Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can break most of the chemical bonds in organic matter, and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light can cause significant harm to humans and objects. In response, UV-shielding materials have been developed to fulfill various commercial requirements, including UV-shielding windows, food containers, contact lenses, and masks. While existing UV shielding materials are suitable for daily use, their effectiveness diminishes in high-temperature, high-pressure, corrosive, and radioactive environments. Organics fail at high temperatures, and films or coatings tend to flake under harsh conditions; glass is constrained by its inherent mechanical brittleness. In response, researchers are actively engaged in the development of UV-shielding materials with high melting points, robust mechanical strength, optimal optical properties, and long-term physical and chemical stability to withstand diverse extreme conditions, including aerospace, high temperature, and acidic and alkaline environments.

Credit: Journal of Advanced Ceramics, Tsinghua University Press
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can break most of the chemical bonds in organic matter, and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light can cause significant harm to humans and objects. In response, UV-shielding materials have been developed to fulfill various commercial requirements, including UV-shielding windows, food containers, contact lenses, and masks. While existing UV shielding materials are suitable for daily use, their effectiveness diminishes in high-temperature, high-pressure, corrosive, and radioactive environments. Organics fail at high temperatures, and films or coatings tend to flake under harsh conditions; glass is constrained by its inherent mechanical brittleness. In response, researchers are actively engaged in the development of UV-shielding materials with high melting points, robust mechanical strength, optimal optical properties, and long-term physical and chemical stability to withstand diverse extreme conditions, including aerospace, high temperature, and acidic and alkaline environments.
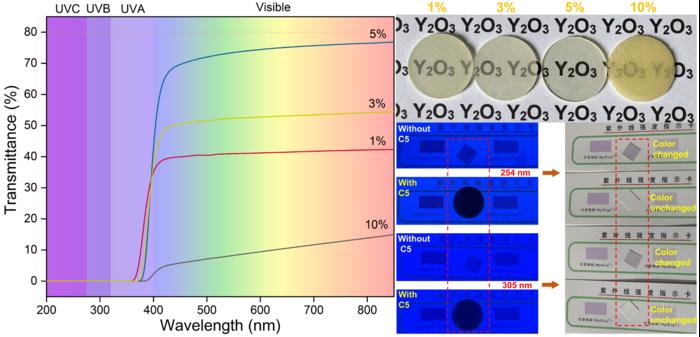
To address these problems, a research team from Sichuan University has developed a new UV-shielding material: Ce-doped yttria transparent ceramic. Transparent ceramics are polycrystalline materials with optical transparency that are formed by pressing and sintering. In contrast to traditional UV-shielding materials such as resin and glass, transparent ceramics typically exhibit superior chemical stability and enhanced thermomechanical properties, including thermal-shock resistance, toughness, strength, and thermal conductivity. They subjected cerium dioxide and yttria raw materials to a series of preparation processes to obtain Ce-doped yttria transparent ceramic. Cerium dioxide serves not only as a UV absorber but also as an effective sintering aid for yttria transparent ceramics. Due to the absorption in the visible region of tetravalent cerium, the UV cutoff edge of the yttria ceramic shifted from 250 nm to 375 nm. This shift grants UV shielding capabilities to yttria transparent ceramics, resulting in 100% shielding for UVC and UVB and approximately 95% shielding for UVA.
The team published their work in Journal of Advanced Ceramics on July 24, 2024.
Their results indicate that Ce-doped yttria transparent ceramics exhibit excellent mechanical and thermal properties. Additionally, the optical quality of Ce-doped yttria transparent ceramics remains stable even after prolonged exposure to harsh environments, including acidic and alkaline conditions, UV radiation, and high temperatures. Compared to traditional UV-shielding materials such as coatings, films, polymers, and glass, these UV-shielding transparent ceramics offer superior stability and longevity. Consequently, Ce-doped yttria transparent ceramics are highly competitive as UV-shielding materials, particularly in extreme conditions such as space, radiation reactors, and high-temperature environments.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U21A20441 and U22B2070).
About the Authors
Dr. Jianqi Qi is a professor in the College of Physics, Sichuan University. He received his BSc degree in Physics from Sichuan University in 2004. He received his Ph. D degree in condensed matter physics from Sichuan University in 2009. He was a visiting scholar at the University of California, Davis from 2013 to 2014. His research focused on the service performance of materials under extreme conditions (high temperature, high pressure, strong impact and radiation environment, etc.)
Mr. Cong Zhang is a Ph.D. candidate at the College of Physics, Sichuan University. His research focuses on developing transparent ceramics for radiation detection and shielding.
About Journal of Advanced Ceramics
Journal of Advanced Ceramics (JAC) is an international academic journal that presents the state-of-the-art results of theoretical and experimental studies on the processing, structure, and properties of advanced ceramics and ceramic-based composites. JAC is Fully Open Access, monthly published by Tsinghua University Press, and exclusively available via SciOpen. JAC’s 2023 IF is 18.6, ranking in Top 1 (1/31, Q1) among all journals in “Materials Science, Ceramics” category, and its 2023 CiteScore is 21.0 (top 5%) in Scopus database. ResearchGate homepage:
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
Journal
Journal of Advanced Ceramics
Article Title
Designing highly transparent cerium doped Y2O3 ceramics with high mechanical and thermal properties for UV-shielding in extreme conditions
Article Publication Date
24-Jul-2024