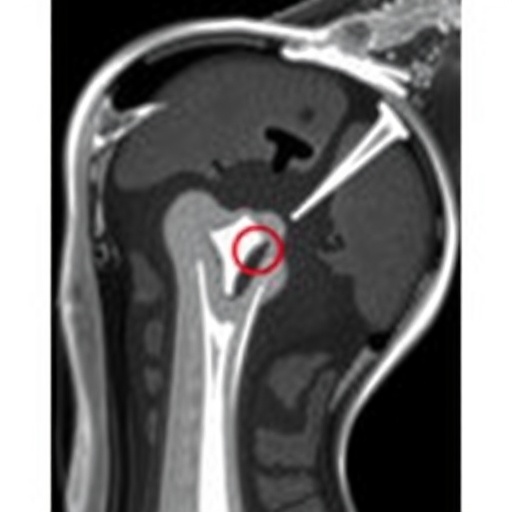
In the realm of pediatric radiology, the challenges posed by diagnosing shoulder conditions in adolescents can often confound even the most experienced clinicians. A recent study highlighted in the journal Pediatr Radiol sheds light on the often ambiguous signals noted in MRIs of the supraspinatus tendon, an integral component in shoulder mechanics and mobility. This analysis by Tung et al. involves a meticulous investigation into the subtleties underlying MRI findings, which can present a diagnostic dilemma for many health professionals in the field.
The significance of the supraspinatus tendon cannot be overstated; it plays a crucial role in initiating arm elevation and maintaining shoulder stability. Given its importance in everyday movements, any abnormalities that arise within this tendon may have profound implications for an adolescent’s quality of life, particularly as they engage in sports and other physical activities. The study underscores the need for heightened awareness and understanding among radiologists and clinicians regarding these signal alterations observed in MRIs.
MRI technology, while immensely valuable in visualizing soft tissue structures like tendons, can sometimes yield results that are ambiguous or misleading. The inherent nature of MRI images frequently leads to interpretations that are open to considerable variability. Adolescent patients often present unique challenges, as their musculoskeletal systems are still developing. This phase of growth and maturation may cause dynamic changes in tendon appearance, adding layers of complexity to the diagnostic process.
In this recent study, the authors meticulously explored various aspects of supraspinatus tendon signal alterations. They provide a comprehensive overview of MRI characteristics and their potential implications. The findings indicate a broad spectrum of signal changes that could either reflect normal developmental variations or indicate pathological changes warranting further exploration. Such nuances in MRI interpretations can easily lead to misdiagnosis or unnecessary interventions if not adequately addressed.
The research also emphasizes the importance of clinical correlation when interpreting MRI findings. A thorough clinical examination, in conjunction with imaging studies, is essential for establishing an accurate diagnosis. Clinicians are urged to avoid isolated reliance on imaging when assessing the health of a patient’s shoulder. The integration of clinical symptoms and physical examination findings becomes paramount in the decision-making process.
Furthermore, the authors touch on the significant role that advanced imaging techniques could play in enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Newer modalities, such as high-resolution MRI or ultrasound, are discussed as tools that might provide clearer insights into tendon pathology, ultimately aiding in more accurate diagnostics. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of these techniques might reduce diagnostic dilemmas, offering clearer pathways for treatment.
A particularly fascinating aspect of this research is its focus on the variability of MRI signals within different demographic populations. This includes considerations for variations in body types, levels of physical activity, and the presence of underlying conditions. Clinical paradigms tend to generalize findings based on adult populations, which may not adequately represent adolescent conditions. A deeper understanding of these factors can lead to more tailored and effective treatment approaches for younger patients.
The implications of misdiagnosing these signal alterations can be far-reaching. Incorrect assessments could lead to inappropriate rehabilitation protocols, unnecessary surgeries, or the overlooking of conditions that could significantly impede an adolescent’s ability to participate in sports or daily activities. Consequently, this study serves as a clarion call for greater emphasis on education and training within the medical community, ensuring that practitioners are equipped to interpret pediatric MRI findings with the required expertise.
As youth sports participation continues to rise globally, so too does the importance of accurate diagnostics in this demographic. With more adolescents engaging in high-impact physical activities, the demand for precise interpretations of shoulder MRIs will undoubtedly grow. Medical professionals must not only be aware of common conditions associated with the supraspinatus tendon but also maintain a comprehensive awareness of the conditions unique to the adolescent population.
The findings of Tung et al. encourage ongoing dialogue among pediatric radiologists, orthopedic surgeons, and primary care providers. Collaborative discussions can foster shared understanding and promote standardized protocols for assessing supraspinatus tendon health in adolescents. This interdisciplinary approach is vital in reducing variability in diagnosis and ensuring that every patient receives optimal care.
In conclusion, the research surrounding supraspinatus tendon signal alterations in adolescent MRI interpretations presents a complex yet fascinating picture of pediatric radiology. As the medical field continues to advance, dedicated studies like this one are essential to unraveling existing ambiguities and enhancing diagnostic accuracy. By bridging the gap between imaging technology and clinical practice, healthcare professionals can provide better outcomes for their patients while navigating the challenges presented by dynamic growth patterns and varied clinical presentations in adolescents.
In the intricate world of pediatric musculoskeletal radiology, such comprehensive investigations of MRI signal alterations not only add to the existing body of knowledge but also pave the way for improved clinical practices. As we look to the future, embracing a more nuanced understanding of these issues will undoubtedly lead to enhanced diagnostic pathways and ultimately, better health outcomes for adolescent patients.
Subject of Research: MRI signal alterations in the supraspinatus tendon in adolescents.
Article Title: Supraspinatus tendon signal alterations on adolescent shoulder MRIs: a diagnostic dilemma.
Article References: Tung, E.L., Bixby, S.D., Stamoulis, C. et al. Supraspinatus tendon signal alterations on adolescent shoulder MRIs: a diagnostic dilemma.
Pediatr Radiol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-025-06416-x
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-025-06416-x
Keywords: Supraspinatus tendon, MRI, adolescents, pediatric radiology, signal alterations, diagnosis.