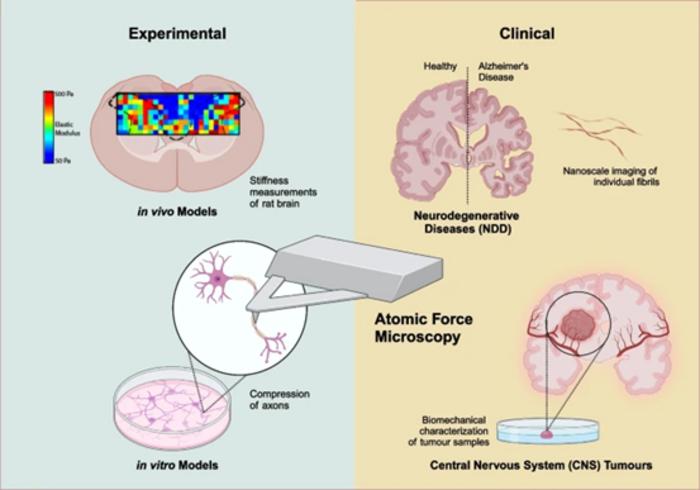
Neurological disorders are becoming an increasingly significant societal burden, highlighting the critical need for improved diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), known for its nanometre-scale resolution and piconewton-scale force sensitivity, offers ground breaking insights into the biomechanical properties of brain cells and tissues and their interactions within their microenvironment.

Credit: All authors
Neurological disorders are becoming an increasingly significant societal burden, highlighting the critical need for improved diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), known for its nanometre-scale resolution and piconewton-scale force sensitivity, offers ground breaking insights into the biomechanical properties of brain cells and tissues and their interactions within their microenvironment.
The team led by Chwee Teck Lim from National University of Singapore, provide an review of the significant role of AFM in neurobiological research and its emerging clinical applications in diagnosing neurological disorders and central nervous system (CNS) tumours.
This review delves into the application of AFM in non-clinical settings, where it characterizes molecular, cellular, and tissue-level aspects of neurological disorders in experimental models. This includes studying ion channel distribution, neuron excitability in genetic disorders, and axonal resistance to mechanical injury. In the clinical context, this article emphasizes AFM’s potential in early detection and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), through biomarker characterization in biofluids such as cerebrospinal fluid and blood. It also examines the use of AFM in enhancing the grading and treatment of CNS tumours by assessing their stiffness, providing a more detailed analysis than traditional histopathological methods.
AFM has proven to be a powerful tool, greatly enhancing our understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of neurological disorders in experimental models. Despite its promise, there are also challenges in integrating AFM into clinical practice, such as sample heterogeneity and data analysis complexity, and discusses emerging solutions such as machine learning and neural networks to overcome these hurdles. These advancements, combined with commercial nanotechnology platforms, herald a new era in personalized treatment strategies for management, treatment and diagnosis of neurological disorders.
Journal
Med-X
Article Title
Atomic force microscopy in the characterization and clinical evaluation of neurological disorders: current and emerging technologies
Article Publication Date
3-Jun-2024