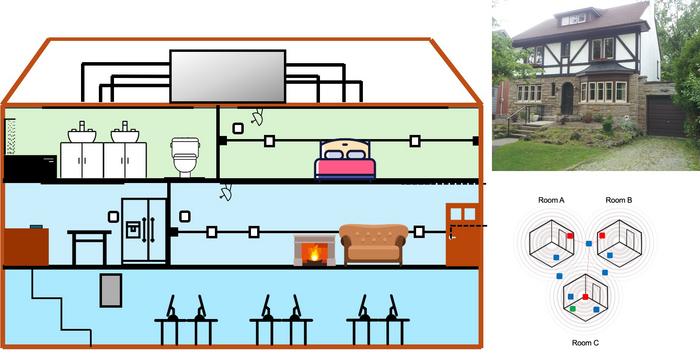
A groundbreaking advancement in healthcare technology has emerged from McMaster University in Canada, where researchers have developed a novel Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)-based Indoor Positioning System (IPS) designed specifically to monitor the mobility of older adults within their living environments. This innovative system promises to revolutionize aging-in-place care, offering healthcare providers a cost-effective, low-power, and easy-to-install solution that overcomes many of the existing limitations of indoor tracking technologies.
Traditional Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, while ubiquitous and reliable outdoors, fails to deliver accurate location data inside buildings due to signal attenuation and obstruction by walls and ceilings. This gap has long posed a serious challenge for healthcare applications that require precise indoor location tracking, such as fall detection, emergency response, and activity monitoring for elderly populations. The McMaster team’s BLE-based IPS presents a transformative alternative by harnessing Bluetooth signals emitted by strategically placed wireless beacons combined with wearable tags to continuously and accurately estimate a person’s location within enclosed spaces.
The core innovation lies in the system’s utilization of Bluetooth Low Energy technology, which is both energy-efficient and accessible. The IPS involves small beacons, each plugged into standard wall outlets throughout the home, emitting Bluetooth signals that are picked up by wearable tags on the individual. These signals, when analyzed in conjunction with data from motion sensors also incorporated into the system, enable the continuous tracking of user location with remarkable accuracy. The research demonstrates a 96% accuracy rate in location detection, underscoring the system’s potential for real-world deployment in dynamic residential settings.
Notably, the system is designed for practical, low-barrier implementation. It dispenses with the need for complex professional installations or detailed architectural floorplans that typically inflate costs and complicate setup. With just five beacons, the entire system can be installed for roughly $200, making it a financially viable option for widespread adoption, especially in community and home care environments catering to aging populations.
For validation, the research team installed the BLE-based IPS within two different suburban homes, including the unique McMaster Smart Home for Aging-in-Place (SHAPE) facility, a century-old house transformed into a cutting-edge research site. The system’s performance in these settings confirmed its robustness and adaptability, with the combination of Bluetooth signals and motion sensors enabling precise location detection across various rooms and living spaces even as users moved about naturally throughout the day.
The implications of this technology extend beyond eldercare. Researchers emphasize the system’s versatility for tracking both individuals and critical medical equipment in dynamic environments such as hospitals and long-term care facilities, where the ability to monitor movement in real-time can significantly improve safety protocols and streamline operations.
From a technical perspective, the BLE-based IPS employs signal strength measurements—known as Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)—to estimate distance between beacons and the wearable tag. Sophisticated algorithms analyze these signals, adjusting for noise and signal variability common in residential environments, to triangulate the wearer’s position. To augment the system’s accuracy, motion sensors provide contextual data that help differentiate between stationary and active states, further refining location estimates.
This context-aware monitoring capability is poised to dramatically enhance patient safety and caregiver efficiency. Continuous mobility data can alert caregivers to prolonged inactivity—potentially signaling a fall or medical emergency—while also enabling tailored interventions that support independence and quality of life for older adults living alone.
The research team, led by Dr. Qiyin Fang of McMaster University, underscores the importance of low-cost, user-friendly design in encouraging adoption across existing homes, offering a practical path toward integrating smart technologies into aging-in-place strategies. Funding support from prominent Canadian research foundations and networks, including AGE-WELL and the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), has been pivotal in driving this project forward.
Looking ahead, the team envisions further enhancements to the BLE-based IPS integrating machine learning techniques to improve predictive analytics and personalization. Additional research will explore scalability across diverse housing configurations and incorporation with other smart home technologies, aiming to create comprehensive digital ecosystems that safeguard aging populations while respecting user privacy.
This breakthrough aligns with wider trends in digital health innovation, where real-time, context-aware monitoring solutions are becoming instrumental in managing chronic conditions, reducing hospitalizations, and enabling greater autonomy for vulnerable populations. The McMaster BLE-based IPS thus represents a significant step toward fulfilling the promise of technology-enabled aging-in-place.
As the global population ages, demand for scalable, reliable, and affordable mobility monitoring technologies will only intensify. This Bluetooth-based system provides a glimpse into a future where technological integration within everyday environments supports safer, healthier, and more independent lives for older adults worldwide.
For healthcare providers, policymakers, and technology developers, the McMaster team’s research offers a compelling blueprint for the development of indoor location systems that balance precision, privacy, and practicality—hallmarks necessary for transformative impact in the domain of eldercare and beyond.
Subject of Research: People
Article Title: A BLE based turnkey indoor positioning system for mobility assessment in aging-in-place settings
News Publication Date: 17-Apr-2025
Web References:
DOI link: http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pdig.0000774
References:
Wang H, Ganesh G, Zon M, Ghosh O, Siu H, Fang Q (2025) A BLE based turnkey indoor positioning system for mobility assessment in aging-in-place settings. PLOS Digit Health 4(4): e0000774.
Image Credits:
Qiyin Fang and Guha Ganesh, CC-BY 4.0
Keywords:
Bluetooth Low Energy, Indoor Positioning System, Aging-in-Place, Mobility Tracking, Elderly Care, Digital Health, Smart Home Technology, Real-time Monitoring, Healthcare Innovation, Wireless Beacons, Fall Detection, Context-Aware Systems