which stand to benefit significantly from the collaboration between diverse data types.
However, along with promise come significant challenges, particularly around data collection. The review underscores issues pertaining to data volume, annotation challenges, biases in data sets, and privacy concerns—with each representing critical hurdles to the effective application of medical AI. Prof. Wong emphasizes the need for establishing regulatory environments that enable secure data sharing while protecting patient privacy. This dual imperative of data accessibility and security is crucial for the sustainable development of AI-driven healthcare solutions.
To fully harness the capabilities of AI in healthcare, a concerted effort towards algorithmic refinement and standardized evaluation protocols is necessary. Collaboration among researchers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory bodies will be paramount in smoothing the path to the effective adoption of AI in clinical practice. This collaborative approach is not only essential for technical refinement; it also forms the basis for building trust among stakeholders and constituents affected by medical AI implementations.
The potential for medical AI to revolutionize healthcare is vast. These advanced models can offer increased diagnostic accuracy, tailored treatment suggestions, and improved patient outcomes. This shift represents an opportunity to redefine patient care, moving towards systems that proactively address health issues while respecting individual needs. The transformative power of medical AI, however, cannot be fully realized without ongoing research, innovation, and careful ethical consideration.
As we look to the future, the role of foundation and large language models in healthcare promises to be pivotal. By enhancing diagnostics, personalizing treatment approaches, and ushering in a new era of patient care, these models stand at the forefront of a healthcare revolution. Nonetheless, for the full extent of these benefits to be realized, the ongoing challenges associated with their implementation must be addressed with urgency and responsibility.
In conclusion, the integration of AI models in medicine holds immense potential for transforming healthcare holistically. The key lies in cultivating a collaborative ecosystem complete with robust regulations, secure frameworks for data management, and continual advancements in technology. The implications of these advancements go far beyond immediate clinical applications, embodying a vision for a future where healthcare is not only more efficient but fundamentally more humane, driven by insights drawn from comprehensive data analysis and the innovative use of artificial intelligence.
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Leveraging foundation and large language models in medical artificial intelligence
News Publication Date: 5-Nov-2024
Web References: Not available
References: DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003302
Image Credits: Zhuo Sun from The Third People’s Hospital of Changzhou
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Medical AI, Foundation Models, Large Language Models, Healthcare Innovation, Data Privacy, Diagnostic Accuracy, Multi-modal Models, Disease-specific Models, Collaboration in Healthcare