WASHINGTON, April 9, 2024 — A city’s skyline — the distinctive shapes and arrangements of its buildings — impacts the safety of its population during floods. When the streets flood, pedestrians can be swept under the current and injured or killed. With climate change and rising urbanization, the likelihood and severity of urban flooding are increasing.

Credit: Zhong-Fan Zhu
WASHINGTON, April 9, 2024 — A city’s skyline — the distinctive shapes and arrangements of its buildings — impacts the safety of its population during floods. When the streets flood, pedestrians can be swept under the current and injured or killed. With climate change and rising urbanization, the likelihood and severity of urban flooding are increasing.
Not all city blocks are created equal. In Physics of Fluids, an AIP Publishing journal, researchers from Beijing Normal University, Beijing Hydrological Center, and the China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research investigated how city design contributes to pedestrian safety during flooding.
“Climate change leads to an increasing trend of extreme precipitation events in terms of frequency and intensity,” said author Zhong-Fan Zhu. “Rapid urbanization alters the hydrological properties of the underlying surface in urban areas. For example, previous forestland, wetland, and agricultural land have been paved to construct impervious, urban lands. These factors contribute to frequency occurrences of urban flood events.”
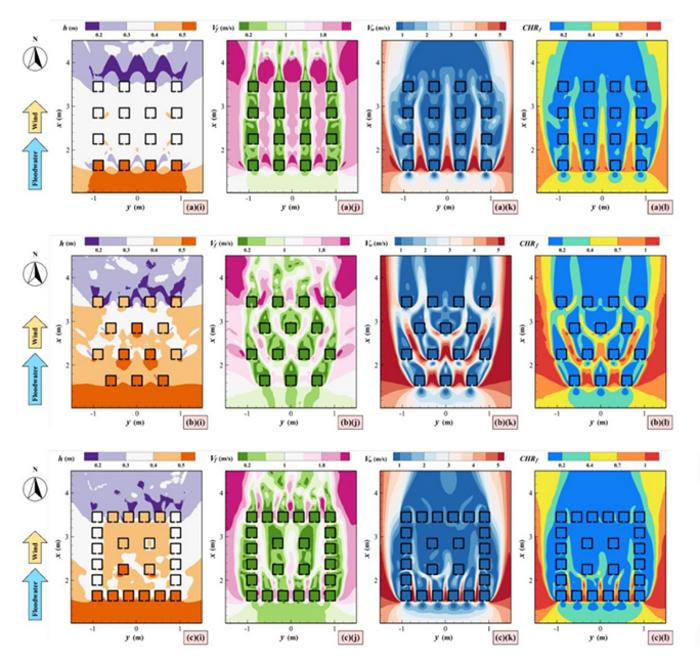
The researchers experimentally identified the flood conditions that make pedestrians vulnerable and utilized computer simulations of different city block patterns, building heights, and street widths to assess the configurations that best protect people.
Each city has unique buildings and building configurations. The team simulated three different urban block layouts: buildings neatly arranged and equally spaced in columns and rows, buildings offset and staggered, and a square tightly outlined by buildings with just four buildings enclosed within.
When buildings are arranged in a line, as in the grid and enclosed layout, they provide a zone of safety by blocking some of the water and wind. The staggered approach has none of this protection and more danger zones due to increased water and wind circulation.
Altering the building shape can also protect pedestrians. Rounding or adding recesses to building corners significantly reduced areas of dangerously high floodwater and windspeed. However, this intervention also somewhat decreased the safety zone.
Wind was a critical, yet complex, factor in determining safety.
“In some cases, the floodwater does not cause pedestrian instability, but adding the wind force will lead to a dangerous situation,” said Zhu. “However, in other cases, the wind will help to maintain pedestrian stability and protect against floodwater. It seems like that wind is like a ‘double-edged sword.’”
Different building height arrangements can help mitigate the negative impacts of wind.
Cities looking to expand should consider enclosed block arrangements, buildings with rounded or even circular footprints, and potentially consult with a physicist.
###
The article, “Physical vulnerability of pedestrians under the joint effect of wind and floodwater and its application in urban block flooding: Effects of urban block layout, building form and building array skyline,” is authored by Lu-Feng Gou, Zhong-Fan Zhu, Shu-You Liu, Ding-Zhi Peng, and Da-Wei Zhang. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on April 9, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0191951). After that date, it can be accessed at https://www.doi.org/10.1063/5.0191951.
###
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pof.
###
Journal
Physics of Fluids
Article Title
Physical vulnerability of pedestrians under the joint effect of wind and floodwater and its application in urban block flooding: Effects of urban block layout, building form and building array skyline
Article Publication Date
9-Apr-2024