It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.

Credit: Can Knaut via OpenStreetMap
It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.
That’s exactly what Harvard physicists have done, using existing Boston-area telecommunication fiber, in a demonstration of the world’s longest fiber distance between two quantum memory nodes to date. Think of it as a simple, closed internet between point A and B, carrying a signal encoded not by classical bits like the existing internet, but by perfectly secure, individual particles of light.
The groundbreaking work, published in Nature, was led by Mikhail Lukin, the Joshua and Beth Friedman University Professor in the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Harvard professors Marko Lončar and Hongkun Park, who are all members of the Harvard Quantum Initiative, alongside researchers at Amazon Web Services.
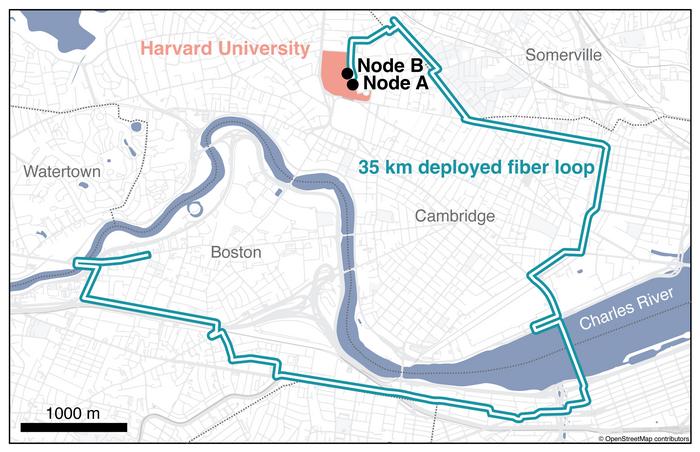
The Harvard team established the practical makings of the first quantum internet by entangling two quantum memory nodes separated by optical fiber link deployed over a roughly 22-mile loop through Cambridge, Somerville, Watertown, and Boston. The two nodes were located a floor apart in Harvard’s Laboratory for Integrated Science and Engineering.
Quantum memory, analogous to classical computer memory, is an important component of an interconnected quantum computing future because it allows for complex network operations and information storage and retrieval. While other quantum networks have been created in the past, the Harvard team’s is the longest fiber network between devices that can store, process and move information.
Each node is a very small quantum computer, made out of a sliver of diamond that has a defect in its atomic structure called a silicon-vacancy center. Inside the diamond, carved structures smaller than a hundredth the width of a human hair enhance the interaction between the silicon-vacancy center and light.
The silicon-vacancy center contains two qubits, or bits of quantum information: one in the form of an electron spin used for communication, and the other in a longer-lived nuclear spin used as a memory qubit to store entanglement (the quantum-mechanical property that allows information to be perfectly correlated across any distance). Both spins are fully controllable with microwave pulses. These diamond devices – just a few millimeters square – are housed inside dilution refrigeration units that reach temperatures of -459 Fahrenheit.
Using silicon-vacancy centers as quantum memory devices for single photons has been a multi-year research program at Harvard. The technology solves a major problem in the theorized quantum internet: signal loss that can’t be boosted in traditional ways. A quantum network cannot use standard optical-fiber signal repeaters because copying of arbitrary quantum information is impossible – making the information secure, but also very hard to transport over long distances.
Silicon vacancy center-based network nodes can catch, store and entangle bits of quantum information while correcting for signal loss. After cooling the nodes to close to absolute zero, light is sent through the first node and, by nature of the silicon vacancy center’s atomic structure, becomes entangled with it.
“Since the light is already entangled with the first node, it can transfer this entanglement to the second node,” explained first author Can Knaut, a Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences student in Lukin’s lab. “We call this photon-mediated entanglement.”
Over the last several years, the researchers have leased optical fiber from a company in Boston to run their experiments, fitting their demonstration network on top of the existing fiber to indicate that creating a quantum internet with similar network lines would be possible.
“Showing that quantum network nodes can be entangled in the real-world environment of a very busy urban area, is an important step towards practical networking between quantum computers,” Lukin said.
A two-node quantum network is only the beginning. The researchers are working diligently to extend the performance of their network by adding nodes and experimenting with more networking protocols.
The paper is titled “Entanglement of Nanophotonic Quantum Memory Nodes in a Telecom Network.” The work was supported by the AWS Center for Quantum Networking’s research alliance with the Harvard Quantum Initiative, the National Science Foundation, the Center for Ultracold Atoms (an NSF Physics Frontiers Center), the Center for Quantum Networks (an NSF Engineering Research Center), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and other sources.
Journal
Nature
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Entanglement of nanophotonic quantum memory nodes in a telecom network
Article Publication Date
15-May-2024